Swelling - what's behind it?
definition
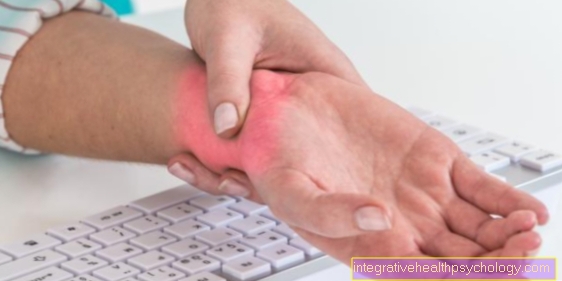
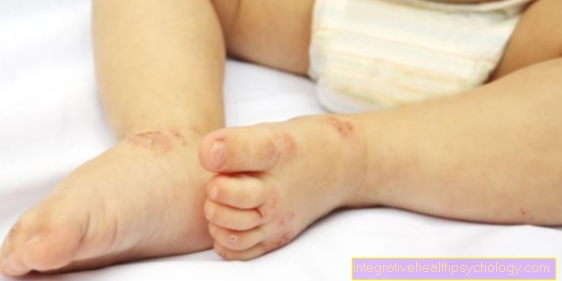
A swelling is a protrusion of tissue caused by different causes that can occur in different places on the body. Often, swelling is combined with redness and pain on pressure.

Causes of swelling
The causes of swelling are numerous. The most common cause is inflammation, which in principle can occur in all regions of the body. In the case of inflammation, the immigration of pathogens activates the immune system. Then cells of the blood that are responsible for the immune response, but also other substances, so-called mediators, are brought into the inflammation area. In order to bring as many cells of the immune system to the scene as possible, the flow of blood into the area is accelerated and the blood vessels dilate. Flammable fluid will build up in the area where the pathogen has entered. As a result, the area swells and also reddens, and swelling can also be triggered by non-inflammatory edema formation.
For various reasons there is an influx of liquid. The most common cause of this is congestion in the area of the lymphatic system. With a long bent leg e.g. It can happen that the lymphatic fluid cannot flow out in the usual way and that it accumulates around the blood vessel, which can lead to this swelling. Unilateral swelling in the area of the leg can always be an indication of a thrombosis and must be clarified.
Read more about this under: Thrombosis in the leg and Detect thrombosis
An allergic reaction can also lead to tissue swelling due to fluid.
In addition to inflammatory and non-inflammatory edema, in which increased fluid leads to swelling of the body area, swelling can also occur due to tissue proliferation. In the case of tumor formation e.g. diseased tissue multiplies so strongly that it swells in this area. However, a tumor is not always to blame for the proliferation of tissue under the skin. For infections e.g. It can also lead to a swelling of lymph nodes, which can be felt enlarged in the classic parts of the body, such as armpits or neck, and thus cause swelling.
In some cases, edema can also develop due to decreased excretion. For example, in patients whose kidneys are not working properly, kidney-related edema can often be seen on one part of the body. The reason lies in a reduced protein production by the kidneys. As a result, there is less protein in the bloodstream and the fluid is drawn from the blood vessels to the periphery, which can cause the tissues to swell.
Read about this too: Causes of edema
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
More symptoms of swelling
On the one hand, swelling can occur in isolation, this would be e.g. the case with edema swelling that is not caused by inflammation. However, swelling can also have some accompanying symptoms. The pain and redness often accompany the swelling. The reason is that inflammatory cells are washed into a certain area of the body by the immune system in order to eliminate pathogens that have penetrated there. In order to ensure this as quickly as possible and to bring the blood to its destination quickly, the blood vessels in this area are made wide. More blood flows into the area and gives the already swollen area a reddish color.
Depending on where the swelling occurs on the body, it can also lead to discomfort when moving. E.g. eyelid swelling narrow the view.
Swelling caused by an allergic reaction is often itchy from other immunological cells that have washed into the area. This itching is triggered by the body's own substance histamine. In the event of an allergic reaction, this substance is washed out many times over, which can lead to severe itching. In addition to the itching, the allergy can also cause a rash. In the case of strong allergic reactions, so-called anaphylactic reactions, life-threatening general symptoms also occur, which can accompany swelling. Mention should be made of a fast pulse rate, high blood pressure, sweating, restlessness and shortness of breath.
How do I recognize a swelling?
The swelling itself is a visual diagnosis. In addition to the assessment, the examiner will also always feel the abnormal area in order to assess the consistency of the swelling. To clarify the cause, it is crucial whether the swelling is firm, coarse, soft, painful or movable and whether a dent remains after pressure.
