Cartilage damage
General
Cartilage is one of the connective and supporting tissues. It consists of cartilage cells and the intercellular substance surrounding them. Depending on how this substance is composed, a distinction is made between hyaline, elastic and fibrous cartilage.
Bald cartilage describes the condition when there is no more cartilage. For more information, read the article at: Bald cartilage - is it dangerous?
Cartilage tissue in general is very Resilient to compression and bending, which is why it can be found on the one hand on parts of the body that are exposed to high pressure loads in everyday life (such as joint surfaces) and on the other hand in areas that must have a high degree of elasticity (such as the auricle and the outside) Ear canal). Cartilage tissue in adults contains neither vessels nor nerves. So it has to be supplied in a different way. This supply takes place by diffusionwhich means that the nutrients passively migrate from their higher to the lower concentration. The articular cartilage gets the nutrients it needs to survive from Synovial membrane (Synovia). Cartilage in other places has a so-called Cartilage skin (Perichondrium) that fulfills the same function.

Classification
In order to better classify cartilage damage, the classification is used Outerbridge, in which grades 0 to 4 are differentiated.
- Grade 0: no existing cartilage damage;
- Grade 1: the cartilage is completely preserved, but softens, especially under pressure;
- Grade 2: the cartilage is a little roughened on the surface;
- Grade 3: the cartilage is torn down to the bone, whereby something like a crater-shaped defect can be found in the tissue;
- Grade 4: the cartilage is completely lost down to the bone, so the bone is exposed.
It is important, however, that the extent of the objectively ascertainable changes in the cartilage cannot always be reconciled precisely with the extent of the patient's complaints. Some patients hardly have Pain, although severe damage can already be proven, others have a very high level of suffering, although hardly anything can be determined with the help of examinations. For this reason, it is important to discuss and plan the treatment very well with the person affected, because of that Wellbeing and not that X-ray image should be restored.
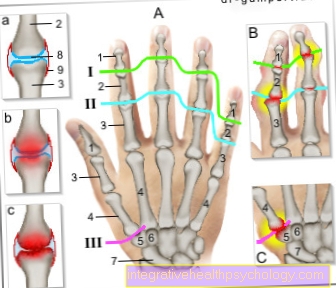
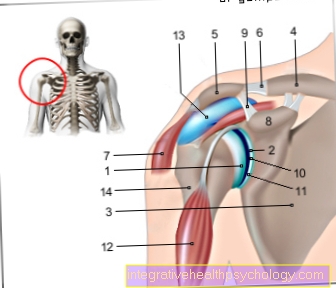
Illustration of a cartilage damage

- Articular cartilage
(hyaline cartilage) -
Cartilago articularis - Cartilage remodeling zone
in bones -
Zona ossificationis - Joint body (articular gnar
of the femur) -
Femoral condyle - Femur -
Femur - Articular cartilage -
Cartilago articularis - Outer band -
Ligamentum collaterale fibulare - Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Fibula - Fibula
- Shin - Tibia
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
causes

