Circular hair loss
introduction

Circular hair loss is also known as alopecia areata. This disease results in well-defined, round, bald spots on the hairy scalp. Beard hair or other hairy parts of the body can also be affected. These spots can enlarge or become more frequent over time. Both sexes can be affected both in childhood and in adulthood. Circular hair loss is the most common inflammatory hair loss disease with around 1.4 million people affected in Germany.
Causes of circular hair loss
An autoimmune reaction of the body is assumed to be the cause of the circular hair loss. The hair roots are falsely attacked by cells of the immune system, so that hair growth is hindered as part of an inflammatory reaction and the hair eventually falls out. This creates larger bald spots over time, which can, however, grow over again on their own. In some cases, however, the areas can remain bald, which can ultimately lead to a loss of all hair on the head (alopecia totalis) or even all of the hair on the body (alopecia universalis).
In addition, a genetic predisposition for circular hair loss is assumed, as 10-25% of those affected can observe similar cases in their own families. However, the exact cause of the disease has not yet been conclusively clarified. Various trigger factors are discussed that could trigger the development of circular hair loss.
These include stress, trauma, infections, allergies, pregnancy, the use of certain medications and an injury to the scalp.
You might also be interested in: Hair loss in women, hair loss during pregnancy
Thyroid as the cause
The thyroid is an important organ that produces the thyroid hormones and releases them into the bloodstream. Disturbances in this organ function can lead to diverse changes in various metabolic pathways and thus cause symptoms. This also includes a change in the structure of the hair or hair loss.
An overactive thyroid, i.e. an excess supply of thyroid hormones, typically leads to hair loss. However, it is not a circular but a diffuse hair loss. The hair does not fall out in defined areas, but becomes lighter overall.
However, autoimmune thyroid diseases can actually be associated with circular hair loss. In particular, an increase in certain autoantibodies, namely the TPO antibodies and the Tg antibodies, is observed. Autoantibodies are antibodies that are directed against the body's own proteins and thereby cause autoimmune diseases.
Cortisone as the cause
Cortisone is not only an important endogenous hormone, but also a drug that is used in many ways.
It can have an effect on the calcium metabolism and lead to a calcium deficiency, especially if taken for a long time. If the calcium deficiency persists for a long time, this has a negative effect on hair growth. The hair simply does not grow or grows hardly at all.
However, cortisone does not cause hair loss, especially circular hair loss.
Fungal diseases as a cause of circular hair loss
Fungal diseases can lead to various types of hair loss. Such fungal infections of the hairy head are also known as tinea capitis. They affect people of all ages, but tinea capitis is more common in children.
The most common pathogen is the fungus Microsporum canis. Often transmitted through cats and guinea pigs, it causes hair loss on the scalp. The areas are about the size of a coin and show fine scaling. With the help of drugs that kill the fungus (antimycotics), scar-free healing and hair regrowth can be achieved.
This is to be distinguished from tinea capitis profunda, which leads to scarring, circular hair loss. Fungal pathogens such as Trichophyton verrucosum cause painful hair loss, which is accompanied by a strong inflammatory reaction of the skin. Painful, oozing lumps and crusts are a typical side effect. General symptoms such as fever, fatigue and swelling of the lymph nodes are also characteristic of tinea capitis profunda.
Read more on the topic: Fungal infections on the body and head
Symptoms
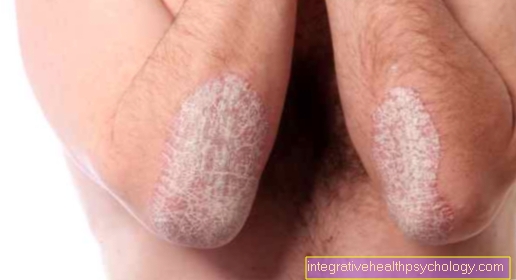
With circular hair loss it comes to one patchy hair loss, through which sharply defined, bald, oval or round areas form on the otherwise hairy skin. Everyone can be affected Body partsthat have hair growth. The head hair is most frequently affected, followed by beard hair (in men) and finally other body hair.
