Pain in the hand
Causes and forms of hand pain
There are multiple causes of hand pain. They range from serious traumatic causes to more harmless minor trauma to chronic causes that can trigger long-lasting symptoms.
Find out more about: Pain

Acute causes
The most common acute causes of hand pain include fractures of the hand bones (both wrist and carpal bones). Fractures of the hands are mostly caused by trauma. The most common trauma that causes fractures in the hands is fall. When falling, those affected usually try to catch themselves with their hands at the last second. This often leads to non-physiological movements in the wrist or finger joints when it occurs.
Often the hand is twisted backwards, which can lead to forearm fractures. But carpal bones can also be affected in this case. Finger bones are most often fractured when the fingers are entrapped. As a rule, it is jamming on car doors or the like.
In the case of trauma of whatever kind, in which the hand or fingers are involved, the cause is clear, but the damage that has arisen only becomes clear in a closer diagnosis.
After the actual fall, fractures usually lead to severe and unreliable pain. This pain can be provoked by movement in the hand and is intensified. Furthermore, there is swelling in the area of the fracture.
A so-called fatigue fracture in the bones of the hand can also lead to pain. As a rule, no trauma, such as a fall, can be remembered or even the smallest injuries are sufficient to cause a fracture of the hand or the hand bones. As a rule, fatigue fractures always occur when bad posture causes particular stress on the bones and muscles. Patients suffering from overt osteoporosis are also affected.
Read more on the subject at: Broken wrist
Furthermore, after a trauma, the capsule may tear or tear, as well as stretched and torn ligaments, which can lead to severe pain.
Read more on the subject at: Torn ligament on the wrist and ligament injuries on the wrist and pain in the right arm
Appointment with a hand specialist?
I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You can find me at:
- - orthopedics
14
Directly to the online appointment arrangement
Unfortunately, appointments can only be made with private health insurers. I ask for understanding!
Further information about myself can be found at -
Chronic causes of hand pain
- the most common cause of pain in the hand and wrists is osteoarthritis and arthritic changes.
Mention should be made here of the so-called rhizarthrosis, which is the most common form of arthritis in the hand. This form of osteoarthritis affects the thumb saddle joint, which causes severe to very severe pain when moving.
In rhizarthrosis, a distinction is made between an acute traumatic form and a chronic form, which is a late stage of polyarthritis of the hands. - In addition to rhizarthrosis, wrist deformations can also cause pain at rest or during exercise. The most common cause of joint deformities is rheumatoid arthritis.
- Another cause of pain in the hand can also be tendonitis, which is caused by overuse of the fingers when moving.
- In addition to diseases of the bones, ligaments, capsules and tendon sheaths, pain can also be caused by irritation of the blood vessels or nerves in the hand and wrist. In the so-called carpal tunnel syndrome, there is a narrowing of the nerves running on the palm side (so-called median nerve). In addition to pain, especially at night, there is paresthesia in the form of tingling sensations.
- In rare cases, skin disorders on the hand can also cause pain.
Diagnosis of pain in / on the hand

When choosing the diagnostic means, the most important thing is what exactly is causing the pain in the hand.
Used by the patient Accident or trauma reports, represents the diagnosis of choice X-ray of the hand represent that one Exclude fracture should. Also chronic changes and all Types of osteoarthritis can be determined by an X-ray.
Is there a suspicion that a Ligament or capsule involvement caused the pain in the hand, should a Magnetic resonance imaging of the hand that can show the soft tissues of the hand well. If a carpal tunnel syndrome is suspected, a Measurement of the nerve conduction velocity Provide an indication of whether the nerves are affected by a carpal tunnel that is too narrow.
In addition to the diagnostic means, the Medical interview (anamnesis) and physical examination not be waived.
Where is your pain?
Pain in the thumb
The thumb takes on a special function when grasping, as it has greater mobility compared to the other fingers. Pain in the thumb can appear very differently. For example
- a punctual pain in the joint
- a pulling pain that may radiate into the arm
- a painful swelling with noticeable tenderness
occur.
Often the mobility of the thumb is restricted by the pain and it is difficult to grasp.
