Swelling on the Neck - What May be the Cause?
introduction
Although the neck is rarely given much attention, it is an extremely important part of the body. The neck is the connecting piece between the head and the trunk.
In addition to the large blood vessels, it also houses the trachea, which connects the upper and lower airways, and the esophagus, which connects the mouth and stomach. The throat also contains the thyroid gland, many lymph nodes and nerves, and the cervical spine, which contains part of the spinal cord. For this reason, it is very important to take a closer look at changes such as swelling on the neck and observe them.

In principle, every neck swelling, especially if it occurs very suddenly or is subject to major changes or grows rapidly, should be clarified by a doctor.
In particular, long-standing and / or painful swellings should be examined, since they could hide inflammatory processes or even malignant changes.
The reasons
Our neck houses many important organs and structures in a very small space. These include conductive structures such as the trachea and esophagus as well as large arteries and veins. On the other hand, the neck also contains organs such as the thyroid gland, a large number of lymph nodes and, of course, muscles. A swelling on the neck can therefore have a wide variety of causes.
These include:
- Thyroid disease
- Lymph node swelling
- Salivary gland diseases
- abscess
- Cervical cyst
- Throat fistula
- pitted processes
- Tumor diseases
- Lymph gland cancer
- Lipoma
Which cause is ultimately responsible for the swelling depends on the one hand on other symptoms that the patient feels. On the other hand, factors such as exact appearance, texture and location, painfulness and the patient's history play a role.
Swelling - what could be behind it? Read more about this here.
The abscess as the cause
An abscess is a tissue cavity filled with pus that arises as a result of an infection. This ultimately leads to a melting down and encapsulation of the infection source, i.e. the formation of an abscess. In principle, this process can occur in any region of the body or in any tissue.
An abscess on the neck is in urgent need of treatment, since many important structures are close together and this should definitely prevent the infection from spreading.
The starting point for an abscess on or in the throat are, for example, purulent tonsillitis, inflammation of the middle ear or teeth. Lateral neck cysts can also become infected and develop into abscesses. Typical symptoms are fever, malaise and pain in the respective area, swelling of the nearby lymph nodes and painful swelling in the neck area, which can also be red and warm.
After the diagnosis has been confirmed, the treatment of abscesses typically involves opening and emptying them, and possibly administering an antibiotic.
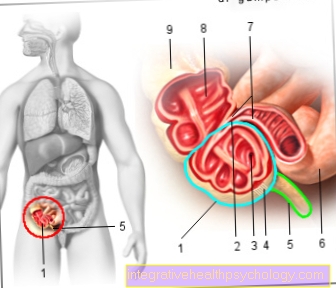
The cause of the lymph node swelling
Lymph nodes swell as part of various diseases. Many lymph nodes are in the neck region. The most common cause of lymph node swelling is infections such as a cold or flu. The lymph nodes in the neck region swell evenly. They can then be touched more often, which is otherwise not possible. After an infection, a lymph node can sometimes remain enlarged.
Lymph nodes also swell with cancer. As a rule, however, only individual lymph nodes or individual groups of lymph nodes swell. So there is no symmetrically distributed swelling of the lymph nodes as in an infection. In addition, the consistency of the lymph nodes is rather coarse.
Also read the article: The lymph node cancer.
The thyroid as the cause
Various diseases of the thyroid gland also cause swelling in the neck. An enlarged thyroid is called a goiter (or goiter). A goiter develops e.g. from iodine deficiency. In Germany, goiter due to iodine deficiency is rare, as iodine is added to foods such as salt.
Autoimmune diseases such as Graves disease, which lead to an inflammatory process in the thyroid gland, can also cause thyroid swelling. In addition, cancer of the thyroid gland also causes swelling. There are also a few medications that can cause thyroid swelling as a side effect.
The insect bite as the cause
After an insect bite, the affected tissue swells. In the case of harmless mosquito bites, however, the swelling is not very pronounced. Depending on the insect, the swelling on the neck can also be more pronounced and cause further discomfort.
If the neck swelling is very pronounced, it is advisable to consult a doctor or a pharmacy. Drugs such as Fenistil gel, or cortisone, will help reduce swelling. In some cases, a mosquito bite can become infected. The swelling increases. The sting becomes painful and overheated.
If you suspect that the insect bite is infected, you should definitely consult a doctor. There is a risk of sepsis. In addition, the localization on the neck is very unfavorable for an infected mosquito bite.
The allergy as the cause
Allergies can vary in severity. Reactions such as reddening and localized swelling may only occur mildly. In the worst case, life-threatening anaphylactic shock occurs. Among other things, this can lead to life-threatening swelling in the throat. In the worst case, this progresses so far that breathing becomes impossible because the airways are blocked. Insect bites in the mouth can do a similar thing.