For the investigation of the cause, it is always important at which location the swelling is. Slight swellings on the ankles or ankles, which occur especially on warm days, do not require further treatment if there are no symptoms. On the other hand, unilateral swelling of the legs must be carried out with an ultrasound examination (with a view to possible thrombosis)Doppler examination) to be clarified.
Facial edema should be checked for blood protein deficiency. Rough hardening in the armpits or groin indicates swelling of the lymph nodes, which can be normal with an infection and will disappear within a few days. However, if the swelling persists, an ultrasound should be performed in this area in order to clarify the cause of the long-lasting lymph node swelling.
In principle, all other suspicious swellings on the body can also be easily diagnosed by an ultrasound examination. Liquid appears dark in the ultrasound image, whereas an interplay of light and dark areas rather suggests tissue growth. Every diagnosis must of course be supported by a detailed medical survey. The patient should be asked whether there are allergies, since when the swelling has existed and whether he has had such complaints before.
Swelling of the face
A swelling in the face occurs partly physiologically i.e. it has no disease value. For example, this occurs in many people after getting up and is an expression of the blood pressure that is downregulated during the night and rises again after getting up. The swelling should go away within 2 hours of getting up. Unusual new facial swelling, whether during the day or after getting up, should be clarified by a doctor. This could be due to a protein deficiency, which can also be triggered by kidney damage.
There could also be an allergic reaction of the body to various substances such as shower gel, detergent, pollen, etc. behind the swelling. Heart failure would initially cause swelling in the leg or both legs, but facial swelling can also occur in this context. When diagnosing swelling of the face, the kidneys, the heart, the proteins and the blood count should always be checked. When looking for the cause, it should always be asked whether the patient has accompanying symptoms such as itching or similar, which might explain the facial swelling by an allergic reaction.
Read more about this under: Swelling of the face
Swelling of the eye
Eye swelling is often caused by an allergic reaction. Depending on the season it can e.g. Pollen increases the release of histamine, which means that the vessels in certain areas become wide and the area swells due to the influx of liquid. Most of the time, eyelid swelling that is allergic is also associated with itching of the conjunctiva and tears in the eyes and runny nose.
Eyelid swelling can also result from conjunctivitis. Classically, the conjunctiva would be reddened here and the conjunctiva would be swollen. In the event of conjunctivitis, the eyes would be stuck together with pus even in the morning. If the person concerned feels a foreign body sensation in the eye and eyelid swelling is present, a foreign body (sawdust, dust particles) could have got into the eye and possibly also under the eyelid and inflamed it. If the eyelid is swollen on one or both sides, an ophthalmological examination should be carried out quickly in order to clarify the cause.
It can also always happen that the normal field of vision is restricted in its scope due to the swelling of the eyelid. If the patient also reports visual disturbances, an ophthalmologist should be consulted very quickly.
Read more about this under: Swelling of the eyes
Swelling on the eyelid
Most swellings on the eyelids are caused by allergies. Pollen and other seasonal allergens can cause allergic edema in the eyelid and cause it to swell. This often severely restricts the patient's field of vision. Another cause of eyelid swelling is barley or hailstones, which can appear in the eyelid area and are often painful.
Swelling on the eyelid can also be treated symptomatically. This is often achieved by cooling with a damp compress with cold water or by dabbing chamomile tea. Of course, the cause of the eyelid swelling should be found out and treated accordingly.
Read more about this under: Eyelid swelling
Swelling behind the ear
Swelling behind the ear may be caused by a lymph node. Here you can feel a small, round induration and swelling behind the ear. This can be tender or painless. It would be important to check whether lymph nodes in another area of the body are also swollen or tender and whether there is an infection (e.g. cold, etc.). An infection-related lymph node swelling is harmless and will subside once the infection has healed. Lymph nodes in the area of the ear can still be palpably enlarged a few weeks after an infection.
Read more about this under: Lymph node swelling behind the ear - how dangerous is it?
Extremely painful swellings behind one ear can also indicate inflammation of the mastoid cells, which are located in the bony mastoid process behind the ear. The disease, also known as mastoiditis, is dangerous and should be treated as soon as possible. Mastoiditis often occurs after an otitis media. Characteristically, the swelling behind the ear is very painful on pressure and the ear tends to protrude slightly outward from the other ear. Quite often, those affected also have severe earache and accompanying symptoms such as fever and deterioration in their general condition.
Read more about this under: Swelling behind the ear - what causes it?
