Pelvic fracture
definition
A pelvic fracture describes a fracture of the bony parts of the pelvis.
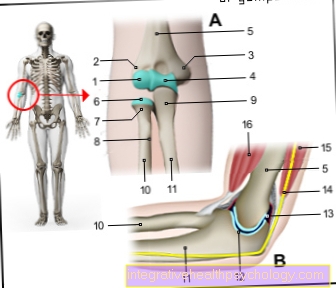
The bony pelvis is made up of the hip bone and the lowest part of the spine, the sacrum.
The hip bone, in turn, consists of three bone parts: the iliac bone, the pubic bone and the ischium, which are separate parts during the first 15 years of life and only then completely fuse together to form the hip bone.
Looking at the pool from above, you can actually see a ring shape, hence the name pool ring. Functionally, the pelvis is used to transmit power from the spine to the lower extremity. At the same time, it protects the organs located in it, such as the urinary bladder, uterus and intestines.

Pelvic ruptures are rare, but when they do occur mostly serious injuries. The main causes of a pelvic fracture are serious accidents with great Violence in question such as in the event of a traffic accident or a fall from a great height. In younger adults, such a fracture occurs mainly in the so-called Polytrauma in front. A multiple trauma is a serious accident in which at the same time injured several parts of the body or organs and at least one injury or a combination of both life threatening is. Around every fifth multiple trauma patient has an injury to the pelvis.
in the older age, especially from the age of 70, occasionally already cause Minor injuries fracture of the pelvis with little force. Small accidents, such as falling over the carpet at home or falling on black ice, can cause dangerous pelvic fractures in old age. In advanced age are of this particularly affects womenbecause they often have a "Bone loss“ (osteoporosis) consists.
A pelvic fracture often occurs in Combination with other injuries on. In older people, for example, a pelvic fracture occurs more frequently in combination with a Femoral neck fracture so that this must always be considered. Often there is also a participation of Acetabulum (Acetabulum). The hip joint is then directly affected by this fracture / injury.
How long does it take to heal?
The healing time depends largely on the type or severity of the pelvic fracture. If the pelvic fracture is stable, the average healing time can be given as four to eight weeks. During this time, the pelvis should not be stressed. Beyond these eight weeks, however, the load is initially limited and pain can still occur, but the worst is over. An unstable pelvic fracture is usually operated on and healing can take longer. After the operation, the patient has to stay in bed for about four weeks. The patient can then gradually return to everyday activities. Nevertheless, it is important that the patient is mobilized passively through physiotherapy while they are in bed rest in order to avoid muscle breakdown. In the case of a complicated multiple hernia, the patients often have to remain in bed as much as possible for months.
Physiotherapy plays an important role in healing. Therefore, also read: Physiotherapy for a pelvic fracture
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Initiation
The pelvic fracture can be divided into different degrees depending on the severity Types organize.
One possibility of classification is that ABC classification according to AO (Working group for osteosynthesis issues). Here, the pelvic fractures are divided according to the criteria Pelvic stability and the Power flow of the Spine on the Hip joints in type A, B and C.
At the Type a is the Pelvic ring stable and not completely broken through at any point, only torn. Of the Power flow from the spine to the hip joints is still here intact. This type of fracture is primarily about Breaks or tears in the Edge area.
The pelvic fracture from Type B is rotationally unstable because it leads to a complete break of the anterior part of the pelvic ring. The rear part is stable here. This fracture type also includes the so-called "Open-book fracture". Here it comes to a complete Severing the symphysis ligaments, as well as the anterior ligament portion of the iliac / sacrum joint. On the affected side, the basin can then be opened like a book, hence the name "Open-book". Also with this type of fracture is the Power flow from the spine to the hip joints stable.
With the pelvic fracture from Type c lies a total instability as the injury affects both the anterior and posterior pelvic rings. This fracture type represents the most serious fracture of the pelvis. It is important here at which point the rear pelvic ring was severed. There are several ways to do this: either through a Fracture of the sacrum or the iliac bone or a rupture of the sacroiliac joint (so the joint between the iliac and sacrum).
