Almonds
synonym
Medical: tonsil (s)
Latin: tonsilla
definition
Tonsils are secondary lymphatic organs in the area of the oral cavity and throat.
They serve the immune defense. As part of bacterial colonization, they can become painfully inflamed, which is colloquially known as angina. Enlargement of the tonsils (Hyperplasia) is not uncommon. It occurs mainly in children and can, among other things, lead to an impairment of nasal breathing.
Read detailed information on the subject: Lymphatic organs

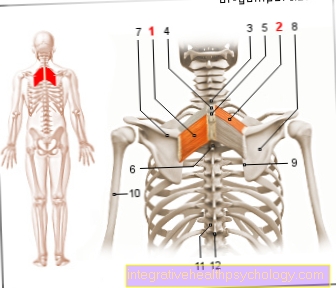
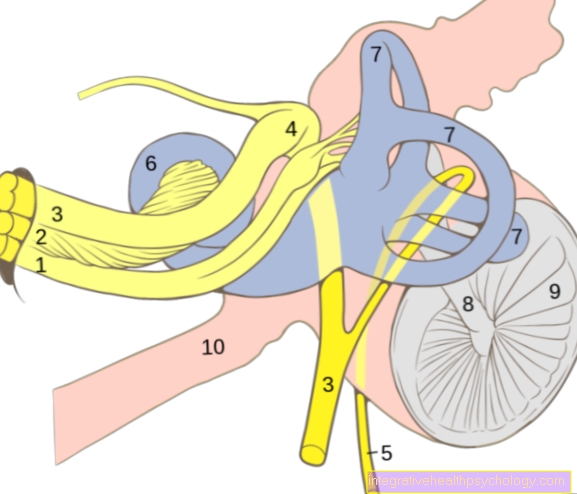
Figure almonds

