Pelvic ring fracture
introduction
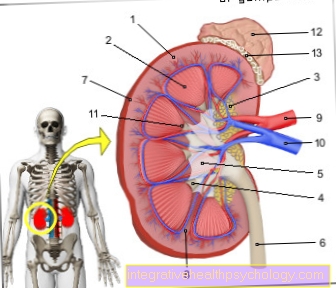
The pelvic ring fracture is a broken bone that interrupts the integrity of the so-called pelvic ring. The term "pelvic ring" (Cingulum membri pelvini) comes about through the view of the pelvis in cross section, in which the pelvic bones are connected and arranged in a ring shape.
The pelvic ring represents the connection between the spine and the lower extremity. Its main task is to impart stability in standing and walking. It is crucial for the upright posture, serves as a place of attachment to various muscles and is therefore important for movement. The bony pelvis also protects internal organs of the lower abdomen.

definition
A pelvic ring fracture results in a fracture that affects the integrity of the Pelvic ring is interrupted. Pelvic ring fractures are based on the AO classification (working group for osteosynthesis issues) which serves as an international classification system for bone fractures.
- Of the Type a describes a stable pelvic ring fracture. This means that the break, for example in the edge area of the Beck vanes is localized, but the pelvic ring structure is not affected and disrupted. This fracture is the most favorable prognostic form, because the pelvic bones do not move significantly and there are usually no serious accompanying injuries.
- In the Type B fracture If the pelvic ring becomes unstable, the pelvis can no longer withstand rotational loads. Hence the type B fracture is also called rotationally unstable pelvic ring fracture designated. Such a fracture occurs, for example, in a Crack of the front connection of the pelvic blades, so the Symphysis, on what makes the Basin opened like a book can be (open-book fracture).
- At the Type c lies a complete instability of the pelvic ring in front. So it is not only in the rotational component but also opposite vertical load unstable. This occurs especially with complex injuries to the pelvis, on the one hand the anterior pelvic ring affected and on the other hand also the sacrum or the joint between the sacrum and the pelvic blades (Articulatio sacroiliaca) is injured and thus a anterior and posterior interruption of the pelvic ring present.
causes
Causes of a Pelvic ring fracture are mostly severe traumathat act on the body from the outside. For example, pelvic ring fractures are common Falling from great heights or in traffic accidents on.
In older people who have osteoporosis as their underlying disease, pelvic ring fractures occur even with minor trauma, for example with simple falls, because of the Osteoporosis the bone mass and stability is reduced and the bone can be overloaded and break even with light stress.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Symptoms
The main symptom of a pelvic ring fracture is severe pain in the hip area. This pain usually results in a relieving posture of the pelvis and leg. The mobility in the hip is also restricted. In addition, there is often swelling and bruising over the fracture site.
Due to the interruption of the pelvic ring, the pelvic stability is reduced. This results in an abnormal mobility of the pelvic bones, which, depending on the type of fracture, can be displaced against each other, which is not possible with an intact pelvic ring. The pelvic ring fracture can even be seen in a pelvic asymmetry that is pelvic diagnostics. Particularly in the case of unstable fracture forms, accompanying injuries to adjacent organs and soft tissues can occur. If nerves have been injured, movement in the leg may be restricted or sensitivity disorders of the skin over the hip or leg may result.
If blood vessels are injured, it can lead to circulatory disorders in the adjacent area on the one hand, and bleeding can occur on the other. This bleeding is potentially life-threatening because, on the one hand, large blood vessels like the Iliac artery, the leg kicks, can be affected and there can be enormous blood loss in a short time. On the other hand, in the case of an unstable pelvic fracture, a large amount of blood can collect asymptomatically in the pelvic area without being noticed. Due to the instability of the pelvis, the accumulation of blood can push the fracture fragments further apart and thus create space for more blood. There is a high risk of shock and, as a result, bleeding to death. The urinary bladder, ureter and intestine are also adjacent to the pelvic bones, which can also be injured in the event of fractures, which can then be seen, for example, in the form of bloody urine.
diagnosis
The classic diagnosis of a pelvic ring fracture is based on medical history, physical examination, and imaging.
In the anamnesis, the doctor asks about the course of the accident, the symptoms and accompanying current restrictions. Also of interest are existing underlying diseases that can affect bone stability, for example whether osteoporosis or bone tumors are present.