Pain in the thumb can result from sprains, broken bones (Fractures) or torn ligaments. For example, the Bennett fracture (Fracture of the base of the first metacarpal bone) often to severe, pulling pains up to the thumb saddle joint. Also the so-called "Ski thumb", a tear in the collateral ligament of the thumb, can lead to severe pain and swelling in the area of the thumb.
Joint wear and tear, such as osteoarthritis of the thumb saddle joint (Rhizarthrosis), lead to thumb pain. In some cases, thumb pain is also caused by acute joint inflammation (e.g. reactive arthritis).
In the course of a gout disease, uric acid crystals can build up in the joints. An acute gout attack can also show up as a reddened and swollen thumb joint.
A common cause of thumb pain is the so-called Quervain Disease (Tendovaginitis stenosans de Quervain). This term describes a special form of tendinitis in the area of the muscles of the thumb that is triggered by excessive strain.
Depending on the cause of the thumb pain, very different treatment options can be considered. In the event of fractures or torn ligaments, the thumb is immobilized in a splint and then treated with physiotherapy. Rhizarthrosis often requires immobilization first so that the inflammatory process in the joint can subside. An operation with correction or replacement of the joint is also possible.
Read more on the topic: Pain in the thumb, pain between the thumb and forefinger, sprain on the thumb
Pain in the finger
Finger pain can have many different causes. Very often finger pain is caused by a inflammatory or degenerative (wear-related) illness again rheumatoid arthritis or the arthrosis caused. But also Strains, Bruises, Broken bones (Fractures) and other diseases (e.g. Dupuytrenin's disease) are possible.
The pain in the fingers often leads to one Restriction of movement, this is usually increased after certain loads such as stretching, bending or after carrying heavy loads. Since our hands are very important for almost every activity in everyday and professional life, there should be pain in the fingers medically clarified in good time in order to avoid health risks. Sometimes a finger disease (e.g. rheumatic diseases) to incapacity for work lead, which is why timely treatment is all the more important.
The four finger (the thumb is described separately) are part of the hand and are formed by a skeleton of three bones, which are supported by the Finger joints are connected to each other.Sprains, strains or a broken finger usually go along with pain Swelling such as Bruising hand in hand. Also Nerve damage (e.g. as a result of a Sugar disease) or benign soft tissue tumors (Ganglion, "over leg") can lead to pain and restricted mobility in the area of the fingers.
see also: Finger joint pain
Little finger pain
A typical sign for a so-called Ulnar sulcus syndrome or Ellenrinnen Syndrome are tingling and nocturnal pain in the little finger and ring finger. The elbow nerve runs at the level of the elbow joint in a narrow bony canal (so-called "musician's bones"). In ulnar sulcus syndrome, the pain in the little finger can also be provoked by tapping this bone canal. If the nerve is constricted for a longer period of time, the internal muscles of the hand may even shrink, which is manifested in weakness in the spreading or spreading of the fingers. As a rule, the nerve at the elbow has to be surgically exposed and relocated out of the bone canal.
The little finger (as well as the ring finger) can also be from the so-called Dupuytren's contracture to be affected. Dupuytren's disease is the name of a benign, scarring disease of the connective tissue (Fibromatosis) the palm and fingers. There is a change in the connective tissue of the hand, as a result of which more nodules and strands form on the fingers and in the palm of the hand. These nodules can put pressure on nerves and cause severe pain. In the course of the disease, there is often such hardening of the connective tissue that the affected fingers (usually the little fingers and ring fingers) can no longer be actively stretched, resulting in a flexion contracture (fingers remain flexed). The exact cause of Dupuytren's contracture has not yet been fully clarified, but the disease occurs more frequently in men over the age of 50.
Read more about this under: Pain in the little finger
Pain in the finger joints

The most common cause of pain in the finger joints are degenerative processes or signs of wear and tear in the finger joints. This is a finger joint arthrosis, in which the cartilage layer of the joint gradually wears away. In most cases, osteoarthritis occurs in the end joints of the fingers (Herbenden osteoarthritis), less often in the middle joints of the fingers (Bouchard's arthrosis). At the beginning of osteoarthritis of the finger joints, there are often no symptoms, which is why the disease remains undetected for a long time. Later there is severe pain in the finger joints, combined with swelling, stiff joints and difficulties with fine motor movements (e.g. unscrewing a bottle).
