Broken fibula
Synonyms
Fibula head, fibular head, outer malleolus, malleolus lateralis, head fibulae
Medical: Fibula
English: fibular
definition
In medicine, a fracture of the fibula is called a fibular fracture. The fibular fracture can be closed or open, whereby with an open fibular fracture, the broken bone parts protrude through the skin.
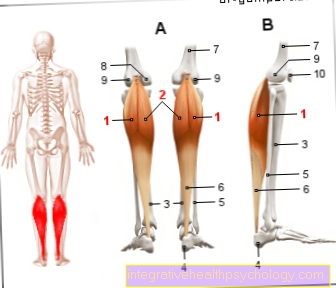
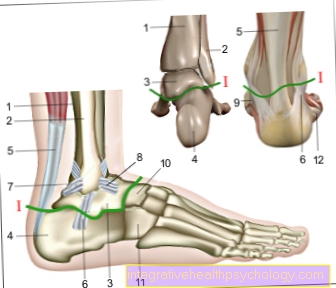
In addition to the shinbone (tibia), the fibula forms one of the two prominent bones of the lower leg.
An isolated fibular fracture rarely occurs, mostly in connection with other fractures or impairment of the upper ankle joint (ankle). This is due to the fact that the lower part of the fibula, together with the distal part of the tibia and the trochlea tali (a joint roller on the upper side of the ankle body (corpus tali)), forms the upper ankle joint (articulatio talocruralis). Most commonly the distal part of the fibula is affected (outer malleolus fracture), in which the lower, distal tip of the fibula is broken.

- Calf community -
Corpus fibulae - Shin community - Corpus tibiae
- Femoral shaft -
Corpus femoris - Tibia-fibula joint -
Articulatio tibiofibularis - Fibula head - Head fibulae
- Interbone membrane of the
Lower leg -
Membrana interossea cruris - Shin and fibula tape adhesive -
Syndesmosis tibiofibularis - Fibula bone -
Lateral malleolus - Shin bones -
Medial malleolus - Kneecap - patella
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Outer ankle fracture and syndesmosis tear
The most common "disease" of the fibula is the outer malleolus fracture, which is divided into Weber A, B or C depending on the severity of the fracture. Most often this breaks Fibula during sports.
Further information is also available at: Fibular fracture
In rare cases, the close fiber connection between the tibia and fibula in the ankle joint area (Syndesmosis) tear. In most cases, such injuries must be surgically immobilized in order to achieve permanent stability of the ankle joint.
causes
The cause of fibula fractures, in combination with injuries to the upper ankle, is usually one blunt force from the outside on the lower leg. The fracture of the fibula is usually the result of indirect force, in combination with a fracture of the outer ankle and lower leg. Such blunt external violence occurs especially when exercising "dynamic sports", with rapid rotational movements, such as in soccer.
In addition to these "dynamic sports", there are also Traffic accidents, occupational accidents, a Buckling of the ankle, strong turning movements in the area of the upper ankle and one dislocation or a Subluxation of the talus (Talus), for such an injury pattern of the fibula and the upper ankle joint.
Concomitant symptoms
An isolated fibular fracture is rare. Most often there is a distal fibular fracture, which also affects the upper ankle or the fibular head. In addition to these injuries, this can also be Syndesmosis tape, injured as part of a fibular fracture. The syndesmotic ligament is a tight, collagenous or elastic ligament structure or ligament connection that is located in the distal area between the shin and fibula. The syndesmosis ligament, in the area of the tibia and fibula, is also called syndesmosis tibiofibularis.
Read more about the topic here: Syndesmosis tear
The syndesmosis tape keeps the distance between the two bones of the lower leg, i.e. the distance between the tibia and the fibula, constant. In addition, the syndesmosis band serves to stabilize the Ankle fork (Malleolar fork). Injuries to the syndesmotic ligament always result in changes in the upper ankle. These injuries must be used to preserve, as well as protect, the upper ankle from a arthrosisto always be treated.
Pain
In the case of a closed fibular fracture, pain in the fibula and pain in the distal part of the fibula are the predominant symptoms. At the same time, the injured area can be swollen due to the damage to surrounding structures (vessels, tissues or nerves). Since the syndesmosis ligament is usually additionally injured in a fibular fracture, damage or injury to the syndesmosis ligament can lead to pain over the upper ankle, especially in the anterior part of the upper ankle.
Read more on the topic: Fibula pain
diagnosis
The diagnosis of a fibular fracture or a distal fibular fracture, with involvement of the upper ankle joint, is made via a X-ray diagnostics, with an x-ray in 2 levels, for the complete representation of the joint.
Since a fibular fracture usually also injures the syndesmotic ligament, an MRI examination is necessary for clarification.