In the event of an allergic shock, action must be taken quickly. Drugs that have a rapid decongestant effect, such as antihistamines, must be given. The most common triggers of allergic shock are food and insect bites.
Read more on the topic: The allergic reaction.
The symptoms
The symptoms of neck swelling can vary depending on the underlying condition of the swelling.
In inflammatory diseases, painful swelling is typical, which can also be accompanied by reddening and warming of the affected area. If the inflammation is strong, general symptoms such as fever, fatigue and tiredness, as well as headaches and sore throats, are not uncommon.
If, on the other hand, it is a disease of the thyroid gland, a wide variety of symptoms can occur, depending on whether the disease is accompanied by an overactive or underactive thyroid. Generally speaking, an overactive thyroid shows symptoms that indicate an overactive metabolism. Symptoms of an overactive thyroid include difficulty sleeping, weight loss, diarrhea, and a high heart rate. An underactive thyroid can have the exact opposite symptoms, i.e. increased tiredness, weight gain and constipation.
Tumor diseases, which should also not be ignored as the cause of swelling in the neck, are often characterized by the so-called B symptoms, which lead to fever, night sweats and unwanted weight loss. Lipomas as the cause of the swelling, however, are not associated with any other symptoms.
Difficulty swallowing as a symptom
Doctors speak of dysphagia when they have difficulty swallowing. Dysphagia has many different causes. Among other things, various pathogens (viruses, fungi, bacteria) can lead to swelling of the lining of the mouth and throat, which leads to difficulty swallowing.
Severe swelling, which also affects swallowing, can also be caused by abscesses (accumulation of pus). An abscess in the mouth can be caused by tonsillitis or tooth root inflammation. In a few cases cancer, e.g. a cancer of the larynx, behind which there is difficulty swallowing and a swelling in the neck.
The causes of difficulty swallowing? You can find out more here.
The diagnosis
At the beginning of the diagnosis of any illness there is a consultation with a doctor. The aim of this conversation, known as the anamnesis, is to collect as much information as possible about the patient's condition and complaints so that further diagnostics can be carried out in a targeted manner. This includes questions about the patient's previous illnesses, relevant illnesses in the family and which medication the patient is taking.
The anamnesis is followed by a physical examination, during which the swelling itself, but also the rest of the neck, is examined. It is particularly interesting how big the swelling is and what consistency it has. In addition, the examining doctor may examine the oral cavity and routinely listen to the lungs and heart. In the next step, blood tests can be carried out. Above all, parameters such as the inflammation values and the blood count are informative and can provide information about infections.
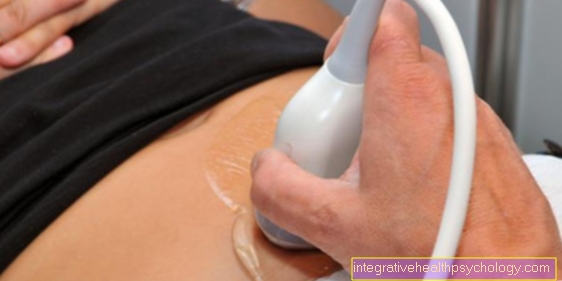
Depending on what the suspected diagnosis is, the family doctor can refer you to a specialist who will carry out further diagnostics accordingly. For example, endoscopic examinations of the upper airways or the esophagus can be performed. In many cases, imaging methods such as sonography (ultrasound), color Doppler (which can show the blood flow in organs) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRT) or computed tomography (CT) are also helpful. Furthermore, the removal and analysis of a tissue sample can often provide information, for example for the diagnosis of lymphatic cancer.
The therapy
The therapy for swelling on the neck depends on the underlying disease and therefore varies greatly from case to case.
In the case of an enlargement of the lymph nodes as part of an inflammation, for example, no treatment is necessary because the lymph node inflammation subsides on its own. Waiting is usually the first choice here. If the lymph node inflammation is the result of bacterial inflammation, for example of the tonsils, the underlying disease is usually treated with antibiotics.
An enlargement of the lymph nodes for which no cause can be found always carries the risk of a malignant, i.e. malignant tumor disease. If this is the case, a microscopic examination of the respective lymph node is usually carried out. The further therapy of the lymph gland cancer then depends on the result of the examination.
The administration of antibiotics is also appropriate in the case of bacterial inflammation of the salivary glands. If this is viral, however, symptomatic therapy, i.e. pulpy food, moist compresses and pain relievers, is used.If there is repeated inflammation of the salivary gland, surgical removal may be necessary.
