Swollen fingers
introduction
Swollen fingers can have many causes. In addition to an injury, such as a sprain, general underlying diseases can also lead to swollen fingers. In this case, the swollen fingers typically appear on both hands.
The accompanying symptoms and the situations in which there is a swelling can be indicative of the cause and thus also the optimal treatment.

causes
There are many different causes for finger swelling. Disturbances in the metabolism with changes in the electrolyte ("salt") and protein balance usually lead to water retention. If there are too many salts or proteins in the tissue, they can draw water with them, which leads to the development of edema. The most common causes include:
- Heart failure ("heart failure")
- Thyroid disorders
- Diseases the kidneys
- Taking cortisone
- revision
Circulatory disorders or heart problems can affect the blood circulation and thus be responsible for a backlog of blood and consequently swelling of the fingers.
Inflammatory diseases such as osteoarthritis, rheumatism or gout can also ensure that more fluid escapes into the tissue due to the inflammation and the messenger substances that are released in the process. Similar mechanisms are also the cause of finger swelling after an accident or injury to the fingers.
After illnesses or operations in the area of the lymphatic system, e.g. after removal of lymph nodes as part of a cancer, swelling of the fingers can also occur. Connective tissue diseases, including "Collagenoses"But diseases such as fibromyalgia or scleroderma can also be responsible for swollen fingers. Swelling often occurs in connection with pain and restricted mobility.
In addition to these various causes, the fluid pressure acting on the vascular system can also be responsible for the swelling. The blood "sinks" in the hands when they are not used for a long time and passes into the tissue, similar to how the fluid builds up in the feet and lower legs after long periods of sitting.
Finger swelling can also occur when the finger is overstretched. Please also read our article on this: Overstretched finger
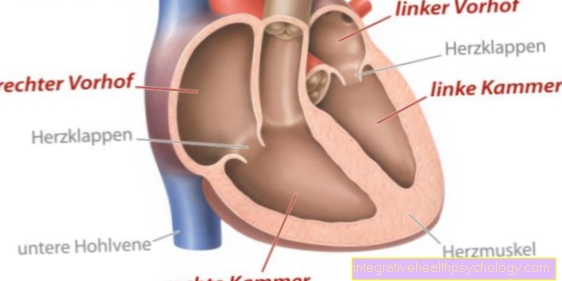
Heart failure as the cause of swollen fingers
If the right heart is weak, water can also collect in the hands and feet. '
Due to the heart's inadequate pumping capacity, blood from the right heart backs up into the veins of the body and collects in the hands and fingers, where fluid then passes from the vessels into the tissue. It comes to so-called cardiac Edema (caused by the heart). Concomitant symptoms of cardiac insufficiency are exertion-dependent shortness of breath, blue discoloration of mucous membranes and fingertips and a general decrease in exercise capacity.
More information can be found here: Symptoms of heart failure
Thyroid disorders
Thyroid disorders can also affect the hands and fingers.
If you have an underactive thyroid, your fingers and hands can swell. The circulation of the blood is slowed down in the case of an underactive thyroid due to the changed hormone level. The thyroid hormones have an impact on the power of our heart, affect the metabolism and the energy balance. If the thyroid gland is underactive, the heart rate slows and the blood pressure is lower.
Fluid accumulates in the tissue. The hands and eyelids in particular are affected by the swelling when they are underactive.
For more information, see:
- Symptoms of an underactive thyroid
- Thyroid hormones
Gout as a cause of swollen fingers
In gout, a metabolic disorder leads to an increased concentration of uric acid in the blood, which is then deposited in the joints in the form of uric acid crystals.
This can cause severe inflammation and pain, which can also be accompanied by swelling that restricts movement. Gout attacks are aggravated by the consumption of alcohol and meat. They last for several hours to days and then subside again. If the gout attack occurs on the fingers, one speaks of "Chiragra'.
However, the metatarsophalangeal joint of the big toe is more frequently affected.
Also read under topic: Symptoms of gout
Swollen fingers from overwork
The joints and muscles can be stressed through increased work with the hands. Overuse can lead to irritation of the structures of the hand and subsequently to swelling in the sense of a mild inflammatory reaction.
Such overuse is a sign that the fingers have been subjected to excessive strain and should be avoided to protect cartilage, tendons and ligaments.
Swelling should be viewed as a warning signal from the body.
