Myasthenia gravis
Synonyms
- Myasthenia gravis pseudoparalytica
- Hoppe-Goldflam Syndrome
- Erb Goldflam Disease
Also read the following topics:
- Muscular dystrophy
- Duchenne muscular dystrophy
- Myotonic dystrophy
- FSHD
Summary
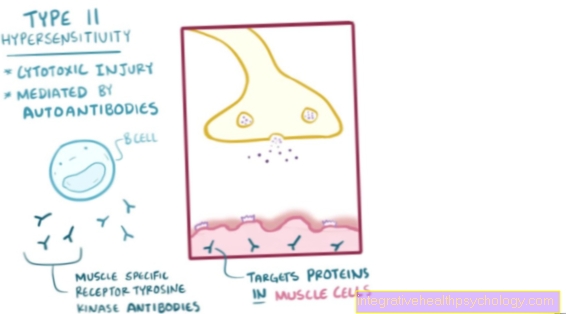
The Myasthenia gravis is a disease of the switching point between nerve and muscle (neuromuscular endplate; see anatomy Musculature) from the group of auto-aggressive diseases. The immune system the affected person produces (auto) antibody against the receptors (receivers) for the messenger substance that triggers the translation of a nerve impulse into a mechanical action (muscle contraction). This leads to a progressive destruction of these receptors with the result that an increasingly weaker muscle action (muscle weakness) takes place in response to a nerve impulse.
If left untreated, myasthenia gravis runs continuously to varying degrees and can be fatal if the Respiratory muscles. Medicinal measures to influence the immune system of those affected can slow down or even stop the progression of the disease. On the other hand, there are many common drugs (e.g. Anesthetics), which can worsen the symptoms of myasthenia gravis, so that those affected are advised to have a "Myasthenia Pass“To be issued to inform first-aiders and therapists of this fact.
definition
The Myasthenia gravis is a Autoimmune diseaseleading to progressive damage at the transition point between annoy and muscle leads. The destruction of receptors for the messenger substance at the coupling point causes pathological increased fatigue and weakness of the affected muscles.
frequency
Myasthenia gravis occurs with a frequency of 4 - 10/100000, the disease occurs more frequently either between the ages of 20 and 40 or between the ages of 60 and 70, and very rarely once in childhood. Women are affected more often than men.
causes
Myasthenia gravis is caused by an autoaggressive process of the immune system in which the immune system produces antibodies against receptors in the neuromuscular endplate.
In many cases a change in the Thymus (immunological organ in childhood that usually regresses in adulthood).
As with many autoimmune diseases, there is some inherited component. In rare cases, symptoms of myasthenia gravis can also occur in connection with other diseases, e.g. B. Overactive thyroid gland, Rheumatoid arthritis or other autoimmune diseases. Mental and physical stress as well as secondary illnesses can exacerbate the symptoms of myasthenia gravis.
Symptoms
The disease usually begins in places where a relatively small number of them join a neuromuscular junction muscle fibers is supplied by a nerve. This is the case with Musclesthat should enable fine-tuned movements, such as B. the eye muscles. The affected muscles show a tendency to fatigue too quickly when used; the symptoms worsen accordingly over the course of the day and when a movement is performed several times.
This is expressed e.g. B. in increasing One or both upper eyelids droop (Ptosis) when looking up (= Simpson test), also show up early Double vision when looking sideways due to involvement of the eye muscles. Other muscle groups affected early on are the facial, throat (increasing during the meal difficulties swallowing) and masticatory muscles. The Speech can appear slurred, the face of those affected sagging and the Mimic expression sparse.
Clinically, different classifications are made according to age at onset or severity of the symptoms.
As the process progresses, the limbs can also be quickly fatigued and weak under load, so the sick can have difficulties climbing stairs or a waddling gait exhibit. The involvement of the respiratory muscles can also occur suddenly and suddenly (myasthenic crisis) and is a very serious complication of myasthenia gravis.
Note: symptoms
Overall, the disease shows one very great variability in appearance: Even with individual sufferers, the affected muscle groups, the triggering stress and the strength of the symptoms change.
Exclusion diseases (differential diagnoses)
The main differential diagnosis is that Lambert-Eaton Syndrome, which occurs particularly in conjunction with tumor diseases. Symptoms and disease mechanisms are basically similar, but the blood test shows different antibodies than those of myasthenia gravis, including the picture in the electromyogram (Electromyography/ EMG) is another.
Furthermore, there are theoretically other diseases of the Nervous system and the muscles like multiple sclerosis, Muscular dystrophies or Poliomyositis ("Polio"), the z. Some of the symptoms are similar to those of myasthenia gravis. In most cases, these diseases can be ruled out with a careful medical history and physical examination.
Diagnosis
Basic diagnostics include taking the medical history, physical examination with a neurological focus and the "Tensilon test“.
Info: Tensilon test
At the Tensilon test a drug is administered that has an inhibitory effect on the enzyme which is normally responsible for breaking down the messenger substance at the nerve-muscle switch point. This drastically increases the availability of the messenger substance at the neuromuscular endplate and the symptoms of myasthenia gravis decrease significantly for about 5 minutes within a very short time.
When examining the electrical activity of the muscle in the Electromyogram (EMG) shows a characteristic picture (decrease in the height of the deflections with prolonged exposure).
In the blood can 80-90% of those affected antibody against the messenger substance receptors on the neuromuscular endplate. If this does not succeed, one has to Muscle tissue sample can be removed for microscopic examination. To rule out the presence of a change in the thymus, an X-ray of the Rib cage prepared.
therapy
The therapy is based on influencing the patient's immune system with cortisone (cortisone) or other active ingredients that reduce the production of antibodies against the messenger receptors. Inhibitors for the enzyme that breaks down the messenger substance are administered symptomatically; in the myasthenic crisis, these are administered intravenously. These inhibitors are not entirely unproblematic, since an overdose can lead to a serious "cholinergic crisis", which clinically manifests itself like poisoning with weed killer (nausea, vomiting, muscle cramps, sweating).
If an enlargement or change of the thymus is actually detected in the clarifying examination, it is usually removed surgically, which can lead to a causal improvement in the symptoms. In this case, an attempt can be made to gradually end the immunosuppressive therapy after 2 - 4 years.
forecast
The disease progresses slowly and is still fatal in 10-20% of cases. If the disease remains limited to individual muscle groups, the prognosis is good. Those affected are advised to contact interest groups in order to exchange information about living with the disease and to get a "Myasthenia Pass"To get, who in an emergency informs helpers and therapists about the presence of the disease.