If the cause of the swelling in the neck lies with the thyroid gland, it is usually treated with medication, in the case of excessive thyroid enlargement and thyroid nodules also surgically or with radiation therapy. Neck cysts and fistulas are also treated surgically and, if necessary, antibiotics.
Jugular vein thrombosis, on the other hand, requires drug treatment with heparin (a blood thinner) and antibiotics to prevent sepsis. In order to avoid further thrombosis, however, the underlying underlying disease must also be treated.
The duration and forecast
A swelling in the neck can have different causes. As part of an infection, there is often a swelling of the neck, as there are many lymph nodes there, e.g. if you have a cold, take action to support the body's immune defenses. They often swell in the process. This swelling usually disappears as the infection subsides. Occasionally there is the possibility that a lymph node remains enlarged after an infection.
However, swellings also form with inflammation. Examples are e.g. infected insect bites or injuries. Here, too, the swelling recedes again in the course of the treatment.
But swellings can also form on the neck due to thyroid glands or tumor diseases. These have an individually different duration and prognosis.
The causes of unilateral swelling of the neck
As already mentioned, a number of diseases can cause neck swelling. For this reason, it is first important to narrow down the range of possible causes. First of all, this is possible by looking at exactly where the swelling is.
On the side of the neck there are mainly muscular structures. These are rarely involved in the development of swellings. The lymph nodes in the neck region in particular are more likely to be the cause of swelling. As a rule, this is a non-specific inflammation of the lymph nodes, which can lead to painful swelling on the side of the neck and is usually due to a bacterial or viral infection.
Since the lymph nodes of the neck lie in the drainage area of all lymphatic tracts of the head, said infections can originate, for example, in the pharynx, the paranasal sinuses or any other structure of the head.
The enlarged lymph nodes can grow several centimeters in size and remain enlarged long after the infection has subsided. In any case, they should be movable to the surrounding tissue. Otherwise, the possibility of a malicious process must be considered.
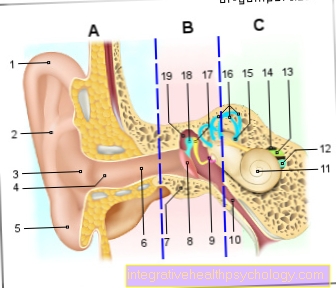
If the swelling is directly below the ear on the side of the neck, a disease of the salivary glands or inflammation of the salivary gland can also be considered as the cause.
The causes of a swelling in the front of the neck
At the front of the neck, a few centimeters below the larynx, is the thyroid gland. This can be enlarged as a result of various processes, which is then referred to as goiter or goiter. If one considers the entire world population, this is often the result of an iodine deficiency. In our society this occurs relatively seldom due to iodine additives in table salt, for example.
Instead, autoimmune diseases such as Graves' disease or Hashimoto's thyroiditis, inflammation of the thyroid gland (thyroiditis), cysts or, rarely, certain drugs can be responsible for a goiter. Enlarged lymph nodes in the lower neck area are also conceivable as the cause of swelling.
Learn more about this topic: The goiter.
The causes of swelling at the back of the neck
The anatomical structures in the back of the neck are mainly muscles and the spine, which, however, are only very rarely the source of a swelling. A lipoma can be responsible for a swelling in this region.
These are benign ulcers of cells of the subcutaneous fatty tissue, which are of no disease value and therefore usually only represent a cosmetic problem. Lipomas occur very often on the thighs, the trunk, but also in the neck, shoulder and upper arm area.
Further information can be found here: The lipoma on the neck.
The swelling after an operation
Even though medicine today is geared towards making treatments more and more gentle, operations in particular still place an enormous burden on the body. This also and perhaps even more so for operations in the neck and head area, for example after a thyroid operation . Wound pain and swelling of the surgical area are expected and completely natural reactions of the body to the operation. Incidentally, a hoarse or hoarse voice can also be the result of swelling from the anesthesia or the operation itself. However, this will steadily improve in the days and weeks after the operation and is usually nothing to worry about.
Above all, the pain can usually be treated very well and there are also options for treating swelling. Above all, the causes of swelling must be eliminated. Slight water retention due to tissue damage is completely normal and does not require any therapy.
Swelling as a result of infection and poor wound hygiene should be taken seriously. In addition to swelling and pain, wound infections can also be recognized primarily by a stronger reddening of the wound area and overheating. In the case of very severe infections, general signs of infection such as fever and fatigue may also appear. If you observe such changes, this must be clarified immediately by a doctor. In order to avoid swelling on the neck after an operation, it is primarily important to have adequate care and hygiene. Swelling in the operating area should always be carefully observed.
The swelling on the neck with pain
If the swelling observed on the neck is accompanied by pain, it can be assumed that this is an inflammatory disease. Abscesses, inflamed swollen lymph nodes or inflamed neck cysts and throat fistulas can be named as the cause of painful swelling.