At the edge of the bald spots there are so-called "Exclamation mark hair". These are so named because they are broken off and taper towards the end, i.e. become narrower. The bald spots themselves do not show any abnormalities on the skin, so they are neither reddened nor scaly or otherwise dermatologically noticeable. In some people affected, hair grows back in the bald areas. These regrowing hairs are first not pigmented and thinner than the rest of the hair, but later resume the appearance of the normal hair. As further symptoms, however, those affected may have abnormalities on the fingernails. The nails can be roughened, have many grooves or dimples. They are also known as spot nails.
Circular hair loss can in all ages and occur in both sexes, but it most commonly occurs between the ages of 20 and 30.
Diagnosis of circular hair loss
To confirm the diagnosis of circular hair loss, the doctor looks at the clinical picture of the patient. The diagnosis is usually obvious due to the typical visible symptoms. Especially if the patient is additionally over similar cases can report in the family, the diagnosis can be made with great certainty. In addition, a sample of the Scalp, as well as some hair from affected body regions are removed and examined microscopically. Any abnormalities found can help to secure the diagnosis.
The treatment of circular hair loss
There are several options when it comes to treating circular hair loss. First, locally effective glucocorticoid solutions can be applied to the bald areas. These substances then suppress the overactive immune system at these points, so that its damaging effect on the hair roots is dampened. The hair can then grow back better. In order for the therapy to bring visible results, it usually has to be applied consistently over several months.Topical immunotherapy is more promising, in which certain substances (diphenylcyclopropenone (DPCP), dinitrochlorobenzene (DNCB) or dibutyl squared ester (SADBE)) are applied to the bald areas of the skin. These substances stimulate the immune system and in this way cause an immune reaction. The immune cells are directed to the applied chemicals, so to speak, and let go of the hair roots. These then have time to grow back. However, the application of DPCP, DNCB or SADBE can affect the scalp and become red, flaky and itchy.
Which home remedies help with circular hair loss?
The use of home remedies has unfortunately not proven itself in the case of circular hair loss. Infectious causes in particular, such as fungal diseases, should be treated by conventional medicine as quickly as possible in order not to delay healing.
Even non-scarring, circular hair loss, which is often based on intangible causes such as stress, psychological stress or even autoimmune processes, cannot be improved with home remedies. However, especially with such non-scarring hair loss, it is advisable to pay more attention to a balanced everyday life and adequate coping strategies for stress in order not to further promote hair loss.
Read more on the topic: How can you reduce stress?
Can garlic help with circular hair loss?
Garlic is often mentioned and touted as a home remedy in connection with circular hair loss. But whether it actually helps against hair loss can neither be affirmed nor denied.
Before attempting treatment with garlic, you should have a medical examination. Some causes, such as skin infectious diseases or autoimmune diseases, require medication to stop the hair loss.
Often times, there is no tangible cause of non-scarring alopecia. Stress or a psychological stress reaction can also be a cause and cannot simply be cured by a drug. In such cases, some sufferers report that garlic has a helpful effect on their hair loss. In the form of a garlic shampoo or by rubbing the scalp directly with garlic slices, some people affected would have improved.
The effect of garlic in the form of a garlic gel on hair loss has also been examined in a study. Therapy with topical betamethasone, a drug similar to cortisone, has shown a positive effect through the additional use of a garlic gel.
Homeopathic remedies for circular hair loss
Various homeopathic remedies are available for treating circular hair loss. There are no standardized recommendations, so that individual advice from a homeopath or pharmacist is usually necessary. Before starting homeopathic treatment, the cause of the hair loss should be clarified by a medical examination so that conventional medical treatment can begin in good time and the underlying clinical picture clarified.
