Stinging in the left chest
Definition
Stinging in the left chest is pain in the chest area. This pain can squeeze, pull, burn or cause a feeling of tightness or shortness of breath.
The pain is usually temporary, but it can also be persistent. The persistent pain can appear behind the breastbone and from there to the left side of the body. The left arm, left shoulder, or abdomen can also be affected.
Left chest pain is more common than right chest pain because the heart lies on the left side.

causes
The cause of pain can be very diverse. It is possible that the heart is the real cause, but it can also be e.g. the lungs be responsible. The typical causes are listed below.
Angina pectoris describes the feeling of tightness in the chest and is associated with various diseases. It can be a heartache caused by insufficient blood flow to the heart. In the most common cases, the coronary arteries are narrowed by calcifications, the so-called coronary heart disease (CHD). As a result, the heart is no longer supplied with sufficient blood, especially during physical exertion.
A heart attack can also be a trigger for the sharp chest pain. Blood clots that have formed have blocked the coronary arteries. The heart muscle is consequently no longer supplied with sufficient blood at one point, which is why tissue dies. Sharp pains that pull into the left half of the body occur.
High blood pressure or cardiac arrhythmias can also be responsible for causing pain, as well as an inflammation of the heart muscle or pericardium.
Illnesses in the lungs, lungs or pleura can also cause sharp chest pain. These are then dependent on breathing. A pulmonary embolism, pneumonia or bronchitis can be considered as an example.
Nerve irritation or muscle tension are harmless causes. In this case, the pain can be influenced by certain movements.
A stinging stinging in the left chest can also occur as an accompanying symptom of an infectious disease. This is very often the case. Measles, scarlet fever and rubella can be mentioned as examples. So there is inflammation in the intercostal muscles or in the rest of the muscles that surround the chest. The lungs themselves do not have to be affected.
You might also be interested in: Signs of a heart attack
Pulmonary embolism as the cause of the stinging
A pulmonary embolism is the occlusion of one or more arteries in the lung with a blood clot.
As a result, the vessels through which the deoxygenated blood is transported from the heart to the lungs are affected. This blood clot is usually washed up from a leg or pelvic vein. Since the thrombosis usually formed there. If only a small blood vessel in the lungs is affected in a pulmonary embolism, there are no or only mild symptoms. If, on the other hand, a large vessel is closed, those affected have severe symptoms such as stinging in the chest, shortness of breath, painful breathing or racing heart. There can be an acute danger to life.
You can find more information on our website: Pulmonary embolism signs, therapy and prognosis
Tension as the cause of the stinging in the chest
Tension can also be responsible for a stinging or pressure sensation in the chest.
The muscles in the upper body can become tense due to incorrect strain, lack of movement or monotonous sequences of movements and thus radiate pain into the chest. It is more of a superficial pain that originates from the chest itself. Furthermore, this pain can be influenced by certain movements or postures.
You might also be interested in: Chest pain from tension
Stinging in the left chest on inhalation and exhalation
A "knife stab" sensation in the chest may occur when you inhale, making it difficult to breathe. This stinging is a common symptom with many possible causes. It can happen unexpectedly, but it usually doesn't last more than a few breaths. It can become more pronounced through particularly deep and strong inhalation or laughter. Once it occurs, one should become aware of these facts, keep calm, and breathe in slowly and carefully. As a rule, stinging from inhalation is not a serious disease. Stress, tension or anxiety are common triggers. It is important to note that stress can be the trigger, but not always acute in a stressful situation. The stinging often occurs outside of the stressful moments. Furthermore, an infection can be caused by muscle tension (when you breathe in you do muscle work) or a lung disease.
Stinging in the (left) chest can also occur when exhaling. In addition, pain and a feeling of tightness may occur. Often times, the pain worsens when you cough or laugh. If so, symptoms like this suggest a disease of the lungs or ribs. A rib fracture (break of a rib) is often very painful when you inhale and exhale, laugh or cough. Bruises around the ribs are also very painful and uncomfortable.
Another disease that can cause pain and stinging in the chest when breathing is pleurisy. These pains are characterized by the fact that they become more pronounced with deep breathing. If you take a break between inhaling and exhaling, the pain subsides a little.
You might also be interested in:
- Symptoms of stress
- Stinging in the chest when breathing
Heart Attack - Differences In Symptoms In Men And Women?
A heart attack can manifest itself in a number of different ways. There are the classic signs of identification, such as stinging in the chest, a tightness in the chest or pain in the chest region (longer than 5 minutes) that pull into different parts of the left body, shortness of breath or dizziness.
Men mostly suffer from the symptoms mentioned. In comparison, women are more likely to experience so-called unspecific symptoms noticeable. These symptoms can also be described as slight signs of a heart attack, as the symptoms are usually much weaker than in males. It is therefore possible that a heart attack patient may lack the typical sharp pain in the chest. Instead, there is often only a tightness in the chest area. Other non-specific symptoms are vomiting or nausea, upper abdominal discomfort, shortness of breath and shortness of breath. If such symptoms occur for the first time and persistently in a woman, an emergency doctor should be called in any case.