An inflammation of the salivary glands, which are distributed in the area of the lower jaw, can lead to a painful swelling in the neck area. Apart from this, however, a rare acute occlusion of the great jugular vein (jugular vein thrombosis) by a clot is also conceivable as the cause, if other diseases have been excluded.
Pain in combination with a swelling of the neck should always be clarified by a doctor in order to achieve an early healing of the disease. Until then, taking pain medication can help. The pain relievers ibuprofen and paracetamol are particularly suitable, as they have a good anti-inflammatory effect in addition to their analgesic properties.
You can read more interesting information on this topic under: Swelling on the neck under the jaw
The swelling on the neck without pain
If, on the other hand, a swelling in the neck is not accompanied by pain, other possible causes must be considered. Here, too, it can initially be a question of lymph nodes which are still enlarged after a bacterial or viral infection in the head or neck area (e.g. tonsillitis) has subsided. This harmless, unspecific lymph node enlargement is not uncommon and can persist for years and can sometimes be up to a few centimeters in size. It is important, however, that said lymph node can be moved in relation to its surroundings, since otherwise a tumor disease can be the cause.
A swelling in the neck area, which is also not painful, can be caused by an enlargement of the thyroid gland as a result of various diseases. Possible causes are autoimmune diseases, iodine deficiency or an increased need for thyroid hormones during pregnancy or puberty.
Lipoma is also worth mentioning as the cause of neck swelling without pain.
If a painless swelling on the neck persists for a long time, increases in size or is accompanied by other symptoms, a medical evaluation is definitely advisable. Even the best internet platform only allows an assessment of the potential danger of an illness and cannot replace a visit to the doctor.
The swelling on the neck under the jaw
There are two different groups of lymph nodes under the jaw that can swell in the event of infectious diseases such as a cold. Infectious diseases are the most common causes of swelling under the jaw. However, superficial inflammation of the skin also leads to swelling under the jaw. During puberty, for example, this can be the case when the beard begins to grow and the associated shaving, which can lead to irritation and minor injuries to the skin.
In the context of a pronounced inflammation of the roots of the tooth, swelling can occur under the jaw. The root inflammation can spread to the jaw itself. There is severe pain and the tissue swells. Other inflammations in the mouth can also spread to the jaw.
In rare cases, tumor diseases such as Lymph node cancer, causing swelling under the jaw.
For more information, see: The swelling on the neck under the jaw.
The swelling between the neck and the collarbone
The so-called supraclavicular lymph nodes are located above the collarbone. Like all other lymph nodes, these can swell and become noticeable as part of an infectious disease.
The supraclavicular group of lymph nodes also swell in malignant cancers. Swelling of these lymph nodes is at the highest risk of developing a malignant disease. Therefore, you should be particularly careful if these lymph nodes swell. Signs that lymph nodes have swollen as part of a malignant disease are a varying often coarse consistency, an enlargement of over two centimeters and a progressive growth. Breast and lung cancers are particularly common in this group of lymph nodes. The risk of developing cancer increases with age. A doctor can assess the possible risk of cancer and initiate further diagnostics.
Lymph Node Swelling - How Dangerous Is It? Read more about this.
The swelling between the neck and shoulder
There is less swelling between the neck and shoulder. There are also fewer lymph nodes there than in other regions on the neck. Superficial skin injuries and insect bites can cause swelling between the shoulder and neck. In some cases, wounds heal poorly, resulting in impaired wound healing or a hypertrophic scar. This means that this scar produces a lot of connective tissue, which leads to a thickening. In many cases, such a scar will resolve itself over time.
Skin or tissue tumors rarely form on the neck. A distinction is made between benign and malignant tumors. These often have to be removed surgically.
The swelling on the neck in children
Although a swollen throat is a very common concern for parents of children, in most cases it can be considered harmless. In fact, neck swelling in children is usually just the result of an inflammation in the nose, ears or throat.
Lymph nodes are an important part of our immune system and contain large numbers of white blood cells. This is where our immune cells multiply and activate in the event of an infection. Since the lymph nodes of the neck lie in the drainage area of the lymph in the head region, they react particularly strongly to inflammation in the head area. Ultimately, swelling of the lymph nodes in the neck is generally seen as a result of an intact immune system. In addition, an enlargement of the lymph nodes is often more impressive in children, as they are slimmer and have less subcutaneous fat.
If a swelling of the neck often has to be carried out extensively in adults in order to rule out more serious diseases, this is usually unnecessary in children. It is also worth mentioning that lymph node swellings often last longer in children than in adults. It is not uncommon for weeks or months to pass before the swelling has completely subsided.