Pantozol®
Active ingredient
Pantoprazole, usually in the salt form pantoprazole sodium
Explanation / definition
Pantozol® belongs to the group of proton pump inhibitors and reduces the formation of gastric acid. It is used to treat diseases in which increased gastric acid production irritates the sensitive or already damaged mucous membrane of the esophagus (esophagus), stomach (gaster) and duodenum (duodenum).
Dosage forms
Pantozol® is in 20mg and 40mg Dosages available. Usually it comes in the form of enteric coated Tablets ingested. However, it can also be used as 40mg Dry matter to produce a infusion ('Drip') directly into the vein can be acquired. Pantozol® is one of the prescription Medication.
Mode of action
The Parietal cells (Parietal cells) of the stomach produce about 2 liters Gastric juice. The contained therein hydrochloric acid (HCl) splits what is ingested with food protein, kills bacteria and prepares further steps of digestion.
In simple terms, one can imagine that the stomach acid is caused by a pump will be produced. This pump sits in the parietal cells of the gastric mucosa and pumps, e.g. stimulated by digestive hormones, hydrochloric acid in the stomach opening.
The active ingredient pantoprazole binds irreversible (irreversible) to the Proton pumps and thus blocks hydrochloric acid production by up to 90%. Only when the body new Once the proton pumps have been established, gastric juice can be secreted normally again. Not all proton pumps are blocked with a single dose!
With daily intake of Pantozol® the maximum effect is achieved 2-3 days reached.
Dosage and application
The dosage and duration of treatment depend on the area of application; the treating doctor decides here, depending on the existing clinical picture. Pantozol® is swallowed whole with some liquid. To achieve optimal effectiveness, the drug should be around half an hour before meals be taken.
Areas of application for Pantozol®
Pantozol® with a potency of 20mg is often used in prevention (Prevention) of clinical pictures. This includes:
- Recurrence (relapse) of a Inflammation of the esophagus, caused by Reflux stomach acid (reflux esophagitis)
- Recurrence of Ulcers in the stomach or duodenum, caused by the increased intake of certain painkillers or rheumatoid drugs
In addition, Pantozol® 20mg to symptomatic, i.e. treatment aimed purely at the complaints. This includes:
Complaints caused by the Reflux (Reflux) caused by stomach acid into the esophagus
Complaints through acid regurgitation caused
Pantozol® with a potency of 40mg on the other hand, is more likely to apply acute Clinical pictures. This includes:
Acute Inflammation of the gullet (esophagitis) caused by reflux of stomach acid
Stomach ulcers and duodenal ulcer (ulcer)
Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome
Infection with the bacterium Helicobacter pylori, if gastric and duodenal ulcers occur. Simultaneous administration of Antibiotics to kill the bacteria and heal the ulcers ('Helicobacter pylori eradication')
Contraindications
Pantozol® must not be taken if a allergy or. Hypersensitivity against pantoprazole or one HIV-Therapy with drugs of the active ingredient atazanavir takes place.
Without express medical advice, Pantozol® must not be used by children 18 years be taken!
Take special care
As with taking many medications, sufferers with one exist Liver disease also an increased risk when taking Pantozol®. Therefore, the doctor should regularly do the Liver values to detect any deterioration in liver function in good time.
If there is already a There is damage, in many cases an intake of a maximum of 20 mg Pantozol® per day is indicated. If there is an ulcer in the stomach or duodenum, a possible malignant one is recommended Tumor disease to be excluded as a cause.
The doctor should also perform tests to determine whether the bacterium may be present Helicobacter pylori present. If this is the case, antibiotics can be started at the same time. A Inflammation of the esophagus should also be clarified by means of a reflection.
The cause of ulcers lies in the increased intake of Painkillers or rheumatism medicines, it must first be checked whether these drugs can be discontinued.
In the case of long-term or preventive therapy with Pantozol®, the doctor must carefully weigh the benefits and risks. Because up to now not all possible risks of long-term treatment with proton pump inhibitors have been clarified.
Risks
A decreased amount of gastric acid in the stomach, such as is produced when taking Pantozol®, elevated the number of bacteria in the stomach. This results in a slightly increased risk for Infections of the gastrointestinal tract, e.g. a Salmonella infection.
If you take Pantozol® for more than 3 months can he Magnesium levels sink in blood. As a result, e.g. dizziness, exhaustion and Muscle spasms occur. There is also an increased tendency to fracture (Fractures) in the area of the hand-and hip joint, as well as the Spine, especially in the case of therapy with Pantozol® for more than 12 months. Patients with known osteoporosis ('Bone loss') should therefore urgently inform your doctor.
'Use during pregnancy and breastfeeding
Due to insufficient experience and information in animal experiments, the attending physician should carefully consider whether treatment with Pantozol® during pregnancy can be beneficial. Taking it while breastfeeding should be viewed equally critically.
Side effects
Usually Pantozol® is a well tolerated Drug. However, some side effects are known.
Kick frequently a headache, diarrhea, constipation, Flatulence and stomach pain on.
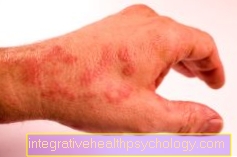
Occasionally, nausea, Vomit, itching, skin rash, Water retention (edema), Vision disorders (Blurred vision) and dizziness reported.
The rare side effects include Dry mouth and Joint pain.
Tread very rarely Inflammation of the liver with liver damage, drop in blood platelets and white blood cells, hives, sensitivity to light, severe skin inflammation (erythema multiforme), Stevens-Johnson syndrome, severe skin damage (toxic epidermal necrolysis), muscle inflammation, kidney inflammation and depression.
Interactions
The simultaneous use of Pantozol® and other, sometimes non-prescription drugs, can lead to undesirable interactions. This includes:
- Increase the effects of phenprocoumon and warfarin (blood thinners)
- Makes atazanavir (an anti-HIV drug) less effective
- Decrease in the effects of ketoconazole and itraconazole (preparations against fungal infections)
- Decreased intake of Vitamin B12- additives
- Reduction of the effect of Pantozol®, with simultaneous use of drugs that Johannis herbs contain