Parathyroid hypofunction
synonym
Medical: Hypoparathyroidism
English: hypoparathyroidism
definition
The parathyroid gland hypofunction (hypoparathyroidism) is a disease of Parathyroid, which leads to a parathyroid hormone deficiency. This lack of Parathyroid hormones leads to one Calcium deficiency throughout the body, making neurological symptoms may occur.
Ethiology
Most common cause of a Parathyroid hypofunction (Hypoparathyroidism) is a surgically induced removal of the parathyroid glands with a partial or complete thyroid removal. Less frequently, the parathyroid glands are through Irradiation, Autoimmune diseases or a long and serious one Magnesium deficiency damaged.
root cause
Parathyroid hormone is a hormone produced in the parathyroid glands that causes the Calcium and phosphate balance regulated. Is there a too high calcium levels in the body, will decreases parathyroid hormone poured out (negative feedback), while a low calcium level leads to an increased release of parathyroid hormones. This in turn influences the Bone breakdown and build-up and thereby regulates the release of calcium from the bones, or the incorporation of calcium into the bones. In case of an Hypoparathyroidism (Underactive parathyroid gland), this calcium metabolism can no longer be regulated. There is a significant reduction in the calcium level in the bloodwhich then produces the clinical symptoms of calcium deficiency.
Symptoms
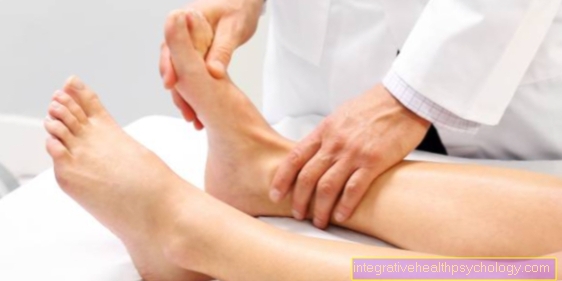
The Symptoms of underactive parathyroid gland are through one massive calcium deficiency and a increased phosphate in blood marked. The calcium deficiency in particular leads to clinical symptoms. A significantly increased one is particularly tragic Susceptibility to convulsions in the Skeletal muscles or in the whole body (Epileptic seizures). The so-called parathyroid hypofunction is typical Paws of the handscaused by cramps. In addition, a calcium deficiency leads to Loss of sensitivity (Paresthesia), Hair loss, drier and rough skin. Clinical signs one Tetany are Contractions of the Facial muscles when brushing the facial nerve 1 to 2 cm in front of the earlobe (Chvostek sign), as well as the Paws position of the hands when inflating a blood pressure cuff above the systolic pressure (Trousseau sign).
Could Thyroid Disease Cause Dizziness? Read more about this under: Dizziness and thyroid
Complications
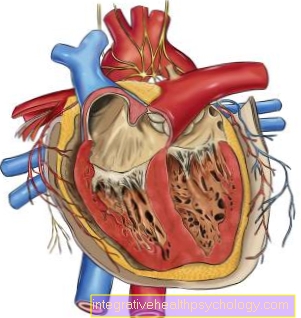
Complications of the underactive parathyroid gland mainly occur if the parathoromonal deficiency is not recognized in time. In children, this can lead to tooth abnormalities, developmental disorders, and short stature. In adults, long-term damage from a parathyroid hormone deficiency can occur if this is not detected early and treated with medication. These include heart problems, cataracts (cataract), Osteoporosis and calcifications in the area of the basal ganglia in the brain. This leads to the so-called driving syndrome. Clinical signs are headaches, speech disorders, and slowly progressing dementia.
Diagnosis

Often lead the clinical picture of the Parathyroid hypofunction in connection with the anamnesis for the suspected diagnosis of the Hypoparathyroidism. The subsequent laboratory diagnostics then provide the evidence and secure the diagnosis. A decreased calcium in the serum should always be the reason for determining the parathyroid hormone level. At a pure hypocalcemia the parathyroid hormone level would be reactively increased in order to be able to provide the body with more calcium. However, if the parathyroid glands are surgically removed or otherwise damaged, both calcium and parathyroid hormone levels are reduced, thus securing the diagnosis of hypoparathyroidism (Parathyroid hypofunction). Becomes a congenital hypoparathyroidism (Underactive parathyroid gland) not discovered in children, can Dental abnormalities and Short stature Be a consequence of this lack. To rule out calcifications that have already formed in the brain, a Computed Tomography be performed. Also a EKG is important to estimate the extent to which the Heart to be able to exclude.
Therapy of parathyroid hypofunction
goal of drug therapy for hyperthyroidism is the maintenance of normal calcium levels in the blood. Often will Dihydrotachysterol or Rocaltrol as Vitamin D analogs in combination with calcium used to maintain calcium levels. Since a calcium level that is too high can lead to an increased excretion of calcium in the urine, calcium should be checked regularly in the case of an underactive parathyroid.
Otherwise you can Kidney stones or one Nephrocalcinosis Be the result of an excessive calcium concentration in the urine. To avoid these side effects, a calcium supplement can be given at the same time Thiazide diuretic be prescribed. This lowers the level of calcium in the urine, thus preventing the risk of kidney stones forming. This level should also be checked regularly.
In the Acute therapy for a tetanic seizure intravenous calcium administration is the drug of choice. The injection should be done as slowly as possible, because otherwise the affected person with Feeling hot, nausea and a headache respond to calcium administration. The lifelong calcium substitution can treat the tetanic cramps well. Long-term consequences like calcifications or cataracts, however irreversible and cannot be treated with calcium substitution.
prophylaxis
Basically, the Parathyroid glands preferably not be damaged or removed with any thyroid surgery. If this is not possible, there is the possibility of autotransplantation. Here, your own parathyroid glands can be planted in muscle tissue. These grow into these areas and continue to produce parathyroid hormone. This possibility will also help with the risk of radiation damage Thyroid cancer utilized. As a prophylaxis, the parathyroid glands are moved to another place in the body before the start of the irradiation in order to protect them.
forecast
If the hormone deficiency is recognized early, it is Parathyroid hypofunction easy to treat through lifelong hormone substitution. However it is not possible to like the long term damage cataract or Calcification in the brain to heal. The same applies to the consequences in children whose hormone deficiency was not recognized at an early stage. Accordingly, the prognosis depends heavily on the time of diagnosis and therapy.





.jpg)











-whrend-der-schwangerschaft.jpg)