Goiter
Synonyms in a broader sense
- Goiter
- Thyroid enlargement
- Enlargement of the thyroid gland
- Parathyroid
- Goiter nodosa
- Goiter multinodosa
Definition of goiter
The term "goiter" (from the Latin struma "gland swelling", pl. Strumae) or goiter describes an enlargement of the thyroid gland. Goiter has an essential cause in iodine deficiency, which is why goiter is found especially in iodine-deficient areas such as the Alps.
Read more on the topic: Enlargement of the thyroid gland, lack of iodine, swelling of the thyroid gland


Anatomical structure of the thyroid gland
- Thyroid lobes
- Connecting piece (isthmus)
Occurrence in the population
iodine is in the earth. Germany is an iodine deficiency area, probably because iodine was lost at the end of the Ice Age with the melting glacier water.
For this reason, around 30% of the Central European population has one Iodine deficiency. Women are affected about four times as often as men. Although the drinking water in Germany is not enriched in iodine, there has been a decreasing tendency in iodine deficiency symptoms in recent years.
The reason for this is certainly the increased consumption of iodine-containing table salt.
A goiter usually develops between the ages of 20 and 40.
Read more on the topic: Iodine deficiency
Classification
According to the external appearance, the Goiter (Thyroid enlargement) divided into the following degrees:
Grade 0
The thyroid gland is not visible or palpable but is still enlarged.
Grade Ia
The thyroid gland is palpably enlarged, but not visible even when the head is overstretched.
Grade Ib
The thyroid gland is palpably enlarged and only enlarged when the head is overstretched.
Grade II
The thyroid gland is visibly enlarged even without hyperextending the head
Grade III
The thyroid is significantly enlarged. Neighboring organs are also affected, e.g. B. displacement or narrowing of the windpipe (see also: Narrowing of the windpipe), neck vessels or esophagus. At this stage, the thyroid gland can grow behind the breastbone.
After the Changes within the thyroid becomes in a
- Struma diffusa (evenly enlarged) and
- Struma nodosa (already existing nodes) differentiated.
After Thyroid function the thyroid is divided into:
- euthyroid (normal hormone production),
- hyperthyroid (increased hormone production),
- hypothyroid (decreased hormone production).
The anatomically normal thyroid is called eutopic. The thyroid, the location of which differs from it - e.g. B. in Rib cage or under the tongue - called dystop.
Goiter nodosa
If Lump in the thyroid gland then this is called Goiter nodosa. It can be various nodular changes act. A nodular goiter can be caused by a benign glandular growth be conditional, a so-called Adenoma. But it can also be benign fluid-filled cavities (Cysts) or to benign scarring or calcification act.
It can be two different types of benign Lump in the thyroid gland form.
- A so-called "cold" knot does not produce hormones and the thyroid is not impaired in its function by the cold lump (euthyroid goiter nodosa). A benign cyst, a cavity filled with fluid, is also counted as a cold lump because it no function owns. Smaller cysts can be caused by a Puncture (similar to a blood sample) can be removed, larger ones may also require an operation.
- A "hot" knot produces thyroid hormoneswhich can lead to too many of the hormones in the blood arrive and thus the Symptoms of an overactive thyroid can cause (hyperthyroid goiter nodosa).
Whether you have a cold or hot lump can be determined with a Thyroid function test, the scintigraphy. To do this, the patient is given an iodine substance that has been radioactively marked. This is particularly strong in one hot knot and thereby makes it "visible". The naming of "hot" nodes is due to the color representation of the scintigraphy. It is shown in the so-called warm colors red and yellow. A cold knot does not absorb the iodine. It is shown with the cold colors blue and purple and can therefore be differentiated.
In most cases are the knots benign, even in iodine-deficient areas. Criteria at which one should think of a malignant lump are for example Family history of thyroid cancer, local Irradiation of the thyroid gland in the past, palpable single nodules and also laboratory findings (increased CEA, calcitonin, thyroglobolin). At a Ultrasound examination an assessment of the goodness or badness can usually also be made.
Becomes an individual in case of a nodular goiter cold knot determined, this applies in Germany until Proof to the contrary as thyroid cancer (Goiter maligna). Luckily, thyroid carcinomas are very rare, the probability that a nodular goiter is a carcinoma is less than one percent. Goiter formations, on the other hand, are very common, which is why step-by-step diagnostics are carried out to assess the risk in order to be able to rule out carcinoma as far as possible. First is a Ultrasonic (Sonography), one Thyroid function test (Scintigraphy) and a Laboratory value control carried out. If thyroid cancer is suspected, a Fine needle puncture carried out to obtain thyroid cells, in case of doubt an operative Goiter removal (Struma resection) to be necessary.
