Fever without symptoms in adults - what's behind it?
What is a fever without symptoms?
Fever occurs when the immune system is working harder. This is usually the case when the body wants to protect itself against pathogens. Fever can also be caused in very stressful phases of life, for example when the immune system is working harder due to increased cortisol release. However, if the fever occurs repeatedly and over a longer period of time without further symptoms, a diagnostic work-up should be carried out, as serious illnesses can also be the cause.
If the cause of the fever is not found, one speaks of the so-called fever of unknown origin.
The duration of the fever can often provide clues as to the underlying cause. Read more about this on the following page: How long does a fever last?

What is the cause of a fever without symptoms?
Viral or bacterial infections, autoimmune diseases and cancer must always be considered as possible causes. In any case, the HIV status needs to be clarified if a fever is detected without any further symptoms.
Diseases, some of which are difficult to diagnose, can initially only be accompanied by the symptom fever. These include, for example, accumulations of pus (abscesses) in organs or an inflammation of the bone marrow (osteomyelitis). M. Still - a subtype of rheumatoid arthritis - can be accompanied by a recurring fever without any further symptoms being noticed. Sarcoid, a disease that can affect the lungs, skin and joints, can only be identified by a high fever.
Furthermore, if the fever persists, possible causes such as malignant lymphoma and leukemia should be considered. Repeated fever is sometimes triggered by pulmonary embolism that does not otherwise become symptomatic.
Medication can also cause a high fever, known as drug fever. The triggering drugs include, for example, cytostatics and antibiotics. Various inherited (hereditary) fever syndromes can also cause fever without further symptoms.
How do you find out the cause of the fever?
It is important to see a doctor if the fever persists. In addition, those affected should pay attention to whether other symptoms, such as abdominal pain or joint problems, have not occurred recently regardless of the fever. In the foreground, the questioning is initially in order to determine possible causes.
This is followed by a physical exam, paying particular attention to swollen lymph nodes or an enlarged liver. It is also important to take a blood sample, which can indicate infections or disorders in the formation of red and white blood cells. The blood should also be tested for HIV (please refer: HIV test).
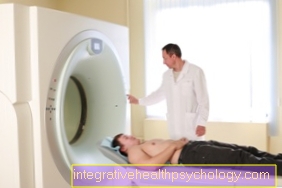
An x-ray of the lungs should be made to detect certain diseases - such as sarcoidosis. Sometimes it may be necessary to take a sample from the bone marrow. This is called a bone marrow aspiration and is done, for example, if there is a suspicion of leukemia. In addition, further apparatus-based examinations such as ultrasound, MRT or CT can be used to establish a diagnosis. Another method that can be used to display both infections and cancer is so-called positron emission tomography (PET).
What can you do if the cause is not found?
If all possible diagnostic examinations have remained without knowledge, it is still important to keep an eye on the fever and its development. Attention should be paid to any other possible symptoms that may be related to the fever.
In some cases an infection - for example with HIV - is not yet detectable and a blood test should be repeated after a few weeks. Repeated blood tests by the doctor are advisable if the fever persists.
It should be clarified that a fever without symptoms can be caused by many different causes. Depending on the underlying cause, the prognosis is good or bad. In general, however, it can be assumed that the prognosis is good if no cause for the fever can be found within six months.
Can a blood count provide an indication of the cause?
The examination of the blood count is an important part of the diagnosis when it comes to fever without symptoms. The blood count counts red and white blood cells and platelets (thrombocytes). This tells you whether the cells in the blood are normal, too low, or too high. A subtype of fever of unclear origin is so-called neutropenic fever, which can be triggered, for example, by certain drugs. This is a decrease in neutrophil granulocytes, which are white blood cells and are important for the immune system. If the neutrophil granulocytes in the blood count are low, fever is often the only symptom. Nevertheless, it is a serious condition, as the immune system is severely weakened by the lack of defense cells and therefore serious infections are favored.
Read more on the subject at: Blood count
Recurrent fever with no symptoms
If the fever occurs repeatedly, it is also referred to as recurrent fever. It is important that recurring fever that cannot be associated with an infection is clarified.
On the one hand, recurrent fever can be triggered by an accumulation of pus (abscess) in the body. Normally, such an accumulation of pus is also noticeable through pain, but, especially if it is located in internal organs, it cannot cause any further symptoms at first.
In addition, Still's disease, a special form of rheumatoid arthritis, is a possible cause of recurring fever. Other symptoms that accompany the fever are also possible here. However, the disease can initially only manifest itself as a fever.
Hodgkin's disease, which is a malignant tumor of the lymphatic system, can also be associated with recurring fever attacks over weeks to months.
Inherited familial Mediterranean fever can cause relapses of fever that can last up to three days. It is often associated with abdominal pain, but it can occur without it. The first fever usually occurs before the age of 20.
Read more on the topic: Familial Mediterranean fever
How long does the fever last?
An exact duration cannot be given for fever without symptoms. In any case, the cause should be found. The fever usually sets in with treatment. In any case, it is important to clarify persistent or recurring fever without symptoms, but also with symptoms.
Also read the article on the topic:
- How do I know if my fever is contagious?
- When should I see a doctor with a fever?