During the subsequent physical examination, the doctor pays attention to whether there is any visible evidence of a fracture, for example asymmetry of the pelvis, swelling or hematoma. Then he palpates the bony pelvis and pays attention to abnormal mobility of the pelvic bones, whether they can slide against each other or whether there is pressure or compression pain in the pelvis. Then it is examined whether mobility and sensitivity in the hip or leg are restricted.
The physical exam is followed by imaging measures. First, x-rays are made in several planes, which allow an initial assessment of the bony situation. In most cases, a computed tomography of the pelvis and the abdomen is used for a more precise assessment. Like an ultrasound scan of the abdomen, this is very important in order to assess the abdominal organs and exclude bleeding and injuries.
In the differential diagnosis, a pelvic ring fracture must be distinguished from bruises of the pelvis as well as from osteoarthritis. Injuries to the knee, in which the pain is often projected into the hip, must also be excluded. This is a very common phenomenon in children.
therapy

The acute therapy at the scene of the accident with justified suspicion of a pelvic ring fracture consists of immobilization and the stabilization of the pelvis using pelvic clamps or ligaments (pelvic sling) so that there is no further displacement of the bone fragments. In addition, this stabilizing compression should keep the pelvic space as small as possible, so as not to create space for potential bleeding to expand. As a result, the internal bleeding compresses itself at best.
The inpatient treatment of a pelvic ring fracture depends largely on the type of fracture and the accompanying injuries.
In the case of a type A fracture in which the pelvic ring is intact, conservative, i.e. non-surgical, therapy is usually used. The focus of the treatment is on adequate pain therapy and early mobilization of the patient using physiotherapy. The break then heals on its own and without complications.
Physiotherapy plays an important role in healing. Therefore, also read: Physiotherapy for a pelvic fracture
A type B pelvic ring fracture that exhibits rotational instability is treated either conservatively or surgically, depending on the severity of the accompanying injuries.
A type C pelvic ring fracture is an absolute indication for surgery. In this case, there is absolute pelvic instability, which is why the overarching therapeutic goal is reduction, i.e. the creation of the original arrangement of the bones in the pelvic ring and adequate fixation and stabilization of the structures involved. If the surrounding tissue is unaffected, the bone fragments are fixed intraoperatively using osteosynthesis procedures, i.e. with the help of screws and plates. However, if the soft tissue is severely injured, surgical procedures that are gentle on the soft tissue must be used. For this purpose a so-called External fixator used. This is a construct that temporarily fixes the pelvic bones and thus prevents the fracture situation from worsening, but has its connecting axis outside the body and thus protects the soft tissue in contrast to other osteosynthesis procedures.
After the surrounding tissue has healed, the definitive operation to restore the bony conditions can be followed. Depending on the injuries to neighboring organs, separate procedures must be used, such as the reconstruction and closure of an injured section of the intestine. Depending on the surgical procedure used, different lengths of bed rest are necessary after the operation, although physiotherapeutic exercises to build and maintain the muscles should also be performed in the case of long bed rest.
Physiotherapy plays an important role in healing. Therefore, also read: Physiotherapy for a pelvic fracture
forecast
The Prognosis of the pelvic ring fracture depends on Severity of the break and especially from the accompanying injuries. With adequate treatment, pelvic ring fractures generally have one very good prognosis.
The Type A fractures usually heal completely and without consequences from and also Type B and C fractures, i.e. unstable fractures, have a good prognosis with adequate care.
Had to fracture operational the general operational risks such as Wound healing disorders and infections affect the prognosis. However, depending on the accompanying injuries to surrounding organs, Incontinence and erectile dysfunction stay behind as a result of the pelvic ring fracture and thereby significantly reduce the quality of life.
prophylaxis
To prevent pelvic ring fractures it is very important to have the Determine the risk of falling of the elderly and to take appropriate measures if the risk is high. For example, they are useful prophylactically stabilizing aids like a walking stick or a walker. Care should also be taken to ensure that factors that encourage falls, such as slippery carpets, are removed and that as few steps as possible have to be climbed. Often can Avoid falls and consequently pelvic ring fractures by wearing closed, non-slip shoes. Also are Balance exercises useful to avoid future falls.
If there is still a high risk of falling despite all the measures taken, so-called Hip protectors be applied. these are special pants, into which upholstery is sewn as protective elements, which can then cushion falls.
Is there a osteoporosis or another underlying disease affecting bone stability, its adequate treatment is very important so that bone stability is restored or at least maintained as far as possible.