Bronchi
General
The bronchial system is the airway in the lungs. It is divided into an air-conducting and a respiratory part. The air-conducting part serves the sole purpose of conveying the breathing air and consists of the main bronchi and the bronchioles. It is also known as dead space, since no gas exchange takes place here. The respiratory part, which is responsible for the exchange of oxygen-poor blood for oxygen-rich blood, consists of the smaller bronchioli and the alveoli (Alveoli).
Infection of the upper respiratory tract is a very common clinical picture, especially in the winter and autumn months, which is why those affected go to the family doctor. In addition to the nose and throat, the lungs and the associated bronchi (bronchitis) are also affected in many cases.
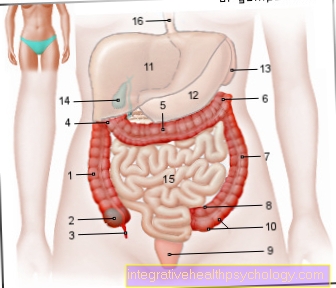
Illustration of the bronchi

- Right lung - Pulmodexter
- Left lung - Pulmo sinister
- Nasal cavity - Cavitas nasi
- Oral cavity - Cavitas oris
- Throat - Pharynx
- Larynx - larynx
- Windpipe (approx. 20 cm) - Trachea
- Bifurcation of the windpipe -
Bifurcatio tracheae - Right main bronchus -
Bronchus principalis dexter - Left main bronchus -
Bronchus principalis sinister - Lung tip - Apex pulmonis
- Upper lobe - Superior lobe
- Inclined lung cleft -
Fissura obliqua - Lower lobe - Inferior lobe
- Lower edge of the lung - Margo inferior
- Middle lobe (right lung only) - Lobe medius
- Horizontal lung cleft (between upper and middle lobes on the right) - Horizontal fissure
Histological structure
The large bronchi contain one multi-row, highly prismatic ciliated epithelium. The smaller the bronchi, the simpler the structure of the Epithelium. Then predominates in the bronchioles single-layer iso- or highly prismatic ciliated epithelium. Under the epithelial layer is located smooth musculature. The muscle layer increases with the smaller diameter of the bronchioles. Furthermore contain the bronchi elastic fibers, such as mucous and serous glands. The ducts of the glands end in the bronchi and cover the mucous membrane with a protective film. On the very outside there is one in the large bronchi Cartilage layer, which stabilizes the bronchial wall. In the smallest parts of the bronchial system, the alveoli (Alveoli) the gas exchange takes place. These are sack-like extensions that result from the small alveolar cells (Type I pneumocytes) and the large alveolar cells (Type II pneumocytes) consist. The type I pneumocytes are used for Epithelial formationthat produce type II pneumocytes Surfactant. This reduces the surface tension of the Alveoli and prevents their collapse. Furthermore serve Alveolar macrophages the cleaning of the alveoli by phagocytizing dust, or breaking it down after bleeding.
Structure of the bronchial system
The entire bronchial system is made up of different types of bronchi. It starts with the windpipe and the two big ones bronchi. These large main bronchi then divide into the two Lungs and branch out to the Lungs tips. In this way the bronchi get smaller and smaller until they are as Alveoli (Alveoli) at which the actual gas exchange takes place. The individual bronchi have different structures and are described in more detail below:

- Bronchiole
cartilage-free small bronchus -
Bronchiolus - Branch of the pulmonary artery -
Pulmonary artery - End bronchiole -
Respiratory bronchiolus - Alveolar duct -
Alveolar duct - Alveolar septum -
Interalveolar septum - Elastic fiber basket
of the alveoli -
Fibrae elasticae - Pulmonary capillary network -
Rete capillare - Branch of a pulmonary vein -
Pulmonary vein
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
and lobe bronchi
The right lung consists of three lung lobes. Due to the anatomical proximity to the heart and the resulting tightness, the left wing only consists of two lobes. As a result, the two main bronchi, which are divided at the so-called bifurcation, branch off into two lobes on the left and three on the right into three lobes. Their diameter is between 8 and 12 mm.
Following the segmental structure of the lungs, the lobes continue to divide. The lung segments were numbered consecutively in order to be able to provide precise descriptions of the localization.
Segment bronchi
Each segment bronchus divides into two branches (Rami subsegmentales). These branches take place up to a diameter of 1 mm. Up to this size the bronchi contain Cartilage in your bronchial wall to ensure that it remains open so that the air you breathe can be transported away.
As the bronchi continue to branch out, the frequency of increases Goblet cells and the Ciliated epithelium from and it imagines annular muscular system under the mucous membrane. A contraction of this muscle system can narrow the bronchi and so e.g. the clinical picture of the bronchial asthma to lead.
