Lipomatosis
introduction
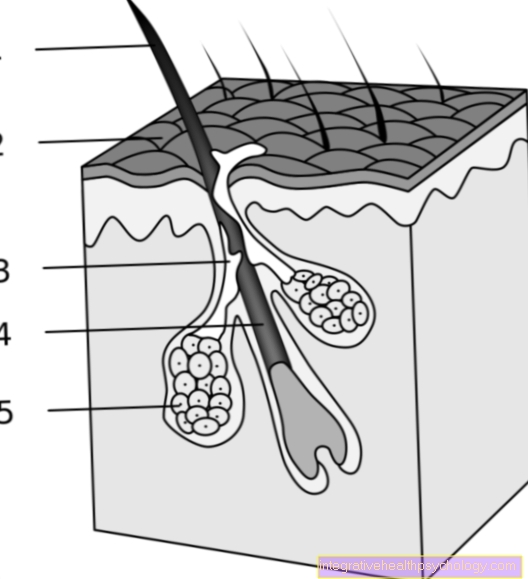
The term lipomatosis describes a diffusely distributed, unnatural increase in adipose tissue affecting various parts of the body. Lipomatosis (Greek: lipos = fat; -om = tumor-like swelling; -ose = chronically progressive disease) is understood to mean several clinical pictures, some of which cannot be completely differentiated from each other, but all have in common increased fatty tissue in the form of tumors. It is a rare metabolic disease with an insufficiently understood mechanism. Lipomatosis can affect various regions of the body such as the head, neck, thighs and upper arms, stomach and back. A form is also known in which the internal fatty tissue of organs such as the pancreas is increased, in some cases the spinal canal is affected.

Lipomatosis is primarily not a malignant disease, but rather as a pathological but benign new formation of adipose tissue (Adipose tissue hyperplasia) and above all creates a cosmetic psychological strain. However, accumulation between or within organs can be associated with increased disease risks.
Different forms of lipomatosis are known. The most common and best-known type is symmetrical (adeno-) lipomatosis, which is also known as Launois-Bensaude syndrome after its first description. A special form that mainly affects the head and neck is called Madelung lipomatosis. There are four types of classification:
- Type I: neck and neck type (Madelung fat throat, localized type)
- Type II: shoulder girdle type (pseudo-athletic type)
- Type III: pelvic girdle type (gynecoid type)
- Type IV: Abdominal type
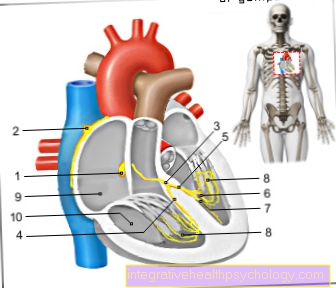
Furthermore, the disease is named after the affected location, e.g. lipomatosis cordis (cor = the heart), i.e. an increase in fat on the heart. A condition that some women experience during menopause, lipomatosis dolorosa, is also known as lipomatosis, but has different causes and mechanisms and is beyond the scope of this article.
causes
The causes of lipomatosis are still the subject of intense focus research. Nevertheless, the processes behind the development of this clinical picture are poorly understood. In some patients there is an accumulation within the family, so that one genetic Component is assumed. It has also been observed that patients with lipomatosis often have additional Metabolic diseases likely to be related to the occurrence of lipomatosis.
Apparently there is an association with diabetes mellitus, an underactive thyroid (Hypothyroidism) or others Lipid metabolic diseases. Many studies associate lipomatosis with longstanding, excessive Alcohol consumption in connection. So it was found that men are around 13 times more often are more affected than women, especially if they are alcohol abusers. At the cellular level, the theory is that growing and reproducing Fat cells no longer react to the body's own signals, widely recognized. Hormones like adrenaline or Norepinephrine can therefore no longer ignite their effect on the cell, so it grows autonomous. This would explain why even in extremely thin patients such as B. Tumor patients who have lipomas persist although most of the remaining fat tissue has been broken down. Another specific cause is treatment of HIV with a specific drug, which in up to 40% of cases is considered to be side effect comes to lipomatosis.
Symptoms
The lipomatosis makes itself clear in the first place Adipose tissue increases noticeable in different parts of the body. Depending on the type, these occur mainly on the head and neck (Type I.), in the area of the shoulder and upper extremities (Type II), on belly, Pelvis and lower extremities (Type III), as well as inner Organs on (Type IV). A rare special form shows lipomas only on the soles on. The tumors are difficult to distinguish from one another and are usually viewed as normal weight gain at the onset of the disease. However, this goes beyond a normal level relatively quickly and there is a significant increase in tissue. The lipomatosis usually occurs in the affected regions symmetrical on. Especially with the shoulder type, observers from the outside initially have the impression that it is the muscle mass of an athletic person with broad shoulders, so that one is here pseudo-athletic habitus speaks. If you feel the tumors of a lipomatosis, they feel rough and firmly on, sometimes a doughy consistency is described. In addition to these general symptoms, it can also occur depending on the type special restrictions. The Madelung fat throat can be so pronounced that the compression of the windpipe and esophagus leads to difficulty breathing or swallowing. A psychosocial aspect is often added in the course. Patients with lipomatosis often suffer from the cosmetic consequences caused by the clearly visible lipomas.