- Palatine almond (blue) -
Palatine tonsil - Pharyngeal tonsil (green) -
Pharyngeal tonsil - Tongue almond (yellow) -
Lingual tonsil - Posterior palatal arch -
Arcus palatopharyngeus - Tongue - Lingua
- Hard palate -
Palatum durum - Soft palate -
Palatum molle - Anterior palatal arch -
Arcus palatoglossus - Incisors -
Dens incisivus - Lower jaw - Mandible
- Hyoid bone - Hyoid bone
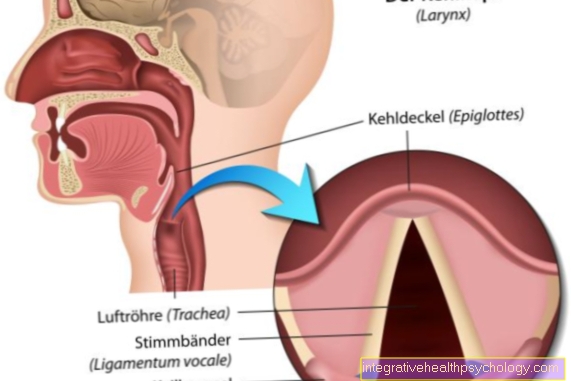
- Epiglottis - epiglottis
- Throat - Pharynx
- Nasal cavity - Cavitas nasi
S - food route
L - airway
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
anatomy
There are four different tonsils:
- The Pharyngeal tonsil (Pharynx) lies in the lining of the roof of the pharynx.
- The Palatine tonsil (Palatine tonsil) is located in the rear part of the oral cavity just before the transition to the throat between the anterior and posterior palatal arch.
- The Lingual tonsil (Tongue almond) lies on the base of the tongue in the area of the tongue root.
- The Tonsilla tubaria (Tuba almond) lies at the mouth of the Tuba auditiva (Eustachian tube / Eustachian tube) in the nasopharynx. The palatine almond and the tubular almond are paired, that is, they occur on both sides of the throat.
The pharyngeal tonsil and the tongue tonsil, on the other hand, are unpaired, so there is only one each. The totality of all tonsils is called the Waldeyer throat ring, it is part of the body's immune system.
Read more about the tonsils
histology
The almonds are part of the Mucosal-associated lymphoid tissue (MALT - mucosa-associated lymphatic tissue).
Lying inside numerous lymph folliclesmade by immune defense cells.
The surface of the Palatine almond and the Tongue almond consists multilayered squamous epithelium. Its surface is greatly enlarged by numerous crypts (indentations in the surface).
The surface of the Pharynx consists Respiratory epithelium (multi-row ciliated epithelium). The pharyngeal tonsil and the palatine tonsil are by one Connective tissue capsule separated from their surroundings.
function
With the tonsils one means colloquially the four secondary lymphatic organs of the pharynx, which also summarized Waldeyer's throat ring to be named. This description means that the almonds are part of the body's defense system, the immune system belong. Lymph nodes and spleen, as Bone marrow, Thymus and even the appendix (appendix, colloquial: appendix) in the intestine form this defense system with the tonsils.
If the tonsils come into contact with one through the lymph or blood antigen come, so with bacteria or viruses, or other components that the body recognizes as a danger, the so-called in the tonsils Immune response initiated.
This immune response takes place through cells that are located in the tonsils and are also partially formed there. These cells become B and T lymphocytes called and belong to the white blood cells. B-lymphocytes can antibody produce that are specifically directed against the recognized antigen. T lymphocytes are directed against already infected cells and kill them off. For this system to work, it is important that the surface that can come into contact with antigens is as large as possible. This is the case with almonds by many deep furrows the case. Overall, the surface of the tonsils would be spread over 300cm² be.
The active defense function of the tonsils used to be valued much less, which is why the removal of them was often carried out preventively, for fear of tonsillitis. It is now known that the tonsils play a major role as a defense organ in the immune system and that a considerable disadvantage arises, if these are removed too early. For this reason, tonsil removal is now only done on children over 6 years old. In children over six years of age, the immune system is usually so developed that there is little to be said against removing the tonsils if they cause problems in the context of inflammation or other problems. From the onset of puberty, it can be assumed that the tonsils will not function well more, and these slowly recede.
Tactility
Usually the tonsils cannot be felt from the outside. In the case of inflammatory changes, however, it may be that these swell considerably and can then also be palpated from the outside. For inexperienced people, however, they can easily be mistaken for swollen lymph nodes, which can be felt in the same place, especially if there is inflammation in the neck area.
The tonsils are much easier to feel from the inside when they are inflamed. Especially with the tongue, those affected can feel the enlarged organs well. The doctor can also feel the tonsils with a spatula from the inside.
Pain
If pain occurs in the area of the tonsils, this is usually due to a very common in Germany Tonsillitis. The type of pain varies depending on the severity of the disease and personal disposition. Mostly kick Sore throat, difficulties swallowing, Tenderness and Temperature sensitivity on. Typically, the pain also radiates into the Ears out. With children who are not yet able to communicate well Earache be a clue of a disease of the tonsils. In some cases there are also a headache related to tonsillitis.
If this type of pain, which is usually severe, is observed, a doctor should be consulted who may be able to confirm or rule out the diagnosis of tonsillitis.
Tonsillitis
If colloquially from "the almonds“The talk is mostly they are Palatine tonsils (Tonsillae palatinae) meant. It is not uncommon for people to settle here bacteria from which then to a Inflammation of the tonsils to lead. This is known as Tonsillitis or colloquially as "angina“.
The bacteriaThe most common causes of such inflammation are beta hemolytic Group A streptococci ( representative Streptococcus pyogenes).
Less common pathogens are:
- Pneumococci
- Haemophilus influenzae and
- Staphylococci
Children and adolescents in particular are more likely to suffer from such tonsillitis. The patients feel a distinct pain in swallowing and often have a significantly reduced general condition with fever.
A look in the mouth is particularly important for diagnostics. At the beginning of the disease you can see a strong one here Reddening of the tonsils, later the characteristic white "Pus“.
To treatment become common Antibiotics used, in particular penicillin. Also procure Schmerzmeans and gargling with disinfectant solution for relief. Tonsillitis usually heals within Days to a few weeks out.
However, it can also Complications arise. So can the inflammation for example also on that heart (Endocarditis), the kidney (Glomerulonephritis) or the Joints (arthritis) overlap or it can be a abscess in the field of Almonds (Peritonsillar abscess) arise.
Differential diagnostic must have causes like that in angina Pfeiffer's glandular fever (Mononucleosis), one diphtheria or Scarlet fever be excluded.
At frequently recurring tonsillitis (recurrent or chronic tonsillitis), especially in childhood, can be a Removal of the tonsils (Tonsillectomy) may be considered as a possible treatment option.
Polyps

Colloquially, polyps are enlargements (hyperplasias) of the pharyngeal tonsil (tonsilla pharyngealis). In technical jargon, these are called adenoids or adenoid vegetations.
They can get so big, especially in children, that they obstruct nasal breathing. The affected children then breathe primarily through their mouths. They also suffer from otitis media more often, as the adenoids can obstruct the connection between the nasopharynx and the middle ear (auditory tuba / Eustachian tube / ear trumpet). Furthermore, the relocation of the auditory tuba can lead to hearing loss, which in the worst case can lead to delayed language development in childhood. Much enlarged tonsils are reduced in size by means of an adenotomy. Rarely, the pharyngeal tonsil can grow back so much that another surgical reduction has to be carried out.