Damage to the articular cartilage has been described in several million people worldwide and can be traced back to a wide variety of causes. In general, chronic triggers can be distinguished from acute ones. The most common acute reason for cartilage damage is an injury, most of which occurs as part of a sports accident or a fall. The cartilage can be damaged to a greater or lesser extent by excessive force on the joint or by twisting or twisting it (this is particularly common in the ankle joint). Most of the time, this defect is limited to one place, but a deep tear or even a detachment of small pieces of cartilage with subsequent trapping in another part of the joint can lead to considerable discomfort.
The chronic cartilage damage is mostly caused by wear and tear. On the one hand, this wear and tear occurs as part of a completely natural aging process. The expert describes the result as osteoarthritis (chronic degenerative joint disease). The joints have to bear more or less of our body weight depending on their location and are subjected to many other loads and movements every day.
Read also the topic: Cartilage flake
Risk factors
The type and intensity of these stresses also affects the rate of wear and tear Cartilage tissue out. Hence it is not surprising that risk factors for cartilage damage in particular Obesity and incorrect or excessive charges such as certain sports and of course one advanced age are.
In addition, certain play genetic factors a role. Some people simply have poor quality cartilage and therefore have a tendency to develop cartilage damage faster than others without their being able to do anything about it. In addition, can also Misalignments and the resulting improper stresses favor the development of cartilage defects. Another cause of cartilage damage can be a long-term immobilization (Immobilization) of joints.
Symptoms
Acute cartilage damage often leads to pronounced pain, sometimes only during exercise, but sometimes even at rest. In addition, many people have limited mobility in their joints. With cartilage damage that develops chronically, symptoms may be absent for a long period of time. Complications in this clinical picture are mainly effusions that result from the reactive fluid storage in the joint and become noticeable as swelling, and osteoarthritis, which almost inevitably develops on the basis of long-term cartilage damage.
The problem with cartilage damage is also that the human body is only able to regenerate cartilage tissue to a very limited extent. This is because this type of tissue is not supplied by nerve cells and blood vessels, which are, however, of great importance for the healing process. It is assumed that only about 4% of the cartilage cells can be renewed, but this sometimes depends on age. That is not enough to be able to correct the damage without outside help. Most of the time, the damage will tend to increase rather than improve over time.
You might also be interested in: Heberden osteoarthritis
Test for possible osteoarthritis
Cartilage damage in the different joints
Cartilage damage in the knee / kneecap

Cartilage damage in the Knee joint are not uncommon. In the course of life one finds natural wear and tear instead of. The knee joint is challenged throughout life through everyday walking and standing. In addition, there is further wear and tear from other stressful activities such as Sports, Misalignments of the knee joint and injuries to the Bone- and Band structures at the knee joint. The chronic breakdown and defect of cartilage in the knee is called Gonarthrosis designated. This lack of cartilage manifests itself in the form of pain during exercise and later also at rest. Furthermore, there are restrictions in mobility on the corresponding knee.
In addition to the described degenerative variant Cartilage wear can result in cartilage damage traumatic (accident-related) arise. Often this happens in the course of Sports- and fall injuries. In this case, a piece of cartilage a few centimeters in diameter breaks out of the cartilage surface. The remaining cartilage of the knee is still intact, as is the underlying bone. With this form of cartilage damage, there are good therapeutic options for the Restoration an intact cartilage surface.
With both forms of cartilage damage there is one Relief of the knee indexed. This means that the patient with gonarthrosis should reduce stressful activities (sport, poor posture, heavy weight) in the long term. In the case of traumatic cartilage damage, regeneration and therapy should also be carried out during the period unnecessarily stressful activities for the knee joint can be omitted.
In both cases, a physiotherapy treatment be helpful to reduce pain and problems.
Another risk zone for cartilage damage in the knee area is the Cartilage between the kneecap and the articular bones. This results in overstimulation and damage to this cartilage zone due to improper stress on the knee. This condition is often caused by misalignments in the knee joint, shortened muscles and also permanent overload from running and cycling, which is why the Runner's knee spoken. This painful state can several weeks stop and lead to the impairment of normal walking. The therapy here consists of a break in training, Voltaren Associations, Ice packs as well Stretching exercises for the muscle groups that stabilize the knee and trunk. Furthermore, the Selection of running shoes be respected. If the problem does not improve, setting a Cortisone injection in the knee and in exceptional cases surgical intervention may be necessary.
Cartilage damage in the hip
The hip joint unlike other joints, has one relatively thin layer of cartilage. This is indispensable for the lifelong functionality of the hip joint.
Damage to cartilage can be the same as to other joints degenerative be. That is, they arise in the course of life Strain and wear and tear. It creates a arthrosis.
Cartilage damage can also occur in the hip traumatic be conditional. Excessive and incorrect loading of the joint, e.g. During exercise, an accident or a fall, the cartilage can be injured and parts of it break off. In the course of the near future one may emerge relatively minor injury a chronic problem develop. The original injury is usually a relatively small area on the cartilage, while cartilage damage that develops over years tends to affect larger parts of the cartilage.
Other causes of cartilage damage in the hip can be found in Metabolic disorders like gout again. Small crystals of substances are deposited in the joint, which the body can no longer excrete sufficiently, and then cause pain and further wear and tear on the cartilage.
Some bacteria cause in the course of infection in the body chronic damage in joints, including the hip joint. This is a bacterial arthritis. Here, the problem should recede through a correctly chosen antibiotic therapy.
Cartilage damage in the ankle
The Ankle joint must hold the entire body weight when moving and resting. The cartilage is exposed to constant stress and is therefore heavily used.
The joint is often exposed to great external forces, which can lead to compression of the cartilage, as well as injuries to cartilage and other joint structures. When the cartilage compresses it can become stronger Bruises and Cracks come. It can also be used here for Splintering of cartilage come.
For other ankle injuries such as Supination trauma The cartilage is also often affected (twisting outwards) and injuries to bones and ligament structures. In addition to crushing and tearing injuries, there is a risk that pieces of bone will splinter and cause acute or long-term damage to the cartilage.
Affected people often have restricted resilience and mobility of the affected foot. Furthermore, pain and instabilities occur, which can be related to the damage to other structures.
Cartilage damage in the shoulder
The Shoulder joint In the course of aging, the place is often responsible for pain and thus for difficulties in movement. This is often due to damage Tendons of muscles of the Rotator cuff conditionally. But also the cartilaginous area of the joint that Glenoid Cavitas, can be affected by wear and tear.
Another cause of discomfort are acute traumatic events such as falls and accidents, in which great forces act on the joint and parts of the cartilage are damaged.
Often cartilage damage is also found in long-term overloading of the shoulder joint in the course of sports where the shoulder is overloaded by one-sided and often performed movements (tennis) or in which unnatural pulling and pushing movements are carried out against the shoulder joint at regular intervals (football).
Furthermore, strong wear and tear can be seen in people who have been working for a long time Weight training exercise.
The first signs of damage are often in the form of restricted mobility, painful movements, Cracking in the joint such as Swelling and weakness.
Diagnostics and therapy