Overstressing the fingers can lead to osteoarthritis in the long term. If you suspect finger osteoarthritis, you can also perform our self-test or read more information here: Osteoarthritis of the fingers
Ingestion of cortisone as a cause of edema
Cortisone is a drug that is used to fight inflammatory and immune reactions. However, cortisone also has an impact on the water and electrolyte balance. It is similar to the hormone Coritsol produced by the body itself and has a comparable effect. In the body, the adrenal cortex produces this cortisol.
Cortisone also affects the water balance and affects the kidney. Less water excreted via the kidneys means that more fluid remains in the vascular system and blood pressure increases. This can lead to fluid retention, especially in the hands and face.
For more information, see Side effects of cortisone
Histamine causes swollen fingers
In the event of an insect bite or an allergic reaction in the area of the fingers, the body releases the messenger substance histamine.
Histamine ensures that cells of the immune system are activated, blood vessels expand and an inflammatory reaction is set in motion. Due to the expansion of the vessels and the permeability of the vascular wall, which is also triggered by histamine, fluid from the vascular system enters the tissue and severe swelling can occur.
Cooling, compression, and medications like antihistamines will help.
Concomitant symptoms
In addition to swelling of the fingers, various accompanying symptoms can occur. Pain often occurs due to the increase in tissue tension. The mobility of the joints can also be restricted by the increase in circumference and tension. Itching can also occur.
The color of the fingers can also change. They are often plump and slightly reddened. A lighter color can be seen on the folds. If the swelling of the fingers is an underlying disease, symptoms such as fever, fatigue, increased sweating or chills can also occur.
A decrease in performance, shortness of breath during exertion or newly occurring frequent nocturnal urination in connection with swollen fingers can indicate a disease of the heart and should also be examined by a doctor. Clarification is then required. Even if simple swellings occur more frequently or in spurts, a medical evaluation is indicated.
Pain in swollen fingers
If swelling occurs in connection with pain, an inflammatory or degenerative process can be assumed.
The pain can occur during exercise and movement, but also at rest. Exercise-related pain often indicates overstrain or can be a sign of osteoarthritis of the finger joints.
If the pain occurs at rest, this indicates an acute inflammation, which can also be triggered, for example, by a gout attack or a rheumatic attack. In addition to the swelling, reddening and overheating of the joint can often be seen.Some connective tissue diseases such as fibromyalgia can also cause painful swelling.
Severe swellings can in themselves be a cause of pain, as they irritate certain sensors in the skin tissue (mechanoreceptors) that report the pain to the ear. An allergic reaction, such as an insect bite in the fingers, can lead to severe swelling and pain in the affected area.
You can find much more information under our topic: Pain in the fingers
Swollen fingers without pain
Painless swellings in the fingers are usually less pronounced and go hand in hand with no inflammatory reaction. Causes for this can be metabolic disorders with water retention in the tissue. A subtle build-up of lymph, in which fluid collects and cannot drain, but also edema formations due to heart-lung diseases can contribute to painless swelling of the fingers.
The fingers may also turn a little bluish, which can be a sign of a lack of oxygen. Simple swelling due to long periods of rest under the action of gravity or swelling of the hands during pregnancy are usually not painful either.
Itching of swollen fingers
Itching of swollen fingers can occur due to the swelling itself, the tension can cause irritation and itching.
In the case of allergic reactions, severe itching can also occur. Small blisters appear underneath, which can be responsible for the itching. This can also be the case with a strong exposure to heat. If itching it should be considered whether there is a contact allergy. So whether the fingers came into contact with certain substances that could have triggered the reaction.
Numbness of swollen fingers
Due to the accumulation of fluid in the tissue, nerves and vessels can be compressed by the increasing tissue pressure.
Nerves cannot withstand permanent pressure well and their function is impaired as a result. It can lead to tingling sensations or numbness.
Activating exercises or elevating the hand is particularly useful in order to relieve the nerve tissue and to reduce the swelling.
Swollen fingers and legs
If swollen fingers and legs occur together, a systemic problem of the whole body, i.e. an underlying internal disease, should be considered.
If the heart is weak, edema can occur in the hands and feet together; this is also possible when taking cortisone or a thyroid dysfunction. If the protein balance is disturbed or the distribution of electrolytes has changed, edema on the fingers and legs can occur at the same time.
Swollen fingers in certain situations
Swollen fingers can occur in certain situations, for example depending on temperature, time of day or posture. A list of typical situations that trigger or increase swelling of the fingers can be found below.