X-ray a.p .: fibula fracture with slight displacement
treatment
In general, however, it can be said that the treatment of the fibular fracture depends on the type of fracture. A distinction is made between the treatment options for fibular fractures between one conservative Treatment and one operative, surgical treatment. If an injury in the area of the lower leg is suspected, the lower leg is initially immobilized with a Orthosis or with a rail provided. Also is a Elevation the injured lower extremity is advised. Then, in order to plan further treatment, it must first be diagnosed precisely whether it is a smooth, isolated fracture of the fibula or whether other structures, such as the upper ankle or the syndesmosis ligament, have been affected as part of the present injury. Is it a smooth, not dislocated Fracture of the fibula, this can be done with the help of a Walking cast are supplied. However, if several structures are affected, they may have to be accessed using Plates, screws or Wire cerclages are supplied.
A Calf joint fracture (Fibular shaft fracture) rarely requires surgery. Cerclagen are Metal wire loops or wire bands that are used in trauma surgery for the osteosynthesis of fractured bone structures. With the help of the Cerclagen, the fractured bone structures are wrapped around in the form of an osteosynthesis (operative connection or merging of two bone fragments) and thus reassembled.
A Fibula head fracture occurs in most cases by striking the head of the fibula directly (e.g. when playing football).
These fractures can possibly result in complications, as there is an important lower leg nerve directly behind the head of the fibula (Peroneal / fibular nerve) which can be damaged by these fractures.
Read more about the topic here Peroneal palsy
Weber A, B, C
The upper ankle fractures are after Weber, depending on the position of the fracture to the syndesmosis, divided into three fracture types (Weber A, Weber B and a Weber C). In these three types of fractures of the upper ankle joint (ankle joint), the syndesmotic ligament is either intact or injured. If there is a Weber A fracture, the fracture is in place below the syndesmosis and the syndemosis is here intact (unharmed). The Weber B fracture has the fracture at the level of the syndesmosis, causing the syndesmosis often injured too is. If it is a Weber C fracture, the fracture is above the syndesmosis, whereby the syndesmosis is always torn.
Read more about the topic here: Ankle fracture
Duration of healing with surgery
If an operation is unavoidable due to the severity of a fibular fracture (dislocated, displaced bone parts, tear or even complete rupture of the syndesmotic ligament), the duration of the healing of such an injury has to be assessed individually from patient to patient. The materials used in the operation such as Screws or plates, can only after complete bone healing as part of another operation removed. After the operation, in addition to physiotherapeutic treatment, there are several more postoperative x-ray controls which serve to describe the course of the healing of the fracture. Thus, a fibular fracture may heal after surgery up to 18 months or last longer.

Duration of healing without surgery
If no surgery is necessary to treat the fibular fracture, e.g. in the case of a smooth, undisplaced (displaced) fibular fracture, the applied Walking cast, depending on the healing process after approx. 6 weeks be removed. Then the pain-adapted stress the lower extremity with the help of a physical therapist. Sometimes wearing extra is one Ankle brace necessary for a certain time.
In this treatment case, too, the duration of the healing of the fibular fracture depends on the patient's individual factors (age, weight, etc.). Thus, this treatment method can also show results more quickly with some patients than with others.
Length of sick leave
The length of time you are on sick leave after a fibular fracture depends on the extent of the injury. At the beginning, the patient usually receives a certificate of incapacity for work 4 - 6 weekswhich can be extended depending on the severity of the injury and the duration of the healing process.
Removal of the plate after surgery
The question of how to remove a metal plate that was used to treat a fibular fracture cannot be answered across the board. Complete bone healing after a fibular fracture must always be considered individually. The removal of the plate is only after complete healing the bony fracture indicated. The current status of bone healing can be checked with the help of postoperative X-ray controls judge. Sometimes there may be reasons for premature removal of the materials used in the operation, such as a metal plate.
These reasons include besides Infections, the subjective disturbance, one Weakening of the bone tissue, incorrect coalescence of the fractured bone, and migration of the metal plate used towards the outside of the lower leg. After an individual assessment of the bone healing by the surgeon, the metal plate can usually be removed after approx. 4-18 months removed.
The removal of the metal plate is under a re-operation carried out. Following the surgical removal of the metal plate, one closes 3 months later final x-ray check on. This final X-ray diagnosis is used again to check the exact repositioning of the fractured bone portions.


.jpg)