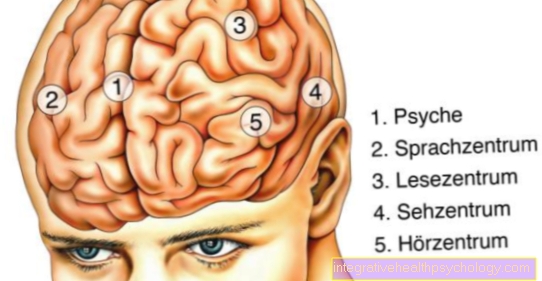
Ulnar nerve
Synonyms

Ulnar nerve
medical: Ulnar nerve
English: ulnar nerve
definition
The ulnar nerve is an important arm nerve. Its course on the forearm is based on the cubit after which it was named.
Like most arm nerves, it consists of fibers that carry sensitive information from the skin and joints to the spinal cord and brain (sensitive afferents) and from motor fibers that send impulses from the brain to the arm muscles (motor efferents).
origin
The ulnar nerve is one of many annoy from the arm nerve plexus, the Brachial plexus, together.
The Spinal nerves from the cervical cord of the spinal cord (C5-C8) assemble directly after exiting the spinal cord to form this bundle of nerves, which is called the arm nerve plexus (Brachial plexus) referred to as.
They all go from this bundle of nerves annoy that take care of the arm.
The nerves of the nerve cord bundle (Brachial plexus) be called :
- Short branches: Subscapular nerve, thoracodorsal nerve, medial and lateral pectoral nerve, medial antebrachial nerve, intercostobrachial nerve;
- Long branches: Musculocutaneous nerve, axillary nerve, radial nerve, median nerve, ulnar nerve
Overview and classification
A nerve contains fibers that transport sensitive impulses from the skin and joints back to the brain (Afferents) and at the same time fibers, via the impulses from the brain to the Muscles sent (Efferents).
Anatomy and course

The ulnar nerve runs from the axel on the inner side of the Upper arm down to the elbow. Behind the protruding bone of the Elbow (Medial epicondyle) it pulls on the front inside of the forearm. All the way he comes under a forearm muscle (Flexor carpi ulnaris muscle) to lie hidden and protected. Unlike its sibling nerve, the median arm nerve, it wanders Ulnar nerve above the carpal tunnel to the palm.
Physiology (motor skills)
The ulnar nerve (ulnar nerve) primarily controls the muscles of the hand on.
The most important of the supplied muscles are:
- Thumb pull (Adductor pollicis muscle): Tightening and flexing the thumb;
- Short thumb flexor (Flexor pollicis brevis muscle): Flexion of the thumb;
- Little finger spreader (M. abductor digiti minimi): Abspraction, extension of the little finger;
- Little finger flexors (Flexor digiti minimi): Flexion of the little finger;
- Worm-shaped finger muscles (Mm.lumbricales): Flexion of the fingers in the base joint, extension of the fingers in the end joint;
- Finger spreader (Mm.interossei): Spread your fingers.
Other muscles supplied by the elliptical nerve:
- Short palm muscle (M. palmaris brevis)
- deep finger flexors (Flexor digitorum profundus muscle)
Physiology (sensitivity)
The sensation of the edge of the hand including the ring finger is supplied by the ulnar nerve. In the palm of the hand the area extends to the middle of the ring finger, on the back of the hand to half of the middle finger.
damage
Injuries to the elbow can cause nerve damage.
For example, a torn ligament on the elbow can affect the ulnar nerve.
When the nerve is irritated at the level of the elbow joint, it becomes noticeable with a painful, vibrating tubercle sensation, which has given the protruding bone the name of the funny bone.
Permanent pressure damage in this area leads to the image of the "clawed hand": The fingers are overstretched in the base joints and bent in the middle and end joints. In addition, there is sensitive skin breakdown on the edge of the hand and ring finger.
Injuries in the area of the wrist lead to such a claw hand, but the sensitivity of the edge of the hand is not impaired.
If other nerves are damaged in addition to the ulnar nerve, complete paralysis of the brachial plexus can also occur.
Read more on the topic: Claw hand