Stop nosebleeds
introduction

Nosebleeds often look worse than it is. When stopping the nosebleed, many sufferers decide to put their head back. However, this is an absolutely wrong measure. The bleeding will increase and blood may run down the throat. There is a high risk of it being swallowed and getting into the stomach, which can lead to nausea and vomiting. Another danger related to this wrong measure is in unconscious patients, because this is where the blood can get into the airways.
Instead, as a first measure, you should tilt your head slightly forward and let it hang loosely. This will lower your blood pressure. To stop the nosebleed quickly, you should compress the nostrils directly below the nasal bone with your fingers, because the source of bleeding in a nosebleed is usually in the area of the tip of the nose. After five to ten minutes you can try to gradually reduce the pressure and watch whether blood is still coming out of your nose.
The so-called ice tie also often provides relief. To do this, you put a cooling pad or a wet, cold cloth on the neck. An alternative position for cooling is the forehead. The cool pack or the ice cubes should always be wrapped in a cloth to prevent freezing of the skin. This method causes the nasal vessels to contract in a reflex and the bleeding is stopped.
If you notice the nosebleed, it is important to remain calm. If this does not happen, the blood pressure rises even further and the bleeding is intensified. If these methods do not work and the nosebleed cannot be stopped within approx. 15 to 20 minutes, an ear, nose and throat specialist should be consulted. If the bleeding occurs from both nostrils, a doctor must also be consulted.
Home remedies
An old home remedy is Cellulose- or Blotting paper under the tongue to lay. A quarter of a handkerchief, for example, is well suited for this. Sucking a lemon wedge is also believed to help some people. This method is often used by athletes.
The dry fabric insert under the tongue is perceived by the body as foreign and then it tries to repel the foreign body, whereby more saliva is produced in order to salivate the foreign body. Besides the increased saliva production there is increased blood flow to the area under the tongue, which in consequence Less blood supply to the nose and the nosebleed stops faster. However, the effectiveness of this method has not been scientifically proven.
Cotton wool
As an alternative to compressing the nostrils, a cotton swab is often pushed into the front part of the nose. The cotton swab can then stop the bleeding from within. It should be able to be removed after about ten minutes. To protect the mucous membrane, the cotton swab is greased with skin cream. Cotton swabs can stick to the mucous membrane if they are not removed early enough. There is a risk of the wound tearing open again if the cotton swab is removed. Compression of the nostrils is therefore the better alternative. For this reason, many doctors advise against using the cotton wool method.
But there is also so-called "hemostatic cotton wool", which has blood-clotting properties and is recommended for nosebleeds.
Tamponade

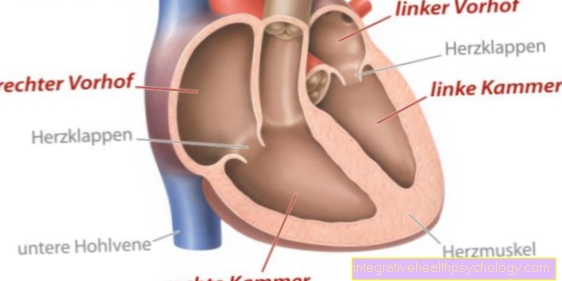
If the nosebleed cannot be stopped by conventional means, an ENT specialist can provide a Nasal packing be performed. One differentiates between one front and one rear Tamponade, which is also called Belocq tamponade A tamponade is a Cotton swab.
A anterior tamponade is mostly carried out when the bleeding is through the so-called Locus Kiesselbachii comes about. This is a Vascular plexus, which is located on the Tip of the nose is located. A compress is usually used for the tamponade, which is pushed into the main nasal cavity. The tamponades should always on both sides can be made so by the other side Back pressure can be exercised. After two to three days, the front nasal packing is removed.In retrospect, the mucous membrane of the nose should be well cared for.
