Retropatellar arthrosis
definition
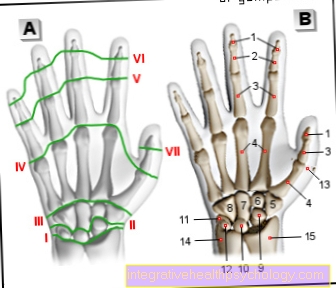
In the Retropatellar arthrosis is it a Articular cartilage wear on the back the patella, so the Kneecap. The joint here is the so-called "Femoropatellar Joint"where the Kneecap ("Patella", Facies articularis) and the Thigh bone ("Femur"; Facies patellaris) articulate with each other.
Further information on general knee osteoarthritis can be found here: Knee osteoarthritis

The patella not only forms part of the Knee joint components but is also a kind Lever arm for the Quadriceps ("Musculus quadriceps"), the tendon of which runs over the patella. The course causes a Extension of the lever arm and thus increases the torque. So one can imagine that communication with this large muscle can put the patella under extreme stress. Such loads can be the Cartilage nutrition, which about the Synovial fluid, the so-called "Synovia“Occurs, disturb. This causes the cartilage to lose its weight substance and Resilience with the result of the Joint wear, so arthritic manifestations. This can lead to massive pain behind the kneecap.
Please also read our article on this Pain behind the kneecap.
Symptoms
Typical Symptomsthat occur in patients with retropatellar osteoarthritis are pain when Climb stairs, at the Going down of slope and at Get up from the crouched position after long periods of sitting. The pain is mostly im anterior region of the knee joint localized. Often it is one creeping process, which starts and starts in slight pain lack of resilience and Inflammation up to Restriction of movement with the greatest pain. With a retropatellar osteoarthritis, a reduced load capacity of the knee joint can occur, as it had previously been too incorrect pressure loads has come. Then it reacts Femoropatellar joint in addition to the signs of wear and tear of the patella with a Power reduction of the thigh muscle. However, this again means that the knee joint, in particular the back of the patella, is more stressed. Because the Quadriceps owns an important Stretching function on the knee joint and thus the wear provoked even more.
The pain that creeps in sometimes goes with you cracking noise and one Feeling of instability hand in hand. Some of the patients also report Teething problems especially after long periods of sitting, i.e. when the knee was in a bent state. As Concomitant symptoms the joint can be affected by the overload igniteso that in addition to the pain also Swelling and Redness occur. In summary, the causes are a Imbalance between burden and Resilience of the knee or the femoropatellar joint responsible for the arthrosis.
Please also read our article on this Symptoms of osteoarthritis.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
diagnosis
As diagnostic measures count next to the clinical and physical examination the imaging procedures as the Magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) and the roentgen. In the clinical examination, a test can do that "Zohlen sign" which one is specific to the Retropatellar arthrosis is. The patient lies on his back with his legs stretched out. The examiner grabs the patella with one hand and carefully pushes it down towards the lower leg and fixes it there. He then asks the patient to tense his thigh muscle, i.e. the quadriceps. This moves the patella back up again.
One speaks of one positive pay sign if it is too at the test too Frictions and Pain comes. This then speaks for a retropatellar arthrosis. The roentgen, which is used in principle for diagnostics, enables a classification of the radiologically recognizable arthritic changes. Based on the stadiums, it can therapeutic approach be planned. One should know, however, that especially in the early stages, the clinical picture cannot match the radiological findings. The Joint space narrowing, osteophytic peripheral attachments, subchondral sclerotherapy and Pseudocysts are the signs of osteoarthritis that can be seen in the X-ray, including retropatellar osteoarthritis. The MRI can also be used to diagnose retropatellar arthrosis, but X-rays are preferred. The advantages of MRI are the very detailed and high-resolution display of the Articular cartilage and that there is no radiation exposure.
Read our articles on this Diagnosis of osteoarthritis and MRI of the knee joint.
Stages of retropatellar arthrosis