You might also be interested in:
- Symptoms of a heart attack
- Drawing in the chest in the woman
diagnosis
In the clinic, blood pressure measurement, pulse measurement, listening to the heart and lungs and heart current measurement (EKG) are used for diagnostics. Another important means of making a diagnosis are the infarct markers in the blood.
When there is a stitch in the left chest, most people involuntarily think of a heart attack. This assumption is based on the pain in the heart region. However, there are many causes of a stinging left chest. The heart can actually be identified as the cause, but this does not mean that a heart attack is also the cause. Because of this, it is very important to watch the pain closely. The doctor should be told when the pain occurs and where exactly it is. If pain on the left side of the heart occurs suddenly, for the first time and very severely, the emergency doctor should be called immediately. If this is a heart attack, the diagnosis must be made quickly and appropriate treatment given.
Concomitant symptoms
The symptoms associated with or accompanying an acute heart attack are usually very pronounced. A main symptom is sudden, persistent (longer than 5 minutes) chest pain. This pain can be sharp and severe. Often they are also described as burning. It is possible that the whole breast is affected. Often, however, the pain is localized on the left.
It can pull from the chest to the left arm, left shoulder, jaw, back or stomach. This pain is followed by restlessness and even fear of death. It is also possible that chest tightness may occur as an accompanying symptom. This is described as pressure or a very strong feeling of constriction in the heart area.
The resilience of the body is clearly reduced. Drowsiness and shortness of breath may occur. In addition, accompanying symptoms such as cold sweats and paleness can almost always be observed. The affected person's skin may appear pale. Furthermore, those affected are plagued by nausea and even vomiting. These are so-called unspecific symptoms, as these also occur with many other diseases.
If you experience such symptoms to an extent that has never been experienced before and last for a long time, an emergency doctor should be called. A heart attack may be the cause.
Palpitations
Palpitations are known to many people and can be a symptom of a stinging in the chest. As a rule, extrasystoles are responsible for this. These can be understood as additional heartbeats. This causes the heart to lose its rhythm. This “stumbling” of the heart is perceived by those affected.
Almost everyone has occasional palpitations in the course of their life. It also occurs in healthy people and for this reason usually has no disease value. However, if the extrasystoles last longer than about 30 seconds or occur regularly after certain activities, it could indicate an illness. Accordingly, those affected should consult a doctor.
Back pain
If you have a heart attack, you experience severe, burning pain in the left chest. This pain can spread to different parts of the body, including the back. This back pain is often described as dull. They occur suddenly and strongly. They are usually more localized in the upper back area. It is also possible that they appear between the shoulders or oriented to the left.
But even with poor posture or excessive exercise, muscle soreness or tension can lead to back pain and stinging in the chest at the same time.
Also read: Heart attack - symptoms, diagnosis, therapy
dizziness
Dizziness is not often associated with a heart attack. However, this can also be one of the symptoms of a heart attack. Dizziness is generally described very differently. Some sufferers perceive sham movements and do not feel safe on their feet. Others have the feeling that everything revolves in them or that the environment revolves around them. There is almost always a tendency to fall. This is described as a downward pull.
The dizziness can also cause nausea and vomiting.
In summary, any patient who is affected by dizziness has problems with balance.
You might also be interested in: Dizzy spells
treatment
Therapy depends on the underlying condition. However, if a heart attack or pulmonary embolism is suspected, a doctor should be consulted as soon as possible.
Since every minute counts during a heart attack, the emergency doctor must be called if there is the slightest suspicion. As a first aider you should ensure calm and check the consciousness and breathing of the person concerned. If there is a cardiac arrest, it should be resuscitated in any case until the ambulance drives up. The emergency doctor supplies the patient with oxygen and medication. These are supposed to relieve both pain and anxiety and prevent the formation of further blood clots. In the hospital, an attempt is made to clear the closed coronary artery as soon as possible. This keeps the damage in the heart muscle as small as possible.
There are two different methods of “clearing” the vessel. The first is primary percutaneous coronary intervention (PCI). The aim of this method is to re-open the narrowed artery so that normal blood flow to the heart muscle is restored. The doctor anesthetizes the patient locally in order to push a small tube (catheter) through the inguinal artery to the blocked vessel. An inflatable balloon is attached to the end of the tube. When the doctor detects the constriction or blockage, the balloon is inflated so that the artery is expanded. As a result, the blood flows again. In addition, a so-called stent can be used at the constriction. This will keep the artery open.
This method is the therapy of choice today. However, this only applies if it can be carried out within 90 minutes of the initial medical contact (emergency doctor). If this is not the case, lysis therapy is used. An active ingredient is injected into the patient, which is supposed to help dissolve the blocked blood clot.
After all of this, the patient receives follow-up treatment with medication and recovers in a rehab facility.
You might also be interested in: Implantation of a stent after a heart attack
Duration and forecast
The duration and prognosis, as well as the therapy, depend on the cause of the breast stitch.
