Polyps
Synonyms in a broader sense
Medical: Polyposis nasi
Nasal polyps
English: Nasal polyps
definition
The popularly named polyps are swollen, bilateral enlargements (hyperplasia) of the nasal mucosa or the mucous membrane of the paranasal sinuses.
They are called polyps because the enlargement of the mucous membrane looks like a fungus on a tree trunk.
The enlargement of the mucous membrane usually starts from the maxillary sinus (Maxillary sinus) or the ethmoid sinus (ethmoid sinus) and grows towards the middle nasal passage. The nasal passages can be almost completely closed when the growth is pronounced.
The exits (ostia) of the paranasal sinuses located there can be affected by the nasal polyps and almost completely closed. The quality of life can be significantly reduced by polyps.

causes
There are various causes that stimulate an increased growth of the mucous membranes. First and foremost are more permanent in children sniff and colds (chronic rhinitis) and Sinus infection (chronic sinusitis) to call. Other pathogens like Mushrooms (Mycoses) that appear in dusty, warm air can promote polyps. In the case of allergy sufferers, mucous membrane growth is also stimulated by pollen and other allergens.
Symptoms
Not infrequently suffer especially Children who have had several colds (runny nose) from an impaired nasal breathing and get a noticeable one nasal voice. The parents always notice it at some point open mouth her child. Even at night you have to keep your mouth open to breathe, you start to snoring, sleeps worse and is limited in its performance during the day. Children then often suffer from Poor concentration and stand out due to their scholastic weaknesses.
You can find more information on the subject of poor concentration in children and other school problems in our pedagogy portal Problems with learning.
Constant mouth breathing leads to infections more often Throat (Pharyngitis), the tonsils (Tonsillitis) and the Bronchi (bronchitis). These infections can in turn mainly in children via the short ear trumpet (tuba eustachii) to one Otitis media (Otitis media) to lead.
A permanent closure of the nasal passage reduces the ability to smell (hyposmia) and also promotes increased secretion production (mucus) of the nasal mucous membrane.
diagnosis
Since the symptoms mentioned above can also have other causes, the ENT doctor looks into the nasal cavities with a special device (endoscope) and looks for the exits of the paranasal sinuses. Here he looks for the origin of the polyps. In addition, an imaging procedure (CT, computed tomography) can make the nasal polyps visible.
therapy
Since the Polyps Unfortunately, they do not regress themselves, they often have to be surgically removed.
The polyps are over the nose cleared and at the same time the exits of the paranasal sinuses expanded. After this procedure, the patient is recommended to regularly clean his nose by inhalation, nasal rinsing and nasal showers (Emser Sole®).
This intervention is risky in that the Nasal mucosa is very well supplied with blood and a complication of the operation is secondary bleeding.
When a allergy is responsible for the development of nasal polyps, it should definitely be treated afterwards.
Which includes:
- Antihistamines
- cortisone Nasal sprays
- long-term desensitization therapy.
Homeopathy for polyps
Various homeopathic remedies are available for supportive treatment of polyps; but this is mainly about the relief accompanying complaints, a strengthening of the immune system or a reduction in inflammatory reactions. If the polyps have already arisen, they cannot be eliminated by homeopathy and thus homeopathy does not replace treatment by a doctor. Well-known remedies of homeopathy in the treatment of polyps are:
- Calcium phosphoricum: For lively, sensitive and thin children
- Calcium carbonicum: For sluggish, plump children who are prone to shyness and fear
- Thuja occidentalis: polyps in the nose, colon or uterus and patients who are prone to colds
A homeopathic treatment should always be supervised by a doctor or alternative practitioner with additional training in homeopathy, who can find the right remedy and the right dosage for the symptoms.
surgery
If the conservative therapies (steroids or antihistamines for oral / application) do not produce the desired result, a operative therapy be tried. There is the endonasal (through the nose) polypectomy and the endonasal operation of the paranasal sinus with simultaneous removal of the polyps. As with all surgeries, medication should be taken before the polyp surgery, especially blood thinners, with the treating person doctor discussed and discontinued if necessary in order to avoid complications during and after the operation.
Endonasal polypectomy
This surgical technique is mainly used at older Patients used when major surgery is not feasible, for example due to a poor general condition of the patient. she will outpatient carried out. This surgical technique often leads to after a short time Relapses (the recurrence of polyps), as the “root” of the polyp remains in the mucous membrane. A complete removal of polyps and diseased mucous membranes is usually recommended. During this procedure, the surface of the mucous membrane is locally anesthetized. In addition, a Vasoconstrictor used, a drug that constricts the blood vessels, making the polyps easier to see and reducing bleeding. It is about pedunculated polyps, which are elongated and narrow at the base, they become with a metallic noose includes and in the area of middle nasal passage pinched off until severed from the base and pulled out through the nose. For polyps with a broad base, a Nasal forceps or a so-called Conchotome used for ablation. The Choanal polyps, which are formed by mucous membrane cells from the maxillary sinus, one of the paranasal sinuses, and grow into the middle nasal passage. These polyps are made using the so-called blunt hook removed after Lange. The stalk of the polyp is grasped, torn with the hook and the polyp is pulled out through the nose. But even with this type of polyp, complete removal with the affected mucous membrane is recommended, because otherwise recurrences can occur. After the operation, the nasal mucosa must also be used Douches and inhalation taken care of to prevent scabs or swelling.
risk: Bleeding and infections as well as injuries to the nerves and surrounding structures are a possible surgical risk.