However, nothing speaks against the supportive use of homeopathic remedies. At this point, some common homeopathic remedies are presented as examples that are used in the treatment of circular hair loss:
- Acidum hydrofluoricum: This remedy is used for circular hair loss. Thinned eyebrows are also typical of this shape.
- Antimonium tartaricum: This homeopathic remedy is used for suddenly graying hair and excessive hair loss after a psychological trauma.
- Selenium: Selenium is recommended for unspecified, circular hair loss.
forecast
In general, people with a milder form of circular hair loss and a shorter course of the disease have a better chance of recovery than people with severe hair loss and a long medical history.
However, classic, non-scarring, circular hair loss has a very variable prognosis overall. In many cases the hair loss heals and the hair grows back within six months, in other people it develops further, for example to diffuse hair loss or total hair loss.
A relapsing course has also been described, in which temporary circular hair loss occurs again and again at intervals of months to years, which then disappears again. Around 70% of those affected suffer one or more relapses of the disease in the course of their life. In a fifth of those affected, the alopecia does not heal and the areas remain bald. Disease relapses are more common when the hair loss is associated with an autoimmune disease.
How long does it take for hair to grow back?
How long it takes for hair to fully grow back depends on a number of factors. The decisive factor is usually the type and cause of the hair loss and the early start of therapy.
A fungal infection of the scalp, for example, heals within a few weeks under antifungal therapy, i.e. effective against fungal pathogens. It can take a few months for the hair to grow back completely. Even with autoimmune hair loss, hair regrowth can take several months.
Scarring alopecia, on the other hand, heals with scarring. In this case, the areas of hair loss unfortunately remain permanently bald.
prophylaxis
There is no prophylaxis against circular hair loss. Since the causes of the disease have not been conclusively clarified, but a genetic predisposition is being discussed, circular hair loss cannot be specifically prevented. Avoiding the trigger factors can, however, have a supportive effect on the sick. So should general Stress relieved and choose a healthy lifestyle.
Circular hair loss in women
Although the classic circular hair loss mostly affects men, women can of course also be affected. This type of circular hair loss occurs more frequently during phases of psychological stress and stress.
One possible cause of circular hair loss, which affects women far more often than men, is traumatic alopecia. This results in damage and changes to the hair structure through pressure or tension. A typical cause is wearing tight braids or other hairstyles. Hair accessories and hoods can also cause traumatic alopecia.
There is also a specific clinical picture that leads to scarring hair loss and mainly affects young women. This is the alopecia atrophicans, also called Pseudopelade Brocq. This disease, the cause of which is unknown, mainly affects women between the ages of 30 and 35. Typical of this rare disease are light, irregularly defined areas of skin on the head that do not hurt or cause other complaints. After a while, the areas become scarred, so that the hair loss persists permanently.
Read more on the topic: Hair loss in women
Circular hair loss on the beard
The circular hair loss can occur Men also occur in the beard area. This form is not as common as the head hair form, but overall it is not uncommon. Most of those affected have only one bald spot in the area of the beard growth, few sufferers complain of several bald spots in the beard. The therapy is identical to the therapy for circular hair loss in the area of the scalp hair. This form does not differ from the others in terms of prognosis either.
Circular hair loss on the back of the head
Circular hair loss is most common on the back of the head. Most of those affected complain of one or two bald spots on the back of the head, in some cases several or even a diffuse or even complete hair loss.
The transition between the back of the head and the top of the head is a very common location for circular hair loss. Fungal diseases can also lead to individual or confluent, i.e. connected, bald spots. Furthermore, wearing heavy hair jewelry or tight hair clips in this area can lead to traumatic hair loss.
A special form of non-scarring, circular hair loss is the so-called ophiasis. This leads to extensive hair loss on the back of the head with the hair on the parting hair remaining. The remaining hair is also typically referred to as a scalp lock. This form of alopecia is usually associated with a poor prognosis and tends to heal poorly.