Fractures of the sacrum are also classified according to Denis. The location of the fracture is with respect to the expected nerve damage of great importance. With a central fracture of the sacrum, often arise multiple nerve failures. In this type of fracture, however, the flow of force from the spine to the hip joints is interrupted.
Symptoms
The main symptom is a pelvic fracture severe pain in the area of Basin. It can be above the fracture area Swelling occur. Possibly one can at the places of the injury so-called Bump marks or bruises detect.
The patient may only be able to move his leg to a limited extent or only with pain. It can also become a Pelvic inclination or one Leg length difference by a fracture of the basin.
If the internal organsthat are normally protected by the pelvis, it can too Bleeding coming from the genitals or anus. Especially the bladder, of the Intestines, and the internal genitals can be affected if the pelvis is injured. Are those running in the basin annoy involved, it may also happen Disorders of sensitivity (Sensory disturbances) or to motor disorders.
diagnosis
The diagnosis of a pelvic hernia includes both physical as well as apparatus-based examination methods. The description of the Accident or fall that caused the pain or restricted mobility.
It is important to touch the Pulse, examining the sensitivity and the Motor skills of Basin and the legs to avoid damage to the blood vessels and the annoy to exclude.
Monitoring of the Blood pressure and the determination of the so-called Hb value (hemoglobin) in the blood important if there is any suspicion of a Bleeding into the pelvis consists. A value below 8 mg / dl is to be regarded as critical. In the case of a fractured pelvis in the context of a Polytrauma up to 4 liters of blood can bleed into the pelvis, putting the patient's life at risk.
May be cleared up by physical exam Swelling palpate or, depending on the severity of the fracture, a Pelvic asymmetry or one Movability of the bones against each other.
If a pelvic fracture is suspected, one should always be included rectal exam as well as an additional one for women vaginal exam consequences.
In order to be able to assess the extent of the injury and to exclude a pure bruise, is through roentgen a Pelvic overview image made. A possible fracture can be identified here.
In order to be able to rule out further injuries Ultrasonic and Computed tomographic (CT) Recordings made. These serve primarily to rule out any damage to the internal organs. The ultrasound examination is performed after Fluid in the abdomen and looked for air to assess the severity of the injury. A so-called Excretory urography should be carried out when there is evidence of a violation of the Urinary tract gives.
Pelvic fracture due to osteoporosis
Older people in particular are affected by a pelvic fracture. Your bones are usually weaker and more prone to fractures. The reason for this is the osteoporosis, which often occurs in old age and especially in women.(Osteoporosis is bone loss.) In patients with osteoporosis, minor trauma, such as falls, are enough to fracture the pelvis, whereas a young adult would not have suffered an injury. On the one hand, patients with osteoporosis are more susceptible to pelvic fractures and, on the other hand, healing is more difficult and correspondingly longer.
Read more on this topic at: osteoporosis
therapy

Therapy differs significantly depending on the extent and severity of the pelvic fracture. If the fracture is incomplete and stable, surgery is usually not necessary. The pool only has to be for a while (about 2-4 weeks) are immobilized and relieved. This means, if possible, lying down most of the time and using crutches while walking.
Sometimes special bandages are used to stabilize the pelvis from the outside. It is also important to start physiotherapy again as soon as possible after the rest period so that the muscles do not break down too much and movement restrictions are eliminated. It is also important that patients who are in pain receive adequate pain medication.
Physiotherapy plays an important role in healing. Therefore, also read: Physiotherapy for a pelvic fracture
In contrast, a complete, unstable hernia almost always requires surgery. If necessary, hemostasis takes place through stabilization from the outside through "Pelvic clamps". Constant monitoring of blood pressure and pulse is particularly important in the case of a pelvic fracture, as this type of injury can lead to massive bleeding from large vessels and both blood pressure and pulse can be signs of circulatory failure due to blood loss. Especially the blood vessels from the supply area of the femoral vein and femoral artery can trigger such massive bleeding. If there has been massive blood loss, emergency care must first take place. The blood loss must be compensated for by giving the patient fluids, blood transfusions and, for example, coagulation factors. Then, in a second step, the fractions are screwed / clad. The operation is often followed by being bedridden for longer than with a stable pelvic fracture.