Swollen fingers in summer
Swollen fingers and hands are common in summer. This is because the fingers and hands are supplied with more blood in order to keep the body temperature constant. We purposely lose heat through our fingers. The increased blood circulation also means that the blood circulation changes and more fluid collects in the tissue, there is a tense feeling in the hands and the fingers swell.
To counteract swollen fingers, you should ensure that you drink enough water in summer to support the circulation of the blood. Activating exercises, such as opening and closing a fist or other grasping exercises, can also improve the return flow from the blood to the heart.
People who already have problems with their veins or who suffer from circulatory problems should avoid sitting or standing for long periods of time in the heat and can counteract the symptoms with compression stockings (against swelling of the feet).
You may also be interested in this topic: Vein weakness
Swollen fingers in the cold
Swelling of the fingers can also occur in the cold. Actually, the body throttles the blood flow to fingers and feet when exposed to cold in order to lose as little heat as possible to the outside world. The narrowing of the vessels leads to a kind of insufficient supply of the tissue.
If the blood vessels close too much in the event of strong cold stimuli, what is known as reactive hyperemia then occurs. The body then opens the vessels in order to supply the tissue with sufficient oxygen again and a lot of blood flows into the fingers. There is warming and redness. The fingers may swell painfully.
If the symptoms are very pronounced, it is called Raynaud's syndrome. The fingers are initially white (no blood circulation) and then bluish due to the lack of oxygen. The reactive hyperemia finally manifests itself as a strong reddening. Raynaud's syndrome can also be triggered by stress.
Further information on this clinical picture can be found at Raynaud's Syndrome.
Swollen fingers in the morning
If painful swellings occur in the area of the fingers in the morning after getting up without any other known cause, rheumatoid arthritis should be excluded.
The swelling is limited to the base joints and middle joints of the fingers, it is relatively strong and painful and the skin can be easily dented. The symptoms persist for a long period of time or occur again and again in relapses. Accompanying swelling can also occur in other joints, for example in the area of the foot. After a certain time after getting up, the swelling will decrease and the mobility in the finger joints will increase again. Nevertheless, the patients often perceive heavy loads as painful and uncomfortable.
In addition to swelling, a rheumatic attack can also be accompanied by fever, fatigue and loss of appetite. Symptoms often occur after a cold or an infection. Arthritis can be clarified by a blood count, which checks for certain antibodies.
Also read our topic: Reactive arthritis
Swollen fingers at night
It is rather unusual for fingers to swell, especially at night. Since the most common cause of swollen fingers is an increased accumulation of fluid in the tissue and this usually improves when lying down, it is rather rare that fingers are swollen, especially at night.
However, the fingers of one hand and possibly both hands can swell due to an unnatural sleeping position, for example if you lie on one arm for a long time. Then the blood flow back to the heart can be squeezed out of the hand and arm and water can be retained in the affected fingers.
With this cause, the swelling should soon subside after getting up. If you wake up because of the swollen and possibly painful fingers, you should hold them up and move them for a while.
Swollen fingers when hiking
On longer hikes, some people notice an uncomfortable feeling of tension and swelling in their fingers after a certain time.
This results from the fact that we let our arms swing down from the body while hiking. We may also carry a backpack. The weight of the backpack on the shoulders and the force of gravity acting on the arms are the reasons why the blood does not flow out of the hands as well and sink there.
Fluid can enter the tissue and the fingers swell, similar to the feet after long periods of standing. To reduce the swelling, alternating opening and closing of the fist and holding up the hand can be helpful. The fit of the rucksack should be checked to make sure that no blood vessels or nerves are damaged by the weight. The swelling of the fingers can be the first sign of the compression of ducts.
Using walking sticks can improve the symptoms, as holding the sticks activates the hand muscles and encourages the return flow of blood and lymph.
Swollen fingers during pregnancy
During pregnancy, not only does the woman's hormonal balance change, the circulatory situation and the composition of the blood also change.
Because the demand for blood increases, the blood becomes "more viscous" and the flow properties change. More fluid escapes into the tissue and the typical edema of pregnancy is formed. In order to improve the electrolyte and protein balance, care should be taken during pregnancy to eat a diet rich in protein and consume a healthy amount of salt. Salts and proteins ensure that the fluid is held in the vascular system and does not enter the tissue. The formation of edema can thus be reduced.
The pregnant woman should also make sure that she maintains a sufficiently high water intake. In order to meet the increased circulatory requirements, enough water should be supplied, which affects the quality of the blood. To counteract existing edema, exercise is the method of choice. The activated muscles pump the fluid out of the tissue into the vascular system and the swelling in the fingers is reduced.