Bronchioles
Due to the loss of the cartilage and the increasingly smaller diameter, the bronchi are now called Bronchioles designated. These have a monolayer ciliated epitheliumwhich no longer has goblet cells and can therefore no longer form mucus. Exclusively by train elastic fibers the opening of the bronchioles is ensured. The bronchioles divide into each 4-5 terminal bronchioles (Terminal bronchioles). These in turn branch further into the Bronchioli respiratorii from which 1-3.5mm long and approx. 0.4mm are far. In some places the wall of the respiratory bronchioles is already penetrated Alveoli (Alveoli) formed. They follow the smallest bronchioles Alveolar ducts (Alveolar duct), the wall of which consists exclusively of alveoli (alveoli). They end in Alveolar sac. The small bronchioles (Terminal bronchioles, respiratorii and Alveoli) are essentially for the formation of the Lung lobes (Lobules) responsible.
Air sacs (alveoli)
The smallest alveoli are from you elastic connective tissue and a fine one Vascular system surround. Due to the branching into the smallest bubbles, each with a diameter of approx. 0.2 millimeters have a very large total surface area, which is responsible for gas exchange. Both lungs together have about 300 million Alveoli, which cover an area of total 100 square meters having.
You can find more information on the topic here: Alveoli
Diseases of the bronchi
Especially in the autumn and winter months it is Respiratory infection a common reason for going to the doctor. In addition to the nose and throat, the large bronchi are also often affected. During the cold season, our immune system is a little slower because our blood circulation is poorer in the cold, but the main reason for the more frequent infections in winter is that we are often in closed rooms, usually with many other people, and the indoor air is with us is mostly warm and humid. Bacteria or viruses also like such conditions and thus multiply faster and can be inhaled more frequently. The pass through the nose and throat area Pathogens then into the lungs and begin on the mucous membrane lined To accumulate epithelium of the bronchi.
Mucous bronchi
As soon as the pathogens settle in the bronchi they lead to one Inflammation of the lining of the bronchiwhat also called bronchitis referred to as. As a result, the cells, which normally ensure a sliding film of mucus on the bronchi, begin to produce a particularly large amount of mucus in order to "hold" the pathogens in the mucus. Large amounts of mucus are deposited in the bronchial tubes and this triggers the coughing stimulus typical of bronchitis, which is supposed to ensure that the excessive mucus can be coughed up.
More information can be found here bronchitis
Sometimes the mucus in the bronchi is so tight that it becomes drug-induced expectorant measures must be taken to loosen the mucus. Most of the time, medication comes along ACC / NAC are used, which can be taken in the form of an effervescent tablet. Just as helpful as the medicinal mucus solution is steam inhalation, which can be carried out with or without the addition of a menthol- or eucalyptus-like substance. If the mucus loosens, it should be coughed up.
The duration of a slimy (also productive) Bronchitis is about 7 days.
More information can be found here Duration one bronchitis
Although bronchitis 90% by viruses triggered, it can also lead to one in the course of the inflammation Settlement of bacteria come in the bronchi. Typically, after a cough that has lasted for days, an increased feeling of illness sets in and the slimy cough is increasing yellowish tougher and then usually takes more than 10 days. In these cases the family doctor can prescribe an antibiotic, although the administration of an antibiotic can reduce the duration of the illness not significantly shortened becomes.
The mucous bronchi can either be determined by the patient himself or by listening to the doctor's lungs. In the case of slimy bronchitis, the doctor hears a typical rattle and the movements of the mucus when breathing.
In rare cases, the pathogen and inflammation can settle into the deeper sections of the lungs (alveoli) and the tissue between them, causing it to become a lung infection with sudden high fever and severe feeling of illness comes.
More information can be found here lung infection
to cough

Cough is one Measure the bodyto remove material (e.g. mucus, pathogens, foreign bodies, etc.) from the bronchi and the nasopharynx. He is often a constant companion infection bronchial tubes and lungs, but can also occur in long-term sinus infections. Depending on how severe the infection is, the longer and more persistent the cough can last.
Cough that occurs with bronchitis take up to 14 days. A cough that is not suspected of being infected should be at the latest after three weeks by a doctor and, if necessary, examined more closely with an X-ray of the lungs.
One distinguishes one dry from a productive, i.e. slimy, cough. It used to be believed that viruses mainly cause a dry cough and bacteria a more productive cough. In the meantime, however, this strict separation has been abandoned. In the course of bronchitis, a dry cough usually develops first, which then turns into a productive cough with phlegm. However, some disease courses can alone with a strong dry cough go hand in hand, which can sometimes last over 14 days.
