Pubic branch fracture
What is a pubic branch fracture?
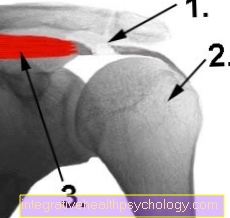
A pubic branch fracture is the breakage of a pubic branch. The pubic branches are large bony processes on the pubic bone (os pubis). There are two branches, the upper pubic branch (Ramus superior ossis pubis) and the lower pubic branch (Ramus inferior ossis pubis).
If one of the two branches is broken, one speaks of an incomplete pubic branch fracture or pelvic ring fracture. If both branches are broken, it is a complete pubic branch fracture or pelvic ring fracture. The pubic branch fracture rarely occurs among the pelvic fractures.

Causes of a pubic branch fracture
Pubic hernias are subordinate to accidental injuries. As with other bone fractures, these usually happen through violent impacts or overload.
Most pubic branch fractures occur during exercise, especially those that require a lot of hip activity, such as skiing. Furthermore, sports that require sitting carry an increased risk of pubic branch fractures.
Traffic accidents are the next most common cause. Motorcyclists and cyclists in particular are at increased risk of this injury. Rarely does it happen that violent sexual intercourse is a cause.
You can find more information on the subject here: Pelvic ring fracture
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
Concomitant symptoms
The most obvious symptom of a fracture is pulling pain in the pelvic area. These can be quite strong and are usually persistent.
The pelvis is connected to both legs and the spine by numerous muscles. This can be very problematic for the patient. With almost every movement, especially when running, when lying down or standing up and when turning the legs or the upper body, these muscles are activated, which means that the muscles exert tension on the pelvis and move the broken bones, which is of course very painful and patients complain of restricted mobility. Even just lying in bed can be painful. Unfortunately, all of this means that the pain is persistent. If the pain is barely pronounced, a break is rather unlikely.
The pain can also radiate to nearby areas of the body, such as the buttocks or lower back. Obvious symptoms can include bruising and swelling. Since there are many nerves in the hip area, it is quite possible that nerves become pinched.
In addition, pelvic organs can be injured, such as the urinary bladder, ureter, intestine and, depending on the gender, the internal genital organs. If the bladder was damaged when it was ruptured, it may cause frequent urination. This can also cause the urine to turn bloody. In men, it is not uncommon for the pain to radiate into the testicles, which is why the patient incorrectly concludes that the testicle is dysfunctional.
You might also be interested in the following article: Pelvic pain
diagnosis
When diagnosing a fracture of the pubic bones, it is very important to ask the patient how the accident happened or how pain was caused. In the so-called anamnesis, the doctor asks the patient questions such as when and where the pain has been occurring and how severe it is, in order to then check the patient for possible causes.
In the case of a pubic branch fracture, the doctor palpates the patient's hip and examines it for external injuries. An imaging method for a detailed examination is essential. Computed tomography (CT) is the most precise way to determine the diagnosis and also shows the severity and extent of the injury. This also allows the therapeutic measures to be planned.
Treatment and therapy - when is it possible to start exercising again?
Treatment is based on the degree of injury.
If there is an incomplete hernia of the pubic bone, no surgery is required, as the hernia usually heals on its own in about 3 months. Relieving the pain is the primary goal here. The doctor usually orders bed rest for a few days and prescribes pain medication. Stabilizing the pelvis is also part of relieving pain.
Then it is important to mobilize the patient, i.e. to encourage movement, in order to prevent blood clots from forming due to lack of movement. Mobilization also counteracts the loss of muscle strength and mobility, which is naturally caused by a lack of movement.
If both pubic branches are broken or bone segments have shifted, surgery is essential. The bone segments are moved back into the correct position and fixed from the outside. The fixation is carried out by so-called fixators. These are plates or rails that are attached to the hip from the outside like a scaffold and keep it stable. Most often, a complicated branch fracture results in profuse bleeding. Treatment also includes stopping the bleeding or removing large bruises as soon as possible. It depends largely on the patient's condition and the extent of the injury when one can put more weight on the hip again, which is why there is no general answer to this question.
The patient can orient himself according to the intensity of the pain. If the pain occurs even with low stress, you should continue to take it easy. When in doubt, it is always advisable to consult an orthopedic surgeon, as he can best assess the course of the disease and healing.
Pubic branch fracture complications
Unfortunately, a pubic branch fracture can cause some uncomfortable complications. One of them is massive bleeding from torn veins.
Injured soft tissues and organs such as the urinary bladder or internal genital organs can delay the healing process and, under certain circumstances, result in permanent functional and movement restrictions. Impotence could be given here as an example.
It can also happen that nerves are damaged when they break and that sensitivity and movement disorders occur in the hip region and on the legs.
Duration of healing
It usually takes about 6-8 weeks for the fracture to heal enough that you can move around again without pain. Complete healing takes about 12 weeks. Protecting or supporting the pelvis with an orthosis can accelerate the healing process. In the case of complicated fractures or displaced fracture segments, healing is delayed and can also lead to permanent bad posture in the pelvis.
















.jpg)

.jpg)