Endonasal sinus surgery with polyp removal
For this surgical technique are a stationary A stay of about a week and a general anesthetic necessary. The incapacity for work depends on the type of occupation and lasts approximately two weeks. This operation will again be a endoscope used and by removing the front Ethmoid cells (anterior ethmoidectomy) allows access to the frontal sinus. Now that will tissue either partially (Windowing) or completely removed, one speaks here of Redevelopment. This is done for the frontal sinus, sphenoid sinus, and maxillary sinus. The operation can include polyp removal, nasal septum correction (Septal correction) or a removal of tonsils and a reduction in the size of the Turbinates be carried out to improve the ventilation of the nose and its sinuses and to reduce the inflammation After the operation, there is initially No smoking. The pickled Tamponade to Hemostasis will be removed by the doctor after about 1-3 days.
risk: The procedure is very demanding and, as with any operation, it can be too Secondary bleeding, Infections and Injuries come from nerves and surrounding structures, bleeding during this operation is not uncommon and may occur electric desolate (coagulates) Need to become. The close proximity to the brain and meninges can lead to inflammation of the brain (encephalitis) or meningitis (meningitis) come. A possible violation of the Skull base goes with a leakage of liquor through the nose (Liquorrhea) and must be treated immediately. Also the Eye muscles and their nerves or the optic nerve can be injured or infected. There may be bleeding into the skin as well Eye socket come. Furthermore, there may be a (temporary) worsening of the Sense of smell come. Because of these risks, although extremely rare, the patient will be closely monitored after the operation. Slight headache and a Head pressure, such as Bruising or Swelling occur more often.
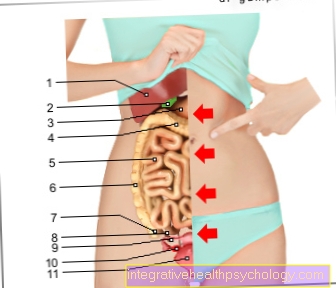
Polyps in the intestines
Polyps in the intestine are thickened new formations of the intestinal mucosa that protrude into the interior of the intestine. The colon is most commonly affected, but can be found in any section of the gastrointestinal tract. Most of these growths are benign, but they can degenerate and thus pose a risk of colon cancer. The larger the polyps, the greater the risk that the cells will degenerate and cancer will develop. With a polyp size of about one centimeter there is a risk of about 1%, with a size of four centimeters the risk increases to about 20%. Polyps in the intestine come in different forms: they can be stalked with a narrow base, sessile and broad-based, bulbous or round. There are also hereditary (e.g. familial adenomatous polyposis, Peutz-Jeghers syndrome or Cowden syndrome) and non-hereditary forms. It is estimated that one in ten have polyps in the intestine, but intestinal polyps usually appear from the age of 6. Bad eating habits (high in fat and low in fiber), little exercise, stimulants such as alcohol and cigarettes and obesity are assumed to be the cause. Polyps in the intestine are usually an incidental finding during a colonoscopy (Colonoscopy), as small polyps often do not cause any discomfort. Symptoms usually only arise when the polyps have reached a certain size. This can lead to irregular stool (such as diarrhea or constipation) and abdominal pain. They can also cause blood in the stool or stool turning black. In this case, a medical evaluation should take place immediately. The diagnosis is made through a colonoscopy. A flexible tube, which is equipped with a camera, is inserted through the anus to the beginning of the large intestine, slowly withdrawn and the mucous membrane of the large intestine is assessed. Even small samples can be taken during the examination, which takes place with the administration of a sleeping pill, in order to clarify possible changes. If the polyp is not too large, it can be removed in the same session if necessary. The examination is carried out on an outpatient basis in specialist internal practices.
Read more on this topic at: These are the symptoms to help you identify colon polyps and how colon polyps are removed
The therapy takes place as described by the Removal smaller polyps by forceps during the Colonoscopy. Larger polyps can be caused by a electrical Noose to be worn away. The removal of the polyps mostly causes no Pain. If the polyps are larger than 3 cm or if there are a lot of polyps, it is usually necessary operated on The affected part of the intestine is often removed. The colon polyps are getting after removal fine tissue examined to make sure they are benign neoplasms. A regular follow-up check, respectively Colon cancer screening is displayed. Colon cancer screening by colonoscopy is the most effective form of early detection of colon cancer and its cost will be from the 55 years of age covered by the statutory health insurance.
Is there any suspicion of a genetically increased risk of colon cancer, preventive measures should start earlier. This also applies to inflammatory bowel disease, as there is also an increased risk of developing colon cancer.