Of the dry cough In contrast to the productive cough, it is usually described by those affected as more agonizing and annoying. In addition, the ciliated epithelium of the bronchi, which during the day has the task of transporting the smallest dust particles upwards from the lungs, largely ceases to work in the evening, which means that a evening cough begins, which sometimes lasts all night and can be extremely dry, so that those affected cannot sleep. There are numerous herbal supplements, such as. Bronchipret, which are said to lead to a reduction in the urge to cough. Proven to help honey very good for coughs. Also non-herbal supplements can be used, come here often Capval or Silomat® is used. The main application of these two drugs is dry cough. In more severe cases of dry, non-productive irritable cough, treatment may be attempted with Codeine to be undertaken. It is important to note here that codeine should only be taken for a limited time in order to keep the possible side effects as low as possible.
These drugs are called Cough suppressants designated. they may not in combination with cough suppressants (like ACC / NAC) are used, otherwise it becomes a dangerous Mucus congestion can come.
Productive and slimy cough is usually described as not so excruciating because of the urge to cough with the coughing up of slimy material, rapidly decreases. In addition to inhalation with steam, a medicinal mucus solution with acetylcysteine (ACC akut®The treatment should cause the mucus in the bronchi to loosen.
Burning of the bronchi
Burning of the bronchi may occur different causes to have. A common cause of bronchial burning while breathing is inflammation of the bronchial mucosa as part of infections. This is not an inflammation of the bronchi or the lungs in the classic sense, but rather one Irritation of the epithelium due to long-term infection. Most of the time it is not the existing infection that causes the symptoms, but the permanent cough that results from it. Especially dry and hard cough can lead to irritation of the bronchial mucous membrane, which the person concerned then feels in the form of a strong burning sensation during inhalation and exhalation. Also special dry air, mostly in the home, can cause a burning sensation when breathing. In this case it is very important that the Breathing air humidified in order not to unnecessarily strain the bronchial epithelium. Steam inhalation can also help reduce the burning sensation in the lungs.
The somewhat rarer but more dangerous cause is this Inhalation of toxins, causing severe and prolonged irritation of the mucous membrane in the bronchi. Mostly it is the inhaled smoke after a fire in an apartment or house that can be extremely toxic and can lead to irritation of the bronchial epithelium, sometimes very long-lasting. The person concerned usually notices after inhaling the smoke Burning sensation on inhalation and exhalation shortly thereafter.
Dilate bronchi
Bronchi can expand and also contract. With bronchitis, they can travel normally or through the mucus lying in them constricts be. The Exchange of oxygen content reduced and be restricted. A bronchial constriction becomes very evident in asthma in particular. This is noticeable in the typical wheezing sound that the patient has during an asthma attack. In this case, the bronchodilator should be dilated with medication. This is done primarily through a so-called Beta 2 mimetic. There are numerous so-called beta receptors in the bronchi, which ensure that the bronchi expand when the receptors are stimulated. In addition to adrenaline and other messenger substances, there are also some drugs that stimulate the receptors. Probably the best known drug from this group is Salbutamol. It is available in the form of a spray and should be inhaled a maximum of 2 times a day if necessary. The expansion of the bronchi usually occurs within a few minutes one and the effect lasts about 5-8 hours.
More information can be found here Salbutamol
It is also used in hospitals adrenaline used in the form of an inhaled mist for bronchodilation, since adrenaline, as described above, also acts on the so-called beta receptors. This method of bronchodilation is mainly used in the children's wards with the so-called "Pseudo croup " Application. However, since adrenaline can pass from the lungs into the bloodstream, this therapy may only be used in hospitals.
Summary
The bronchial system is the entire air conduction and respiratory section of the lung after windpipe designated. This is divided into two main bronchi, which in the right and left lung lobe flow out. This is followed by a further branching of these bronchi according to the structure of the lungs in Segment bronchi and Lobe bronchi. Due to the branches deep into the lungs, the diameter of the bronchi becomes increasingly smaller until they finally reach the Alveoli (Alveoli) with a diameter of only approx. 0.2mm having. These alveoli contain cells that are responsible for gas exchange. In addition, the Surfactant formation of the alveolar cells collapse of the alveoli and thus suffocation. In addition to the decreasing diameter, the wall structure of the bronchi also changes. The large bronchi have a multilayer epithelium, mucous cells and cartilage to stabilize the bronchial wall. The smaller the diameter of the bronchi, the smaller the cartilage tissue becomes. The epithelial layer becomes one layer and the mucous cells decrease. Instead, the proportion of the muscle layer in the small bronchioles increases. This can contract and the clinical picture of a spastic bronchial asthma trigger.
The common diseases of the bronchi include Infections of the bronchial mucosawho have favourited bronchitis. They often lead to one Bronchial mucus and cough. In the event of a strong, dry cough, the bronchial tubes may burn during the course of the disease when breathing in and out. The best way to enlarge the bronchi is with the Salbutamol-Spray, containing a mucus solution ACC acute or NAC. Help against annoying dry coughs that disturb sleep Honey, capval and codeine.
















.jpg)