Further information on this: Edema in pregnancy
Swollen fingers after pregnancy
After pregnancy, the circulation changes again.
The amount of blood increased during pregnancy is now available again to the woman alone. This amount is no longer necessary and more fluid is released into the tissue. Swelling of the fingers and feet may occur. In the course of the puerperium, the circulatory situation normalizes and the edema recedes more and more.
diagnosis
If a patient has swollen fingers, the doctor will first do a physical exam to determine the cause of the swelling. The investigation begins with one anamnese, i.e. the patient interview, in which targeted questions are usually used to make a suspected diagnosis. Appropriate examinations will then follow to confirm the suspected diagnosis or to identify another cause of the swelling.
A simple test can be used to find out whether the finger swelling is due to edema. By pressing in the swollen area, a statement can be made: If there is no indentation, but you can see how liquid can be displaced, it is usually an effusion. A classic protein-rich edema briefly leaves a dent, which then slowly balances out.
If there is a suspicion of an inflammatory process within the joints, imaging methods such as ultrasound can be used to reveal joint wear or signs of inflammation. A blood test should always be done to rule out underlying diseases such as an underactive thyroid or gout.
treatment
Treatment for swollen fingers depends on the diagnosis.
In the case of inflammatory or degenerative diseases of the joints, physiotherapeutic therapy is useful, which is supplemented by the administration of appropriate medication. In the case of metabolic diseases, the basic problem must be treated. In most cases, drug therapy is necessary, and surgery may also be necessary, depending on the organ affected.
If the swelling of the fingers is caused by cardiovascular or kidney disease, drainage therapy with diuretics or blood thinning may be necessary.
Swelling caused by an allergic reaction to an insect bite can be treated with an antiallergetic such as antihistamines in order to stop the acute inflammatory processes.
In many cases, manual lymphatic drainage as part of physiotherapy treatment can be helpful to support the removal of fluids from the tissue. Wraps and bandages can also be used.
Home remedies
In addition to simple exercises that activate the fingers and hand muscles, there are a variety of home remedies that can help with swollen fingers.
Apple cider vinegar tinctures, turmeric and comfrey (devil's claw) are substances that are said to have an anti-inflammatory and decongestant effect. They can be applied locally as a "tincture" or ointment. Tomato juice is said to be a proven home remedy for pregnancy edema.
Proper nutrition, especially a balanced protein and salt balance, plays an important role. The consumption of (pork) meat or milk and yoghurt products can also influence the formation of edema and should be minimized. Existing or long-term symptoms should always be clarified.
Duration
The duration of the swelling depends heavily on its cause. Swelling that occurs as a result of rheumatic changes or in the context of osteoarthritis often occurs in bursts after exercise for a few days and disappears again in the non-inflammatory interval. In systemic diseases, such as heart failure or kidney disease, but also in metabolic disorders, swelling can occur chronically. When the lymph nodes are removed, constant swelling is also to be expected.
Swellings due to gravity should quickly disappear after the muscles have been repositioned or activated. After a trauma, any swelling should subside significantly after about 3-5 days.
The ring cannot be removed from the finger - what to do?
When you can no longer remove a ring from your finger, the most important thing is to stay calm and not panic.
Pulling and twisting hard can make the finger swell even more.
Most of the time it is not necessary to cut or break the ring. In many cases, the ring can be removed with a few simple tricks.
First, you should use a lubricant such as petroleum jelly or vegetable oil and rub it in your finger as generously as possible. By turning it slightly, some grease can also get under the ring. Often the ring can be easily removed now.
Otherwise the hand should be held above head level for at least 5 minutes. This allows more blood to drain off and the swelling of the finger is encouraged.
Another way to reduce swelling is with cold water. The affected hand is immersed in a vessel with cold water for a few minutes. It can also be an advantage to have someone else help you. This should pull the skin in front of the ring slightly taut forwards so that the ring can slide off the finger better. If all of the above methods fail after several attempts, the ring must actually be opened on one side with a small hacksaw and bent apart. Most fire stations or emergency rooms also have a tool that can be used to quickly open the ring. In many cases, a jeweler can repair it afterwards.
But be careful: If the finger turns blue, continues to swell or is in great pain, you should go to an emergency room or at least the fire department or a jeweler to have the ring removed. In addition, caution should be exercised if the finger may be broken. In such a case, under no circumstances should the ring or finger be pulled to avoid worsening the injury.