The staging of retropatellar arthrosis, which can arise primarily or secondarily, is used to assess the cartilage damage, since arthrosis is a degenerative change in the articular cartilage. The “Outerbridge” classification describes the extent to which joint wear has progressed. At a certain stage, the degeneration extends beyond the cartilage, so that the bone can also be affected.
- Stage 0: no cartilage damage recognizable
- Stage 1: The surface of the cartilage is still relatively intact and if so, only the slightest changes in the form of cracks
- Stage 2: surface damaged, structural cartilage damage
- Stage 3: Cartilage damage already deep and clearly visible
- Stage 4: cartilage completely destroyed and bone is also exposed.
Apart from the classification to "Outerbridge" can also be divided into 4 stages within the framework of the imaging diagnostics respectively. With the so-called "Kellgren Lawrence Score" radiological signs of osteoarthritis are used to define the severity. These include the subchondral sclerosis, the Joint space narrowing and the Osteophyte formation. It is important to know that the Correlation between the stages and the actual feeling of illness or limitation of patients not identical is.
- Stage 1: minor subchondral sclerosis
- Stage 2: Joint surface slightly irregular, slight narrowing of the joint space and osteophyte formation
- Stage 3: Joint surface very irregular, joint space narrowing and osteophyte formation
- Stage 4: Joint completely destroyed
Please also read our article on this Arthrosis stages.
therapy
The treatment of retropatellar osteoarthritis consists of several pillars. The drug-based, symptomatic therapy is usually carried out with the Substance group NSAIDs ("nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs"). The NSAID works both against the pain (analgesic), as well against inflammation (anti-inflammatory) and against the temperature increase (antipyretic). This enables pain and anti-inflammatory therapy mostly purely medicinal to relieve symptoms to lead. Another medicinal measure can be a Cortisone Injection in the joint represent. Other substances that can be injected are the Hyaluronic acid or that Glycosaminoglycan, which is an important part of the synovial fluid. Of the Cartilage damage is indeed not reversible again, however, the The degradation process stagnates. This is often an alternative to drug therapy Wearing a knee brace helpful.
Please also read our article on this Treatment of osteoarthritis.

If those conservative therapeutic approaches without success stay, depending on the stage and degree of complaint surgical intervention necessary be. Before each procedure a Jointoscopy (Arthroscopy) performed to assess the wear and tear and the current condition. Intervention can already take place here and in the context of a so-called Abrasion chondroplasty the cartilage growth be promoted. The procedure involves scraping the surface of the cartilage so that it is smooth afterwards. This turns the cartilage into Neoplasm stimulated. The retropatellar arthrosis can also be so advanced that a Indicated use of dentures is. The inserted implant should to Freedom from pain lead and the progression of Prevent retropatellar arthrosis. Depending on how the wear turns out, you can choose between different "Partial dentures" choose.On the one hand, only the area of the thigh bone, i.e. the femur, can be provided with an implant. On the other hand, both mutually articulating components of the Femoropatellar joint, i.e. the back of the patella and the thighbones, can be replaced by an implant. The decision will be individually in individual cases met.
Please also read our article on this Surgery for osteoarthritis and Knee prosthesis.
Bandages for retropatellar osteoarthritis
The Wearing a knee brace can both as Prophylaxis, as well as rehabilitation be useful. The function of a bandage is very diverse. In the area of application of retropatella osteoarthritis are aspects like Massage function, the Pain and irritation reduction, the Promotion of the healing process, the discharge and the stability relevant. A massage function comes from the incorporated Pressure pad, a so-called elastic pad, conditions. The pad also fulfills the function of holding the patella in position when the bandage is worn so that it can do not slip can. A pain and irritation reduction can be achieved through the relief and the massage function.
Today's bandages are despite their supportive function very elastic and sdo not restrict mobility when carried. Usually it is breathable fabrics with appropriate processing of the edges so that the bandage at exercise is not perceived as unpleasant and no pressure marks leaves behind. Since bandages are generally called orthopedic aid This can apply to both the patient and the patient private as well as statutory health insurances usually refunded become.
Degree of disability (GdB) in retropatellar osteoarthritis
Behind the abbreviation "GdB" is the term "Degree of disability". The GdB is defined as a condition in which those affected in their emotional, mental and physical ability and function are impaired to an extent that does not correspond to their age. By definition, a is Period of 6 months crucial. The GdB is in Paragraph 2 of the Social Code IX anchored and is used to assess the extent to which a disease is considered a disability. There is something about the whole thing Score system based on the one Gradation in 10 steps he follows. As soon as more than 20 points can be achieved by a disability speak. With regard to retropatellar osteoarthritis, the points are distributed in the form of a prosthesis after an operation, depending on the restricted mobility. Restriction of movement refers to the ability to bend the knee (Inflection) or stretch (Extension) to be able to. If a partial denture has been inserted, just 10 points can be achieved. 20 to 30 points are the guideline value for a full denture. But it is also important whether only one or both sides are affected: one-sided counts 0-10P. with slight mobility restrictions, 20P. with moderate restriction and 30P. if severely restricted. For the bilateral case, the severity levels apply accordingly 20P., 40P. and 50P.. If there is no restriction of movement despite proven cartilage damage, the one-sided variant can be used 10-30P. and for both sides 20-40P. be awarded.












.jpg)