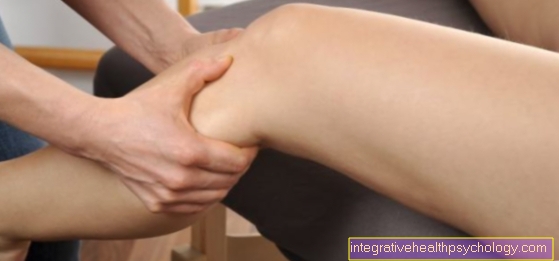
Symptoms of meniscus injuries
General
The menisci are discs of cartilage, two of which are in each knee joint, one inside and one outside. Since they are responsible for absorbing loads and pressure exerted on the knee and stabilizing the joint, excessive stress on the knee often results in damage to the menisci.
The symptoms that can arise when the meniscus is injured are relatively similar despite the different clinical pictures, so that a meniscus damage can be concluded relatively quickly.

Typical symptoms of meniscus injuries
Especially when a meniscus is acutely impaired, as is most often the case with a sports injury, the patient suffers from severe pain, which is most pronounced in the hollow of the knee, but also affects the sides of the knee and / or extends into the lower leg can. Often this pain is accompanied by limited mobility of the knee joint. As a rule, there is a so-called extension deficit, which means that a person affected can no longer straighten the knee and straighten the lower leg, or at least this is only possible with a considerable worsening of the pain.
In the context of a meniscus tear or an inflammation of the joint, joint effusion often occurs, which can then be felt and sometimes even visible in the knee joint. Depending on the location, the effusion can lead to a bulge on the knee or to the kneecap being displaced upwards and, if you push it down with the leg straight, practically "jump" up again in a very specific way.
Also Cysts (liquid-filled cavities) that arise, for example, when the Cartilage badly worn out has been (one speaks here of degenerative changes), can also be used as small swellings stand out in the knee area and point to one Wear of the menisci down. These are typically located at the Outside of the knee or further back on the knee.
Especially when a meniscus If the knee joint is already damaged, even slight stresses may cause it to leave its normal position and be squeezed or trapped.
In addition to the pain, there is often also a snapping sound to hear what is an indication that the Meniscus displaced has been.
When degenerative changes develop over a long period of time, such as in the arthrosis is the case, despite the worn menisci, any Symptoms are absent. Even in people who rarely strain their knee joint, it can happen that injuries to the menisci are noticed quite late because they are hardly noticeable when they are at rest.
Appointment with a knee specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
The knee joint is one of the joints with the greatest stress.
Therefore, the treatment of the knee joint (e.g. meniscus tear, cartilage damage, cruciate ligament damage, runner's knee, etc.) requires a lot of experience.
I treat a wide variety of knee diseases in a conservative way.
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me in:
- - your orthopedic surgeon
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at
Figure meniscus

- Inner meniscus -
Meniscus medialis - Inner articular knot
(Shinb.) -
Medial condyle - Transverse ligament of the knee joint -
Lig. Transversum genus - Kneecap ligament -
Ligamentum patellae - Bursa - Bursa
- Outer meniscus -
Lateral meniscus - Outer joint nodules
(Shinb.) -
Lateral condyle - Anterior cruciate ligament -
Lig. Cruciatum anterius - Posterior cruciate ligament -
Ligamentum cruciatum posterius - Femur - Femur
- Shin - Tibia
- Kneecap - patella
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations













.jpg)