Goiter multinodosa
The nodular goiter is in Germany Very common. Every third adult has an enlargement or one or more lumps in the thyroid gland, being Women affected even more often are as men.
As you get older, however, so does the likelihood of that multiple nodules in the thyroid gland form, one speaks of one Goiter multinodosa. This mainly occurs when the thyroid has been enlarged for years. If there is an existing iodine deficiency the thyroid gland enlarges initially and in the further course there is one nodular remodeling of the tissue, a multinodular goiter.
diagnosis

Examination of goiter
The direct, personal, clinical examination by the doctor is the first and very important measure that serves to establish the diagnosis.
The doctor looks at the neck and palpates the thyroid gland.Depending on the symptoms, other parts of the body can and must also be examined.
Sonographically (ultrasound examination) Goiter
Through the Ultrasonic the situation in the thyroid can be assessed. Here, cysts can be seen and even punctured, nodes can be identified, the volume of the thyroid gland can be measured precisely.
Laboratory chemistry (blood test / laboratory values) Goiter
The blood test with determination of the hormone level (in particular the thyroid hormones) provides information about the function of the thyroid gland. Antibodies that can play a role in thyroid diseases can also be determined in the blood.
Scintigraphic (scintigraphy) at Goiter
Thyroid scintigraphy is used to gain further information in the event of nodules or functional disorders.
A distinction is made between "hot" and "cold" nodes. The nodes that take up the radioactively marked iodine are called "hot". The "cold" nodes are the ones that do not take up iodine.
Puncture at Goiter
Using a fine needle puncture of the thyroid gland, samples can be obtained for a tissue examination under the microscope (histology).
X-ray examinations at Goiter
Help with impairment of neighboring organs X-ray image, CT- or MRI images a better understanding of the extent of the thyroid enlargement and, if necessary, allow better surgical planning.
Symptoms
Makes a small goiter or knot rarely local complaints or noticeable symptoms and is often a Incidental finding during a routine medical examination. An abnormal blood test or an ultrasound scan can reveal a nodular goiter.
In rare cases, the goiter has progressed to the point where the enlargement itself mechanical complications prepares. So the goiter can become one Lump, pressure or tightness in the throat lead to hoarseness, shortness of breath or difficulties swallowing, as well as a Tendency to bronchial infections cause. Some patients complain of one increased sensitivity to touch On neck. In the meantime, the treatment of the goiter is so good and early that there is hardly such a large enlargement of the thyroid gland in Germany that a cosmetic problem exists due to a clearly visible goiter. The goiter can also press on or displace other structures, so it is possible that it will Varicose veins of the esophagus (Esophageal varices) educate the windpipe can be pushed in (Tracheal padding) or the upper Vena cava can be squeezed whatever the blood flow to the Heart obstructed (upper venous congestion).
Often are so-called Concomitant symptoms a goiter caused by the Knot formation (Goiter nodosa) is conditional. For example, if the goiter is accompanied by an underactive thyroid, the typical symptoms arise Symptoms of an underactive thyroid (Hypothyroidism), which require treatment. Here are above all Fatigue, weight gain, and loss of appetite to mention.
Or the goiter leads to an increased production of Thyroid hormones, then you can have an overactive thyroid (Hyperthyroidism) suffer what goes through Difficulty sleeping, nervousness, high blood pressure and diarrhea can make noticeable. If nodular or multinodular goiter causes problems, it must be treated. This can be done as a Drug therapy or with the help of a Radioiodine therapy happen. In some cases, thyroid surgery is necessary.
Causes goiter
Iodine deficiency goiter
The most common cause of one Swelling of the thyroid gland in Germany there is iodine deficiency. In this situation, the thyroid tries to compensate for the decreased hormone production caused by the iodine deficiency by cell division. This leads to the enlargement of the thyroid gland.
You can find more information on the topic here: Iodine deficiency
Hyperthyroid goiter
It is an enlargement of the thyroid gland that takes place due to an increased function of the organ. This is e.g. B. the case of Graves' disease, a disease in which the body's own antibodies attack the thyroid and stimulate the hormone-producing cells.
Goiter maligna
This term refers to the malignant disease of the thyroid gland. There are four different types of thyroid cancer, some of which are treated differently and have different prognoses.
therapy
When treating goiter, the exact cause and origin must first be clarified. E.g. a therapy of Diffuse goiter and Goiter nodosa essential.
In principle nowadays 3 essential therapy optionsn known:
1.) Drug therapy
Iodine deficiency is the most important cause (over 90%) known for the development of the diffuse goiter.
But also with thyroid nodules (Goiter nodosa colloides) it is assumed that insufficient iodine supply plays an important role!