Swelling in the mouth
Swelling in the mouth area is usually caused by a disease of the mucous membranes. As a rule, these are inflammatory changes that can have different causes. Canker sores (small mucosal ulcerations) can cause swelling in the mouth area as well as irritation of the mucous membranes from eating or drinking that is too hot. Allergic reactions to certain substances can also cause the oral mucosa to swell. Mouth swelling, which causes the respiratory tract to become narrowed and thus causes shortness of breath, is relatively rare.
Read more about this under: Swelling in the mouth
Swelling on the roof of the mouth
Swelling in the area of the palate is very often triggered by consuming food or liquids that are too hot. The swollen palate is then caused by irritation of the mucous membrane that spans the palate.
Allergies can also lead to swelling of the palate. Operative interventions such as Dental operations almost regularly lead to swelling in the area of the palate. In most cases these swellings are so minor that the patient hardly notices them and the palate swells again very quickly.
Read more about this under: Swelling on the roof of the mouth
Swelling of the neck
Swelling on the neck occurs with infection-related diseases, such as before tonsillitis. In addition to unpleasant swallowing difficulties, the throat is also often tender on the outside.In addition, there are also lymph node swellings caused by the infection, which can also make the neck swell. Most of the neck swellings caused by an infection are also painful on pressure.
Read about this: Lymph node swelling in the neck - How dangerous is it?
Swelling in the neck area that is not painful on pressure could always be caused by the thyroid gland. Goiter formation, which used to be very common in the past, has become very rare due to the good iodine supply, but the formation of nodules in the thyroid area and sometimes over- or under-functioning of the thyroid gland can lead to swelling of the thyroid gland and the neck. The swelling can usually be felt in the front and a little to the side. If the patient swallows, the swelling typically moves up and down. This is often an indication of thyroid-related swelling. The ultrasound examination, in which you can measure the thyroid gland and see a swelling, is proof.
Read more about this under: Swelling on the neck
Swelling in the knee
Knee swelling is usually caused by inflammation. It is usually the case that constant irritation in the knee joint causes inflammatory fluid to flow into the joint space, causing the knee to swell. The examiner will perform the dancing kneecap test, which will reveal whether there is any fluid under the kneecap. With the patient lying down, he presses the kneecap together from the head and from the foot and checks whether the kneecap lifts off.
Knee swellings occur either with arthritic changes in the knees or with traumatic injuries within the knee joint.
It is important to find out the reason why the knee is swollen. X-ray or MRI examinations of the knee help here. If the knee joint effusion is severe, a knee joint removal must also be considered.
In the event of a traumatic swelling, the knee should be kept calm and protected. A knee sock or repeated cooling pads can help make the knee swell. If the knee swelling is caused by osteoarthritis in the knee, a steady movement such as cycling can bring relief. Knee swelling can also be caused by high blood uric acid levels. Here, urea crystals accumulate in all possible joints and possibly also in the knee joint and cause it to swell. One also speaks of a gout attack. In addition to the swelling, the knee is usually red and painful. In addition to uric acid-lowering medicinal measures, the treatment also consists of cooling with compresses and medicinal anti-inflammatory measures with ibuprofen, diclofenac or cortisone for several days.
Read more about this under: Joint swelling in the knee
Swelling after surgery
Swelling that occurs after surgery is very common. The reason for this is the inflammatory reaction with which the body reacts to the tissue damage caused during the operation. Depending on the operation, a drain is placed in the surgical area for a few days so that inflammatory fluid can drain away. In addition to the swelling, the area can also become red after an operation. Again, these are signs of the body's normal response to the trauma of the surgery.
Rapid healing of the surgical wound and swelling is important. If this decongestion does not occur and the reddening does not decrease, an infection must be assumed that developed during or after the operation. Here antibiotics should then be used.
If swelling suddenly occurs after the operation, bleeding caused by a ruptured blood vessel can always be to blame. Sometimes the swelling becomes apparent with a bluish shimmer. An ultrasound examination can clarify the exact cause. Swelling caused by major bleeding after the operation should be surgically removed.
Read more on this topic at: Swelling after surgery - tips for treatment
How do I treat a swelling?
The therapy of swelling generally presupposes that one knows the reason for the swelling. So you should always first treat the cause that led to the swelling. General measures are always indicated in parallel. These general measures include consistent cooling with ice, which should be carried out several times a day, and anti-inflammatory measures. Medicines such as ibuprofen or diclofenac should be used here in order to quickly reduce the inflammation.
For allergy-related causes, antiallergic drugs such as cetirizine, Fenistil® or cortisone are used as tablets or, in the case of severe swellings, as an infusion. In the case of tumor-related swelling, the underlying disease must be treated. The same applies to swelling caused by thrombosis. Lymphatic drainage should be performed at regular intervals in the case of lymph drainage disorders that can lead to swelling.