To the Cartilage damage Being able to assess more precisely can be next to one X-ray image also one Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI; Magnetic resonance imaging) can be made. The existing defect can be made even more precise with the help of a Jointoscopy (Arthroscopy) determine. This is a minimally invasive surgical technique that has the advantage that it can not only be used for diagnostic purposes, but also directly offers the possibility of some therapeutic approaches.
During this procedure, if necessary, bone or cartilage parts can be removed, the cartilage smoothed and the joint cleaned and rinsed (Lavage or. Debridement).
If the changes are less pronounced, a physical therapy be sufficient to enable a person affected to live a symptom-free life. Can accompany Painkiller and or Shoe insoles are used.
In addition, it is of course first of all important that all risk factors are eliminated or reduced as far as possible. Obesity should be reduced, stressful sports and other overexertion should be avoided, underlying diseases or Misalignments should be eliminated. If these measures are not sufficient to significantly improve the symptoms, there are still some newer methods of dealing with cartilage damage: Especially with younger patients, it is advisable to apply healthy cartilage tissue transplantwhat is previously taken from less affected joint parts.
There are also brand new ones Medication on the market that specifically inhibit certain inflammation triggers that are responsible for the damage to the articular cartilage. These are currently still being tested and very expensivebut promise one very big success.
The last thing that should be mentioned is that currently Cartilage cultures to be explored. In the meantime, one is able to cultivate cartilage cells from blood stem cells in the laboratory and such cartilage cultivation with subsequent transplantation are already being carried out successfully in some areas of Germany.