The daily iodine requirement for an adult is included 150 micrograms. During the pregnancy and Lactation women even need it 250 micrograms.
If those affected now suffer from goiter, they should usually take 100-150 micrograms of iodine in the form of tablets once a day (Iodine substitution therapy).
The doctor usually adds a thyroid hormone to the drug therapy, the L-thyroxine (Levothyroxine).
One speaks now of a "Combination therapy“And hopes for a reduction in the goiter within one to one and a half years.
For some time, however, there has been a great discussion among experts about the long-term success of such combined therapies. Nevertheless, it has established itself over the years and is used in many places!
To the function and the condition of the thyroid You will have regular check-ups with your doctor. To do this, he controls the Thyroid hormones in the blood and by means of Ultrasound machine the decrease in goiter.
Under no circumstances may you change the dosage of your medication yourself. The impression is deceptive: although the thyroid tablets are very small, the amount of hormones they contain is considerable!
2.) Radioiodine therapy
For 50 years, radioiodine therapy has been a gentle alternative to surgery. It is particularly suitable for goiter patients through a Graves disease (Autoimmune thyroid disease) and patients with many lumps in the thyroid gland, especially if this one Hyperfunction cause.
Also for the elderly whose overall condition is undergoing surgery general anesthetic no longer allows, the treatment may be appropriate.
In order to be able to manufacture its hormones, the thyroid gland needs that which occurs naturally in food iodine. For this purpose, it is stored by specialized cells in the gland. In radio-iodine therapy, this principle is used.
After a few preliminary examinations, you will be given a capsule at the hospital radioactive iodide. Outwardly it does not differ from a conventional tablet, but in terms of its effect it does!
By absorbing the radioactive iodide, the substance naturally accumulates in the thyroid cells. Now irradiated the iodide the thyroid from within. The tissue is weakened and eventually shrinks so that the goiter is very effectively reduced in size.
Since radioactive iodide only radiates about half a millimeter, there is no risk that healthy organs or other parts of your body will also be damaged.
Nevertheless, the treatment is subject to this Radiation Protection Act. You are therefore only allowed to leave the hospital as soon as the radiation measured from your thyroid gland is sufficiently low.
In order not to endanger your surroundings, you have to get there until then strictly shielded linger in your hospital room. Unfortunately, the time period cannot be precisely predicted. However, daily measurements guarantee the fastest possible process.
Many patients are very insecure at the beginning of therapy. The Therapy safety however, it has been proven in many long-term studies. There are no risks of unwanted organ damage or long-term consequences.
Comparable total radiation exposure is e.g. even with one X-ray examination reached.
It is essential to mention that the full effectiveness only occurs after a few months. After complete scarring, a doctor regularly checks the metabolic status of the thyroid gland.
Any medication, such as Thyroid hormones, be used in good time.
3.) Operation
Particularly large goiter, but also individual nodes can be surgically removed. The intervention takes place in general anesthetic and is now a routine in many hospitals. One differentiates between one complete removal of the thyroid gland (Thyroidectomy) or Removal of the enlarged parts (Struma resection).
In the past, there was often a risk of accidental Vocal cord nerve damage ("Recurrent paresis"). With modern methods like that NeuromonitoringHowever, such complications could be reduced.
The operation for goiter

Every year in Germany around 100,000 patients take part in the thyroid operated on.
Either the whole thyroid (Thyroidectomy), a Thyroid lobe (Hemithyroidectomy) or single knot (Struma resection) must be removed.
The size, location, type and function of the goiter determine the extent of the operation. If e.g. a malignant enlargement total thyroid removal is indicated.
Even with goiter in the context of a Graves disease, a large part is usually removed.
Separate, benign knots on the other hand, can often be removed without significant loss of thyroid tissue.
Every goiter operation is done under general anesthetic. During the procedure, the patient lies on his back with his neck stretched out. With a small incision, about two cm above the pit of the neck ("Collar cut"), the surgeon opens the front of the neck.
In order to achieve an ideal cosmetic result and to avoid subsequent scarring, he makes the incision in a natural neck fold.
After adipose tissue and thin neck muscles (Platysma) have been severed, the view of the thyroid is exposed.
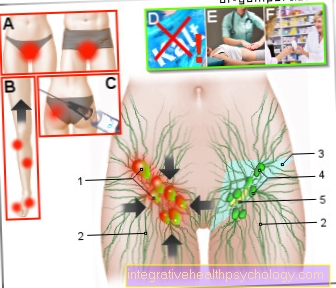
Special attention is now paid to the two Vocal cord nerves (Recurrent laryngeal nerve). They run left and right on the back of the thyroid and are responsible for the movement of the vocal cords responsible.
