Therapy of ADD with antidepressants
Synonyms in a broader sense
Attention Deficit Syndrome, Fidget - Philipp Syndrome, Fidgety Philipp, Psycho-Organic Syndrome (POS), Hyperkinetic Syndrome (HKS), Attention Deficit Disorder, ADD, ADHD, Attention - Deficit - Disorder (ADD), minimal brain syndrome, behavioral disorder with attention and concentration disorder, Fidgety Phil, attention deficit disorder, ADHD, dreamer, "Hans-peep-in-die-Luft", Träumerle.
definition
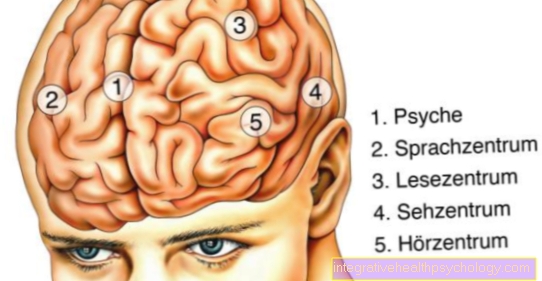
To solve the problem of the messenger substance imbalance of Serotonin, dopamine, and norepinephrine in the brain to be able to compensate and thus the Forwarding of information between the nerve cells of individual brain areas to regulate, drug therapy finds its justification within the framework of ADD therapy or ADHD therapy.
Drug therapies with drugs from the psychotropic drugs division come into question, for example:
- Stimulants (Methylphenidate preparations, stimulants)
- Antidepressants
In general, psychotropic drugs aim to influence the activity and function of the central nervous system (= CNS) in order to have an effect on the emotionality, mood and affectivity (= emotional state). Antidepressants can increase drive and improve mood as well as dampening. This is possible because different groups have to be distinguished that have different effects on the messenger substances. A distinction is currently made between:
- MAO inhibitors
- RIMA (reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor)
- Tri- and tetracyclic antidepressants
- SSRI (Selective - Serotonin - Reuptake - Inhibitors)
- NARI (norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors)
- SNRI (Serotonin - norepinephrine - reuptake - inhibitors)
Drug treatment in children
With regard to the drug treatment of ADD and ADHD, the following can be stated:
- Drug therapy only in clear cases.
- Drug therapy not under six years!
- Side effects can occur individually and are particularly dependent on the medication prescribed.
- The dose and when to take it vary from person to person. Both have to be “tested” in a certain way. The attending physician can approximate the correct dosage based on the underlying body weight and make dosage recommendations.
Drug treatment in adults
Since attention deficit syndrome also occurs in adults, they can also be treated with medication. Choosing the right medication is more difficult in adults. This is due, among other things, to the fact that metabolism in adults is faster and the hormonal balance is composed differently. As with children, stimulants are the drugs of choice here too. Often used is also tricyclic antidepressants, or a mixed combination. Selective serotonin reuptake inhibitors are rarely used at the moment. The fact that, to our knowledge, no drug based on methylphenidate is currently approved for adults is problematic. It can be prescribed by a doctor as part of what is known as an off-label prescription. The costs are rarely covered by health insurances and therefore usually not.
Some testimonials from adults who have opted for drug therapy report that the Effect of the drugs does not occur immediately, but that it can take up to six months before the expected effect is achieved. Since drug therapy is subject to certain conditions in Germany (see above), experience reports are quite rare. Studies also mostly relate to children and adolescents. Adult studies on the topic often show different and inconsistent results.
As with children and adolescents, drug therapy should only be considered if a clear diagnosis can be made. This also includes the differential diagnosis of other personality disorders (Borderline, depressions, Tourette syndrome, ...).
various antidepressants
The different imbalances of the messenger substances claim different groups of drugs that target the imbalance and alleviate or alleviate symptoms. All of the following drug groups are classed as psychotropic drugs. This group of drugs generally includes all drugs that have a psychoactive effect and thus affect the activity of the CNS (= zunbalance Nnervous system). They work at the synapse / synaptic cleft, i.e. exactly where messenger substances are used to transmit stimuli from nerve cell to nerve cell. For more information, see Causes of ADS on the ADS main page.