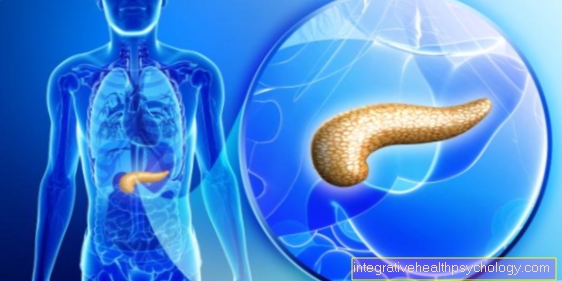
Lipomatosis of the pancreas
With lipomatosis of the pancreas, there is a diffuse increase in fatty tissue within the organ. The glandular tissue is more and more replaced by fat cells and separated from them into larger and smaller parts.
It is believed that dead glandular tissue is replaced by adipose tissue or that the fat cells are deposited in the connective tissue of the pancreas, causing the organ to become fat over time. However, the obesity usually does not impair organ function, which is why lipomatosis of the pancreas does not necessarily require treatment.
Obesity in the pancreas often has no symptoms and is therefore difficult to diagnose. If the doctor performs an ultrasound of the upper abdomen as part of the examination, he usually recognizes the lipomatosis immediately on the basis of the typical tissue changes, which can be shown very clearly in the ultrasound.
The causes that lead to the formation of lipomas in the pancreas are still unknown. However, it is believed that there is a connection between lipomatosis and certain metabolic diseases, namely diabetes and obesity.
If pancreatic lipomatosis needs to be treated, it is either conservative or surgical, depending on the severity. Conservative therapy means weight loss and a strict diet that reduces fat intake, thereby reducing the amount of fat in the pancreas.
Lipomatosis dolorosa
Lipomatosis dolorosa is also called Obesity dolorosa or Dercum disease designated. It is a chronic and progressive disease in which there is a painful increase in subcutaneous fat tissue under the skin.
The causes of lipomatosis dolorosa are not yet known, but the disease appears to be pathological obesity (Obesity) and disorders of the fat and carbohydrate metabolism. A genetic component cannot be ruled out either, since in a few cases an increased occurrence within families can be observed.
The lipomas can appear all over the body except for the neck and face. However, the fatty growths tend to develop on the abdomen, knees, elbows, thighs and the inside of the upper arm.
Affected patients complain of severe pain in the area of the fat deposits and the pain can increase as the disease progresses. The more overweight the patient, the greater the pain caused by the lipomas. Typical accompanying symptoms of lipomatosis dolorosa are dry mouth, headache and swelling.
Doctors diagnose lipomatosis dolorosa using imaging tests such as ultrasound and magnetic resonance therapy (MRI). Often small tissue samples (Biopsies) and analyzed microscopically.
The pain, the one Lipomatosis dolorosa are not treatable by traditional pain therapy, but intravenous administration of lidocaine, a narcotic, can achieve a longer pain-free phase. However, since the administration of lidocaine has severe side effects, long-term therapy in this form is not possible.
No regression of the lipomas can be achieved by reducing weight and the pain is also not reduced. Finally, there is also the option of surgically removing the fatty lumps, but often a lipoma forms again in the same place and relapses.
Breast lipomas
Lipomas can develop in one or both breasts in women. When multiple lipomas form at the same time, it is called lipomatosis.
Breast lipomatosis is a rare disease that is mostly benign. Lumps and swellings form that lie directly under the skin and can therefore be felt from the outside. Under certain circumstances, lipomas in the breast can become very large and cause pain. Usually these lipomas are harmless and do not require treatment.
Lipomatosis in the spinal cord
Lipomatoses that occur in the spinal cord can, depending on their location, compress nerves and nerve roots and thus lead to neurological symptoms. Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) can be used to determine the spread of the lipomas and to confirm the diagnosis.
In order to avoid pressure damage on compressed nerves and to improve the symptoms, symptomatic lipomas of the spinal cord can be removed microsurgically.
