Frey syndrome
definition
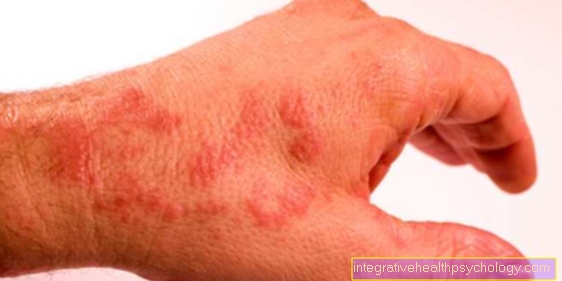
Frey syndrome is also called gustatory sweating, gustatory hyperhidrosis or auriculotemporal syndrome. This is an extremely pronounced sweating of the skin in the face and neck area, which is triggered during eating or any other gustatory stimuli.
Triggers can be eating any kind of food, but also sucking candy, tasting, chewing or biting. This disease owes its name to the Polish doctor Lucja Frey-Gottesman, who described the syndrome in 1923. However, there have been earlier descriptions of "taste sweating".

Causes of Frey's Syndrome
Frey syndrome is caused by a misdirection in the nervous system. It is a damage to vegetative, parasympathetic nerve fibers and the wrong docking of sympathetic fibers to the sweat glands. A nerve branch, the chorda tympani of the facial nerve, which is used for saliva secretion, is misdirected. This faulty nerve contact can be the result of trauma or surgery, for example.
Surgical removal of (parts of) the salivary glands, peripheral facial nerve palsy or inflammation of the salivary glands such as the parotid gland or the mandibular salivary gland can cause Frey's syndrome.
It is assumed that parasympathetic nerve fibers that supply the sweat glands in healthy individuals are damaged during the operation or trauma. After this trauma or surgery, nerve fibers re-form in the area. This incorrectly leads to the docking of sympathetic nerve fibers with the sweat glands, so that they are stimulated by all gustatory stimuli. You sweat profusely with any form of eating, chewing or tasting.
There are also cases described in which Frey syndrome shows up after birth. In most cases, the cause was assessed as birth trauma.
Read more on this topic at: Facial palsy
Accompanying symptoms in Frey syndrome
Frey syndrome is characterized by profuse sweating in the face and neck area when eating food and any other gustatory stimuli such as tasting, chewing, biting and sucking candy. This gustatory sweating is accompanied by pronounced reddening of the skin.
The symptoms are perceived by those affected as extremely unpleasant and often severely limit them in social life.
You might also be interested in this topic: Excessive Sweating- What is the Cause?
Diagnosis of Frey Syndrome
The diagnosis of Frey syndrome is based on clinical symptoms.
The Minor iodine starch test is also available as a diagnostic tool, which makes sweating areas of the skin visible. This test colors the skin regions where excessive sweat is produced and makes them treatable, for example with botulinum toxin.
Duration of Frey Syndrome
If left untreated, Frey syndrome persists.
The treatment options botox and scopolamine ointment work without problems in most cases and achieve good results. Nonetheless, therapy is necessary for life. For example, a scopalamin ointment must be applied regularly. The injection of the neurotoxin botox must also be repeated, approximately every 1½ years.
You may also be interested in this topic: This will prevent you from sweating excessively
Therapy of Frey Syndrome
Frey syndrome can be treated well. The therapy of choice is botulinum toxin (Botox).
The affected areas in the face and neck can be made visible in color with the Minor iodine starch test and botox injected accordingly. This is usually an effective treatment for sweating. Further therapy options are an aluminum chloride solution that is applied locally and an ointment with scopolamine. There is also the option of surgical removal of the tympanic nerve.
Also read: Therapy for excessive sweating
Botox®
Botulinum toxin, or botox for short®, is a toxic metabolic product of the bacterium Clostridium botulinum.
It inhibits the release of acetylcholine, a substance that plays an important role in the nervous system. This effect enables botox® can be used for excessive sweating. When you get botox® Splashes locally under the skin, reducing sweating. In Frey syndrome, the injection is with botox® the means of choice.
More on this: Side effects of Botox®
Scopolamine
Scopolamine is an alkaloid that occurs naturally in nightshade plants such as the thorn apple, henbane or mandrake.
In the form of an ointment, it is supposed to suppress sweating by gustatory stimuli in Frey's syndrome. The scopolamine ointment is applied to the corresponding skin areas on the face and neck.
Also read our article: Botox® cream