The following drug groups are used in the event of a messenger imbalance:
- MAO inhibitors
- NARI (Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor)
- RIMA (reversible monoamine oxidase inhibitor)
- SNRI (serotonin - norepinephrine - reuptake inhibitor)
- SSRI (selective serotonin reuptake inhibitor)
- Stimulants
- tricyclic antidepressants (Neurotransmitters - resumption - inhibitors)
Depending on the necessity and type of imbalance, the attending physician will prescribe medication from the appropriate group.
in case of an AD (H) S become primarily stimulants used. As part of therapy in AD (H) D adults, the use of tricyclic antidepressants may also be advisable.
Treatment of ADD or ADHD with antidepressants
The table is limited to the essential drugs used in ADD or ADHD therapy using antidepressants. The table does not claim to be complete and corresponds to our level of knowledge. Any deviations are possible.
| Surname | Active ingredient | Drug group | For whom? |
| Strattera® | Atomoxetine | Selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitor (NARI) | Children from 6 years of age, adolescents and adults with a clear diagnosis of ADD |
| Tofranil® Imipramine - neuraxpharm® | Imipramine | Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) | Children from 6 years of age, adolescents and adults with a clear diagnosis of ADD |
| Petylyl® - coated tablets | Desipramine | Tricyclic Antidepressants (TCAs) | Adults |
| Trevilor® | Venlaflaxine | Serotonin Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitors (SNRI) | not for children and adolescents (<18 years) |
| Aurorix® Moclix® | Tofranil | tricyclic antidepressant | Adults |
NARI- Selective Norepinephrine Reuptake Inhibitor
The drug Strattera® described in the table has only been available on the German market since 2005. Due to the active ingredient atomoxetine, Strattera® is one of the so-called selective norepinephrine reuptake inhibitors, the NARI.
These drugs ensure that norepinephrine (= red) is not taken up again immediately after it has been released and thus remains in the synaptic gap longer. The drug only has a minor effect on the other messenger substances.

Classic antidepressants
Classic Antidepressants are synonymous with tricyclic antidepressants, the name of which suggests their chemical structure. Antidepressants have a reuptake-inhibiting effect on several messenger systems, i.e. they do not have such a specific effect on certain ones Neurotransmitters.
For this reason, among other things, they are usually only used when the drugs of first choice (stimulants) and NARI do not work accordingly or when depression is added to the clinical picture.
Monoamine oxidase (= MAO) inhibitors
The three letters of the MAO inhibitors stand for monoamine oxidase. This is an enzyme that breaks down the transmitters in the central nervous system. By inhibiting this enzyme, the breakdown of neurotransmitters is also inhibited. As a result, a larger number of transmitters are temporarily available in the synaptic gap.
In the case of ADD, it is the active ingredient moclobemide, which is prescribed, for example, in the form of Aurorix® or Moclix®. Like tricyclic antidepressants, MAO inhibitors are only used when first-line drugs are not effective or are contraindicated.
Side effects
Besides the desired effects of drugs are also getting Side effects, or interactions with other drugs possible. Certain individual circumstances (allergies, health problems) can sometimes ensure that certain medications cannot or should not be used. One speaks of a contraindication.
Please discuss possible side effects with your treating doctor, which - depending on the medication - may differ. He knows you very well and can also tell you why specific medications might be contraindicated for you.
Other ADS topics
- ADS
- ADD causes
- ADD symptoms
- ADS diagnosis
- ADD therapy
- ADS curative education
- ADD psychotherapy
- Depth psychology
- Behavior therapy
- yoga
- Autogenic training
- ADD medication
- Methylphenidate
- Ritalin
- antidepressant
- ADD diet
- ADD and family
- Educational games
related subject areas
- ADHD
- Poor concentration
- Reading and spelling weaknesses / dyslexia
- Arithmetic weakness / dyscalculia
- Giftedness
A list of all the topics that we have published under our "Problems with Learning" page can be found at: Problems with learning A-Z