Uterine polyps

Uterine polyps (Uterine polyps) are mostly benign changes in the lining of the uterus. The polyps can stalked (with a narrow base) or serene (with a broad base) and have a size of a few millimeters to a few centimeters. If the polyp is pedunculated, which is more common, it can grow from the uterus through the cervix into the vagina. Polyps in the uterus can occur at any age, but women in and during the menopause are particularly affected because of the Hormonal changes. The cause of uterine polyps has not been clearly established, but a connection with hormone production and, above all, a dependence on the level of estrogen is suspected. Estrogen is the female sex hormone produced by the ovaries and, to a lesser extent, the adrenal gland. Further risk factors are permanently high blood pressure (arterial hypertension), History of obesity and polyps. Also performing a Hormone replacement therapy and tamoxifen (used to treat breast cancer) increase the risk of polyps in the uterus. They often cause uterine polyps no symptoms. Possible symptoms would be irregular menstruation, very heavy menstruation (Menorrhagia) or vaginal bleeding after the menopause. Postmenopausal vaginal bleeding should be investigated immediately as it is often a symptom of Uterine cancer could be. If the polyp is well supplied with blood, it can too Spotting coming outside of your period (so-called "Spotting"). If it is particularly large, it can cause abdominal pain, especially during intercourse. Labor-like pain can also occur when the uterus tries to reject the polyp.
Polyps can be a cause of infertility if they grow so unfavorably that they can occur Sperm into the uterus or by acting like a natural intrauterine device (spiral) act and one Nesting the fertilized egg into the uterine lining. Miscarriages can also be caused by polyps in the uterus. Polyps of the uterus are not infrequently incidental findings in the gynecological examination. They can be diagnosed by ultrasound, by mirroring the uterus, or by speculum examination (examining the vagina using a special mirror). A Tissue sample helps malicious Recognize degeneration early on. Often, however, uterine polyps are benign New growths. Non-symptomatic polyps do not necessarily need to be removed, but often becomes one surgery devices. The polyps are removed by a curettage (curettage), which takes place under general anesthesia. At Suspicion The operation is expanded accordingly to include a pre-cancerous stage or cancer. The progression of uterine polyps is usually good, after an operation it only happens a lot Rare to recurrence of polyps.
Polyps in the stomach
Polyps in the stomach are newly formed Protuberances the lining of the stomach and often benign. Often there are several polyps at the same time, one then speaks of multiple gastric polyps. Polyps in the stomach often occur after the 60 years of age but can also occur in young people. In addition to the stomach, polyps often affect the large intestine, but they can occur throughout the gastrointestinal tract. The doctor can determine the polyps in the stomach through a gastroscopy and usually during the examination electric remove. Stomach polyps can be classified in several ways: According to their shape (stalked / sessile, spherical, shaggy) and according to their cellular structure, i.e. what kind of Glands occur in the lining of the gastric polyp. Is it the so-called adenomatous type, this can be a preliminary stage of stomach cancer and should be removed from a size over 5 mm. Polyps in the stomach often cause no symptoms, only larger polyps can cause a feeling of fullness or pain in the upper abdomen. Are warning symptoms Vomiting blood or Tarry stool (Blackening of the stool), a doctor should be consulted immediately. A cause for the occurrence of gastric polyps has not yet been established, although bad Eating habits (low in fiber, high in fat) and an infection with the Helicobacter pylori bacterium could play a role. A genetic form of gastric polyps is also known, polyposis syndrome, where the polyps occur in large numbers in the stomach and other parts of the intestine and often affect several family members.
The so-called Adenotomy, i.e. the removal of the troublesome tonsils, is usually carried out in childhood, as the polyps often regress themselves in adolescence. General anesthesia is performed, the polyps are removed and then any polyps Bleeding breastfed with cotton wool. The procedure takes approximately ten to twenty minutes and is a commonly performed procedure. The greatest and most common risk of these polyps surgery lies in one Rebleedingwhich especially on the day and around the 5th-8th Day after the operation can occur, which is why a physical one Protection is necessary for a few days.
Polyps in the toddler

An enlarged pharynx is often referred to as a polyp in young children. The pharynx is part of the body's own defense system and protects the body with the help of immune cells Pathogens. It is above the Suppository behind the nose. An enlarged pharynx alone does not have any disease value, it usually occurs in children between the ages of 3 and 6. However, polyps can be responsible for snoring, nasal breathing, and constant runny nose. Often times the children breathe through it open mouth and have a slightly clumsy language. Recurring middle ear infections in children can also be caused by polyps if they obstruct the ventilation path between the nose and ear; in the worst case, this can lead to the child's language learning being delayed. In these cases, removal of the polyps is often recommended, which is usually the case outpatient is performed surgically. The so-called adenotomy, i.e. the removal of the troublesome tonsils, is usually carried out in childhood, as the polyps often regress themselves in adolescence. General anesthesia is performed, the polyps are removed and then any polyps Bleeding breastfed with cotton wool. The procedure takes approximately ten to twenty minutes and is a commonly performed procedure. The greatest and most common risk of these polyps surgery lies in one Rebleedingwhich especially on the day and around the 5th-8th Day after the operation can occur, which is why a physical one Protection is necessary for a few days.