The posterior nasal packing, on the other hand, is made from the posterior nasopharynx if there is heavy nasal bleeding if it is from Sphenopalatine artery bleeds. This bleeding is more severe than bleeding from the front part of the nose, because the vessels in the nasopharynx are not as finely branched and therefore have a larger diameter. This bleeding cannot be stopped by an anterior nasal packing. The Belocq tamponade is usually performed under local anesthesia, sometimes also under general anesthesia. For the tamponade, a catheter is pushed through the nose into the throat and then pulled out of the mouth with forceps. A thread is attached to the catheter, which is connected to a foam tampon at the other end. Then pull the catheter out over the nose so that the tampon gets into the nasopharynx and there the rear nostril (Choans) can close. Then you fix the thread on the nose. At the same time, a front tamponade is carried out so that the cavity of the nose is closed from the front and back and the bleeding is definitely stopped. The rear tamponade usually remains for a period of two days. Due to the risk of infection with the posterior tamponade, an antibiotic is administered prophylactically.
Vascular obliteration
Anyone who constantly suffers from nosebleeds and feels that their quality of life is burdened by this can lead to future bleeding from the nose through a Obliteration of the vessels in the tip of the nose by means of a Laser treatment, prevent. Sclerotherapy also takes place if the nosebleed does not stop by itself.
Sclerotherapy is usually carried out if the ENT doctor has an Vascular abnormality found in the nose, which is a common nosebleed. This abnormal vessel is then obliterated using a laser.
In addition to the laser method, you can also desolating chemicalssuch as trichloroacetic acid or silver nitrate to burn the vessel.
Another method is the Electrocoagulation in which the vessels are closed by burning. This is also routinely used in operations to stop bleeding from small vessels.
Sclerotherapy only takes place if the source of the bleeding is localized, otherwise a tamponade is performed.
If both methods fail, the vessel can be clamped off with a clip as a last resort. This variant is usually carried out by radiologists.
Medication
If the nosebleed cannot be stopped with the methods listed above, drugs are used. For this mostly vasoconstricting nasal drops, how Xylometazoline, used.
A bleeding disorder is rarely responsible for frequent and heavy nosebleeds. High blood pressure can also cause frequent nosebleeds. Both causes should be treated with medication so that the result does not lead to increased nosebleeds.
Medicines themselves can also cause nosebleeds. These include above all those who Inhibit blood clotting and Blood clots should prevent. For example decrease ASS (Aspirin), ibuprofen, clopidogrel, as well as some Antibiotics and Psychotropic drugs the number of platelets in the blood, making bleeding easier.
prophylaxis
Too dry a nasal mucosa increases the likelihood that blood vessels will burst. It is therefore advisable to keep the mucous membrane constantly moist. The easiest way to moisten the nasal mucous membrane is a saline nasal spray. Alternatively, mineral ointment or petroleum jelly can be applied to the mucous membrane of the nose with a cotton swab in the evening.
Frequent ventilation in the apartment also prevents the mucous membranes from being dried out by the heating air, which is dry, especially in winter.
Violent drilling in the nose and strong blowing of the nose should be avoided 1-2 days after the nosebleed, otherwise the wound may tear open again.
There are many different homeopathic remedies that can successfully eliminate nosebleeds. Read more about this topic under: Homeopathy for nosebleeds
Stopping nosebleeds in children
Especially in children, nosebleeds are often caused by scuffling, blowing their nose or constantly picking their nose. Nosebleeds often occur in children as a result of growth spurts. As a parent, it is important to exude calm so that the child does not get further upset. In children, the same measures to stop bleeding apply as in adults. Most important is that slightly bent posture, the Compressing the ala and the Cooling in the neck.
The child should be told that the Should inhale and exhale. After the nosebleed, you should make sure that the child does not pick their nose or blow their nose heavily, as otherwise the wound may tear. Children also often experience nosebleeds from objects sticking deep in their noses. These items should be removed by the ENT doctor, who has special equipment for this.
In children, should more quickly than in adults, if the nosebleed does not stop, the doctor should be consulted, because otherwise there is a risk of excessive blood loss, which is more difficult to tolerate in children. You should go to the ENT doctor after ten to fifteen minutes at the latest.