Tension, for example, has a very good prognosis and a maximum duration of a few days.
In the case of a heart attack, however, the prognosis depends very much on how quickly the person concerned is treated in a hospital. The faster the better! However, there is no general answer to the duration of the symptoms, because it not only depends on the medical treatment, but also on which area of the heart is affected and how severely.The prognosis of a heart attack patient is based on this. The size of the infarct, the location and the time until therapy are decisive in making a prognosis. The survival of the patient in an acute heart attack depends on whether cardiac arrhythmias or pump failure occur. For the long-term prognosis after a heart attack, it is crucial, among other things, whether cardiac insufficiency develops, whether the cardiovascular disease continues and whether a healthy lifestyle is observed.
You might also be interested in: How can you prevent a heart attack?
Localization of the sharp pain
Stinging on the left nipple
The reasons for a sore nipple, just like stabbing the breast, can have different causes.
A harmless example of a cause would be inflammation from clothing. This inflammation can be caused by abrasive, rubbing or scratching clothing or special textiles. This is mostly a bilateral pain.
Lumps in the breast can also be a trigger. Sometimes there is an external change of the nipple in connection with pain, in this case a doctor should always be consulted. In most cases, however, especially in women, a hormonal change is the trigger. This can affect puberty, pregnancy or even menopause. The symptoms or pain in the nipple occur more frequently during pregnancy or breastfeeding. In combination with overheating, reddening or even discharge, mastitis must be considered in women, which requires medical treatment.
Read more on this topic: Inflammation of the nipple
Shooting on the left costal arch
When patients complain of a stinging of the costal arch, the chest, sternum and ribs are usually affected by severe pain.
A sharp pain in the left costal arch is usually nothing to worry about. Often an injury to the ribs, muscles or nerves is hidden behind a stabbing costal arch. The ribs may be bruised or broken.
It is also possible that incorrect posture, excessive strain or sore muscles cause the symptoms. A pinched nerve can also be an issue.
Only in a few cases is the pain in the left costal arch caused by a heart attack or abdominal disease. If the stomach, spleen or pancreas are responsible for the pain, it is usually located below the left costal arch.
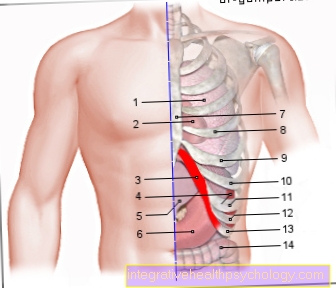
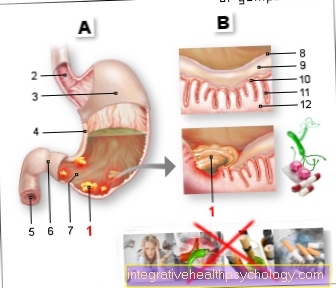
Left costal arch pain
- Left lung - Pulmo sinister
- Pericardium - Pericardium
- Left costal arch -
Arcus costalis sinister - Spleen - Sink
- Liver - Hepar
- Stomach - Guest
- Sternum - sternum
- Rib 5 - Costa V
- Rib 6 - Costa VI
- Rib 7 - Costa VII
- Rib 8 - Costa VIIi
- Rib 9 - Costa IX
- Rib 10 - Costa X
- Colon - Intestinum crassum
The costal cartilages of the 7th - 10th rib
merge into the costal arch.
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Stinging in the left breast during pregnancy
Chest pain during pregnancy is very common. How severe this pain is during pregnancy, however, is individual from woman to woman.
The hormonal balance of women changes, so that the glandular tissue in the breast increases. This not only results in milk production at the end of the pregnancy, but also a feeling of pain and dragging. For some women, one of the first signs of pregnancy is the change in the breast. The pain, which can manifest itself in the form of a pulling or feeling of pressure, is particularly strong in the first few months of pregnancy. Chest pain during pregnancy is therefore quite normal side effects of the changed hormonal balance and therefore nothing to worry about.
For more informations: Chest pain in pregnancy
Stinging in the left chest after a cold
It is possible that chest pain while breathing may persist for a while after a cold.
Usually one had acute bronchitis, one of the most common acute respiratory diseases. Symptoms such as severe coughing with sputum were present. Due to the inflammation of the bronchi, chest pain can occur when breathing in and especially when coughing during a cold. A strong cold with bronchitis has other accompanying symptoms. Even if these accompanying symptoms of a cold, such as fever or tiredness, for example, have subsided, the bronchi can still be very irritated and vulnerable. Even after a cold, this can still lead to chest pain if you inhale and exhale strongly or cough. During this time you should take care of your body and not put too much strain on it.
Another cause could be the spread of the pathogen that has led to myocarditis. This occurs particularly in young, physically active people when the cold is not cured sufficiently and physical stress occurs at an early stage. In addition to the stinging, most of those affected also feel a tight chest, poor performance or even dizziness. Here, too, protection is essential.
For more informations: Duration of a cold

















.jpg)