In case they are accidentally injured, you can long-term damage with voice, language and breathing arise!
In order to minimize this risk, a so-called "Neuromonitoring“Used during the operation. Modern technology makes it possible to precisely monitor the position and function of the nerve through electrical stimulation!
In addition to protecting the vocal cord nerves, the four must absolutely Parathyroid glands, also called epithelial bodies, are protected.
Usually they are in close proximity to the top and bottom poles of the two Thyroid lobe. You regulate that Calcium levels in the human body. If they are accidentally removed or damaged, they can significant, lifelong disorders of the calcium balance occur.
In any case, a pathologist examines the thyroid preparations removed. He examines with a fine microscope (histologically) the exact structure and can thus conclusively assess which type of goiter was present.
The complication rate in goitre operations has fallen sharply, primarily due to the use of neuromonitoring. Usually patients can leave the hospital just a few days after the procedure.
Prophylaxis goiter
The iodine-enriched table salt has contributed to a decrease in goiter frequency in recent years. Due to the extreme spread of iodine deficiency in the Alpine region, Switzerland has decided to enrich its drinking water with iodine.
This measure has enormously reduced the occurrence of goiter there.
Patients suffering from an overactive thyroid gland (hyperthyroidism) should, however, be careful with products that have a high iodine content.
The need for iodine is generally increased during pregnancy and breastfeeding.
forecast
The not malignant goiter can be treated well, so that the symptoms usually go away.
An already existing protrusion of the eyeball from the eye socket (exophthalmus) does not recede even after normalization of the hormone values.
The two most common cancers of the thyroid gland that follicular and papillary thyroid carcinoma, thanks to radioiodine therapy, have the best prognosis of all cancers in the human body.
In almost all cases a complete healing is achieved here. Unfortunately, this is not the case with undifferentiated (anaplastic) thyroid cancer. The prognosis in this situation is very limited.
Goiter nodosa colloides
About 20-30% of the adult population have knots in the thyroid. Often they are discovered by chance, e.g. as part of a routineUltrasound examination of the neck. If the thyroid gland is enlarged as a result of the nodular changes, the doctor speaks of a "Goiter nodosa colloides“.
The likelihood of thyroid nodules increases with age. Also play that gender (Women are more often affected), such as family predisposition a role. Iodine deficiency is also closely related to the development of thyroid nodules. Studies have shown a decrease with an improved iodine supply.
In addition to incidental findings, patients occasionally feel a lump or show symptoms of a malfunction. Understandably, there is great concern at the beginning of the investigation. But 95% of all thyroid nodules discovered are benign (benign)!
After a blood test is done to evaluate the function of the thyroid gland (Measurement of the TSH hormone) and the nodes have been checked with an ultrasound image, a so-called Thyroid scintigraphy.
Through a special nuclear medicine procedure, it shows the activity of the individual nodes: a distinction is made between "cold knots“, "Hot knot", such as "indifferent knot“.
Cold nodules have a low metabolic activity and in rare cases can be an indication of malignant neoplasms.
On the other hand have hot knots an increased activity and can a Overactive thyroid (Hyperthyroidism) cause.
Indifferent nodes are either not representable or do not allow any decisive conclusions.
However, in principle, only one Fine needle puncture can bring absolute certainty. For this purpose, tissue samples are taken from the thyroid nodule with a thin needle. The small procedure only takes a few seconds and causes no pain.
The therapy one Goiter nodosa colloides is diverse. Depending on the type of node, a surgery, Radioiodine therapy or one long-term drug therapy be the right choice.
If e.g. a reasonable suspicion of a malignant neoplasm, such as a Thyroid cancer surgical removal is indicated.
It is not uncommon for the doctor and patient to opt for the so-called "wait and watch“Method: If there is a benign lump with normal function of the thyroid before and the patient does not complain of any complaints, initially nothing is done.
A decision is made about a possible therapy only if abnormalities are observed during regular check-ups.
Summary
The causes for one swollen thyroid gland ("Struma") can be very different. Therefore, the therapy is also tailored to the individual.
At Thyroid dysfunction Conservative measures can be sufficient in most cases. However, thyroid cancer and "cold" nodules are treated surgically.
The malignant tumors often require complex treatment. After surgery Depending on the stage of the tumor, radioiodine therapy may be carried out. According to this, the prognosis is very good in a large number of cases, so that most patients can be considered cured after this entire treatment complex.
Thyroid surgery is not a simple operation. In the hands of the experienced surgeon, however, it is a routine operation that, despite its risks, offers a necessary and sometimes unavoidable treatment option.
In recent years the incidence of Goiter decreased due to the increased iodine intake in the population.








.jpg)