Pain bile
synonym
Atresia of the bile ducts, English: biliary atresia, BA
Classification according to ICD-10? Q44.2
Biliary atresia

General
The biliary atresia is a congenital malformation of the biliary tract.
These are locked (Closure = atresia ).
The disease is only found in newborns and is a common indication for liver transplantation in infancy.
causes
As with many human diseases, the etiology of biliary atresia is not fully understood.
However, there are genetic and inflammatory-infectious components that are very likely to lead to such obstruction of the biliary tract.
There is most likely a connection between this malformation and a viral infection during pregnancy with the Epstein-Barr, cytomegaly, respiratory syncitial and human papilloma viruses.
Furthermore, there are genetic abnormalities in the affected children. If you look at the bile ducts from a tissue perspective, you can see sclerosis ( Laying with connective tissue ) as well as inflammatory changes.
Occurrence
Girls are more likely to have biliary atresia than boys.
The disease has a prevalence of 1 in 20,000 and accumulates in Asia and the Pacific.
One differentiates between a syndromic and a nonsyndromic form.
In the nonsyndromic form of the disease, only the biliary tract is blocked, whereas the syndomal form with other malformations such as Is associated with heart defects.
Symptoms
Newborns with biliary atresia have a prolonged jaundice (in contrast to physiological neonatal icterus), discoloration of the stool (Acholic chair) and the urine turns brown.
In addition, the liver may be enlarged, which is known as hepatomegaly.
The general condition of the children then deteriorates over time, so that weight loss can be observed.
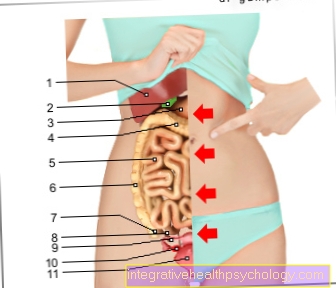
There is an enlargement of the spleen, which can be extremely painful, and ascites in the abdomen.
Digestive disorders and thus pain in the intestinal area can result from the lack of bile acids.
There is also an increased tendency to bleed, as vitamin K absorption is disturbed due to the lack of bile acids.
diagnosis
During an ultrasound examination, anatomical abnormalities such as a reduced gallbladder or deformities in the liver can be seen.
If the findings are uncertain, cholangiography is the best option, in which the bile ducts are visualized using a contrast medium.
There is also the option of doing a liver biopsy.
Read more on the topic: Ultrasound of the abdomen
treatment
Biliary atresia requires treatment in any case, since untreated cirrhosis of the liver develops, which leads to early death.
The infants are usually treated surgically. A liver transplant is usually necessary up to the age of two.
Cholestatic jaundice
General
The bile is a body fluid made by the liver, which is stored in the gallbladder and used for digestion in the duodenum (Duodenum) is delivered.
Disturbances in the outflow of bile can cause jaundice.
Jaundice is generally a yellow coloration of various body surfaces, hence also popularly "Jaundice" called.
root cause
Cholestatic jaundice has a posthepatic cause, i.e. the outflow of bile from the liver into the duodenum through the common bile duct (Bile duct) is disturbed.
Tumors or gallstones can be responsible for this occlusion of the common bile duct. A rather rare cause is congenital biliary atresia.
Read more on the topic: Ultrasound of the abdomen
Symptoms
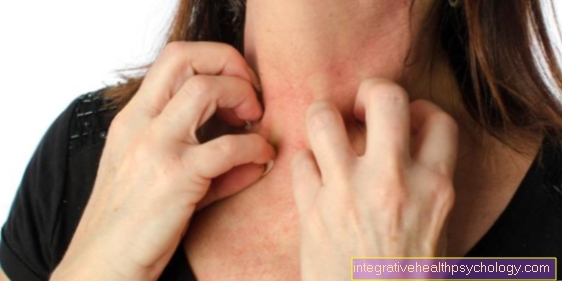
In addition to yellowing of the skin and mucous membranes, severe pain can occur, which manifests itself in the form of biliary colic.
Tumor changes can be painful, but are usually painless in the early stages.
Therefore, especially in the case of painless jaundice, it should be clarified whether the whole thing is based on a malignant change.
Such tumors can originate from the gallbladder, bile ducts, duodenum (Duodenum) or the pancreas go out.
treatment
Treatment depends on the cause of the jaundice.
If the jaundice is caused by gallstones, endoscopic procedures to remove them may be considered.
Under certain circumstances, however, surgical removal of the gallbladder may be necessary. The therapy cannot be generalized and varies from case to case, which is why jaundice should always be clarified by a doctor immediately.
Read more about gallbladder removal here.
Prevention
To prevent post-hepatic jaundice, it is advisable to eat a low-fat, high-fiber diet. This prevents the formation of gallstones.
Cholestasis
General
The term cholestasis describes biliary obstruction.
It is one Backwater various bile components, such as Billiruby and Bile acids, or an impaired flow of bile into the intestines.
A distinction is also made between extrahepatic and intrahepatic cholestasis.
causes
The cause of an extrahepatic cholestasis is a mechanical obstruction of the bile drainage, for example by Tumors or Gallstones.
Intrahepatic cholestasis can be one, for example Viral infection or underlying toxins. Symptoms
The leading symptom of cholestasis is that Jaundicewhich is caused by the lack of drainage of the bile.
Furthermore, a cholestasis manifests itself in nausea, Vomit, fatigue and Loss of appetite.
The stool may be discolored. Colic pain can also occur if the cholestasis is based on gallstones. treatment
so. (Jaundice)
Cholangitis
There are three types of cholangitis.
It is the acute purulent Cholangitis that non-purulent destructive Cholangitis (primary biliary cirrhosis) and the chronic sclerosing Cholangitis. With severe purulent cholangitis you can also Shock, Kidney dysfunction and disorders of the central nervous system occur.
The primary biliary cirrhosis is characterized by itching, jaundice and Hypercholesterolemia out.
The following topic may also be of interest to you: Primary sclerosing cholangitis