Lipomatosis on the thigh
Lipomatosis can also become noticeable on the thigh, although the thighs are not one of the most common locations for this type of fatty tissue increase. Here, too, there is an increase in the circumference of the thigh and the appearance of fat aprons, which are also known as saddlebags on the thigh. Often, however, there is no lipomatosis behind the increase in fatty tissue on the legs, but lipedema. This is an increase in fat, preferably on the hips and legs, which occurs mainly in women. So hormonal causes are suspected. If, however, it is a question of lipomatosis on the thigh, the therapy usually consists of reducing fat by suction or cutting away, whereby the symptoms usually recur.
Intraspinal lipomatosis
Intraspinal lipomatoses are a very rare disease caused by benign tumors of the adipose tissue in the spinal canal. Intraspinal means that the lipomas lie within the spinal canal in the spinal cord. Intraspinal lipomas occur spontaneously, are usually symptom-free and are only discovered and diagnosed by chance. Usually, the lipomas in the spinal canal do not have to be treated.
Depending on the location, a lipoma in the spinal canal can also cause symptoms. Sometimes nerves or the spinal cord have grown into the fatty lump, causing discomfort.
In such cases, the lipoma is surgically removed or, if complete removal is not possible, the size of the fat accumulation is reduced. Intraspinal lipomatosis is sometimes associated with obesity and overweight, so weight loss can improve symptoms.
Epidural lipomatosis
The epidural space is a space in the spinal cord that is formed by the membranes of the spinal cord and is filled with fatty and connective tissue. The fatty tissue is used to cushion the spinal cord in the spinal canal. In rare cases, lipomas form here and one speaks of spinal epidural lipomatosis (SEL).
The disease can be symptom-free or, due to nerve compression, lead to muscle weakness, reduced nerve conduction speed or impaired sensation.
It is believed that there is a connection between SEL and obesity. Depending on the severity, the therapy is carried out by surgically removing the fatty growths or by reducing weight.
Read more about this topic under: Epidural Lipomatosis - Causes, Symptoms and Treatment
diagnosis
Since it is a rare Disease is the diagnosis of lipomatosis Specialists posed. The most important indicators are the rapidly growing ones Fat deposits, mostly with an unusual distribution. E.g. In the case of lipomatosis type I with fatty tissue on the neck and head, it quickly becomes clear that this is a non-physiological picture, while the abdominal-pelvic type is recognized as lipomatosis relatively late. The most important measure in diagnosing lipomatosis is one Tissue extractionthat is examined under the microscope. A histologist or pathologist can use this to make the diagnosis.
therapy
There is no known effective treatment for the cause of lipomatosis, so therapy is limited to symptom control. Due to the special nature of the adipose tissue, conservative measures such as diet and exercise are not very effective in treating lipomatosis. Operative interventions are therefore indicated. Liposuction can help for some time and has visible effects on affected areas. If the tissue is too coarse and interspersed with a lot of connective tissue, the minimally invasive suction of fat is replaced by an operation in which volume can be removed with a scalpel. However, it must be clearly pointed out that these measures are usually only short-lived and have a high rate of recurrence. The tumors usually grow back again. However, relief interventions must be carried out if the fatty tissue restricts organ functions. In some studies it has been shown that treatment with the agent salbutamol, used against asthma, can achieve success against lipomatosis.
homeopathy
Naturopathy advocates the thesis that a lipoma is formed by a disturbed breakdown of metabolic products. Alternative medicine recommends treatment with Bach flowers and medicinal plants to promote the removal of metabolic end products.
In addition, a fast to detoxify and deacidify the body can have a positive effect on lipomatosis and lead to the regression of the tumors.
Lipomatosis and alcohol - what is the connection?
Alcohol is converted into acetate in the liver and used as an energy source by the body. In addition to providing energy, alcohol consumption also means that the body slows down fat burning and stores fat.
Regular and excessive consumption of alcohol is considered to be a risk factor for the development of lipomas, and strict abstinence from alcohol may improve severe lipomatosis.
forecast
Lipomatosis is one chronically progressive Illness. In most cases, the growth of adipose tissue continues, but faster initially and slower as the disease progresses. In some cases, a stoppage of lipomatosis has been observed, especially when concomitant Risk factorssuch as alcohol consumption in particular, have been reduced or eliminated. The extent of lipomatosis can be controlled through regular surgery, although one always has to consider the general risks of surgery like Infections or Secondary bleeding must give up. On the other hand, it can also happen that, following an operation, the increase in fatty tissue exponentially increases.
prophylaxis
Since the causes are poorly understood, prophylaxis against lipomatosis is difficult. It always makes sense to consider those associated with lipomatosis Metabolic diseases such as diabetes or hypothyroidism well controlled. Alcohol consumption, another factor linked to lipomatosis, should be restricted. All of this is especially true when in your own family cases of lipomatosis have already become known. Further, special localizations of lipomatosis are discussed below.



.jpg)













-mit-ten-(titanic-elastic-nail)-oder-sten.jpg)