Due to the proximity of the pelvic bones to the internal organs, complications can always result in injuries to them. Possible bladder and urethral injuries, but also an injury to the intestine or the internal genitals, are important here.
Since multiple trauma is the primary cause of a pelvic fracture in younger people, the treatment of further injuries is just as important and crucial for the patient's recovery. The typical surgical risks such as wound infection, secondary bleeding or wound healing disorders must of course also be considered. The risk of thrombosis is extremely high in the case of a pelvic fracture, so that thrombosis prophylaxis must always be carried out. It must also be taken into account that nerves that run in the operating area can be damaged.
Operative therapy
Whether a pelvic fracture is treated conservatively or surgically depends on the severity of the injury. Is it an unstable type B or pelvic injury C. surgery is indicated. Since a complicated pelvic fracture threatens large blood losses, the patient's circulation is only stabilized before the actual operation to treat the fracture is performed. First, the injured blood vessels are supplied and the pelvis with a so-called auxiliary External fixator (Stabilization system that is introduced into the bone from outside through the skin) or a pelvic clamp stabilizes. In the actual operation to treat the pelvic fracture, the fragments are either screwed together or connected and stabilized using plates. The metal parts inserted into the body, such as screws or plates, usually remain in the body, so that no second operation is necessary. The entire procedure takes place under general anesthesia. After the operation, the patient has to stay in bed for a few weeks.
Physiotherapy is also very important for healing after an operation. Therefore, also read: Physiotherapy for a pelvic fracture
Consequences of a pelvic fracture
A pelvic fracture can under certain circumstances lead to various consequences for the patient. On the one hand, the fracture of the pelvis can lead to accompanying injuries in the area around the pelvis, so that consequential damage to the nerves, urethra, bladder, intestine or vagina can occur. When nerves are damaged, these are often nerves that supply the bladder and intestines. Those affected can then no longer hold their urine and stool - it is incontinence. In men, nerve damage can also lead to impotence. If the hip socket is also affected by the pelvic fracture, the long-term consequence may be a more rapid development of osteoarthritis (joint wear) of the hip joint. If the pelvis is not sufficiently spared during the healing process, so-called pseudarthrosis can occur. Pseudarthrosis is a fracture that does not heal sufficiently. If the time between the fracture and the repairing operation for a hip joint fracture is too long, the head of the femur may die off because it was not supplied with blood for a long period of time. Ossification of the surrounding soft tissue can also occur, which is technically known as heterotropic ossification. One tries to prevent this consequence by irradiating the operating area. The main consequences are after an unstable pelvic fracture (Type B or C) to be expected, while a stable pelvic fracture usually heals without complications without surgery.
forecast
Depending on the severity of the pelvic fracture, of course, the further prognosis also differs, although overall it can be said that this is generally quite good. Stable fractures often heal spontaneously and without complications.
In the case of unstable fractures, the prognosis is also good thanks to the appropriate therapy (with fixation of the fragments with screws or plates). The involvement of other structures such as blood vessels, nerves and internal organs is decisive for the prognosis of a pelvic injury. So-called open pelvic hernias, from which around half of the patients die, have a very poor prognosis. In the best case, the pelvic fracture did not involve the nerves in the area, so that there were no long-term impairments. Very rarely, a healed fracture can develop a so-called pseudarthrosis.
There is little that can be done preventively for a pelvic fracture. The most important thing is to minimize the risk of falling, especially for older people. This can be done primarily by using walking aids, be it a stick, a walker or crutches. It is also useful to eliminate tripping hazards in the apartment, for example not to lay carpets on top of carpets so as not to get caught on the edges. Sturdy shoes are also a sensible consideration to avoid tripping over.