Also read the article on the topic: Pain in the ring finger
Another common cause of sore finger joints is chronic inflammation of the joints (arthritis). Such an inflammation can be caused, for example, by infections with bacteria, by metabolic diseases such as gout or also by chronic inflammatory bowel diseases, psoriasis or ankylosing spondylitis.
In most cases, however, it is rheumatoid arthritis ("inflammatory rheumatism"). Rheumatoid arthritis occurs about twice as often in women as in men and can take very different courses. Rheumatism can begin slowly and initially only affect the little fingers and wrists, it can also occur suddenly and only affect one or a few joints. Typically, rheumatoid arthritis (caused by the inflammation) results in severe finger pain, morning stiffness of the joints, and the joints can swell and be reddened. A general feeling of illness with tiredness, fever, exhaustion and increased sweating can also occur. Rheumatoid arthritis is easily treatable if diagnosed early. The course of the disease varies widely, but chronic joint inflammation often occurs, which can lead to disability and disability, as the joints are progressively destroyed. Rheumatoid arthritis can also affect the heart, lungs, or eyes and cause chronic inflammation. This can lead to various diseases such as pulmonary fibrosis or pericarditis. In addition, people who are affected by rheumatism have an increased risk of other diseases such as hardening of the arteries, osteoporosis, heart attacks or strokes.
Are you more interested in this topic? Read more about this under: Pain in the interphalangeal joints
Back hand pain
In the case of pain in the back of the hand in the area of the wrist, this can have various causes.
There may be tendinitis in the area of the back of the hand or a so-called neuralgia. This is pain in the area where a nerve is supplied, which can be caused by excessive irritation or inflammation. In addition to pain, numbness or tingling can occur here.
Read more on the topic: Back hand pain and metacarpal boil pain
Pain in the navicular bone
Of all the carpal bones, the scaphoid bone is the one most affected by problems.
In addition to the scaphoid fracture, there are scaphoid dislocations (scapholunar dissociation), arthrosis in the wrist and many other causes that can cause pain in the scaphoid bone.
Read all the information on this topic on the page: Pain in the navicular bone
When does your hand pain occur?
Pain in hand when propping up
Pain, mainly caused by the Prop up on the wrist can have various causes.
Cause tendonitis
On the one hand there is a Tendinitis (Tendovaginitis) in question. Tendons connect muscles with bones and run in places where there is a lot of stress and friction. Tendons are protected by a cover (Tendon sheath), in which there is synovial fluid. If there is an overload of monotonous repetitive activities such as Computer work or excessive use of the cell phone, the tendon sheath can become inflamed. For therapy, it is recommended to immobilize the arm using a rail or even one Plaster of paris, as well as omitting the stressful activity.
Cold therapy and, in the case of a chronic course, heat therapy also provide relief. It makes sense to strengthen the muscles in the wrist to prevent relapses.
Cause wrist osteoarthritis
Another cause of pain when propping up can be a Osteoarthritis in the wrist be. Osteoarthritis is a disease that causes wear and tear of the dampening cartilage in the joint area. In the X-ray you can see cartilage atrophy, as well as calcium deposits and later bone deposits.
The pain occurs mainly when exercising, as with Prop up, at the Unscrewing bottles or Carrying heavy purchases. Occupational therapy in particular offers conservative therapy options, for example by adapting an individual splint.
Before an operation in the sense of a partial stiffening comes into question, a minimally invasive procedure as part of a joint cleaning or the severing of pain-causing nerve fibers can be tackled.
Cause carpal tunnel syndrome
That too Carpal tunnel syndrome can cause pain when propping up. In carpal tunnel syndrome, the Median nerve narrowed in its course by the carpal tunnel. This leads to tingling sensations and numbness in its supplying regions at night, as well as pain. The pain occurs particularly with extreme flexion and extension of the wrist (Support your hand), as this increases the pressure in the carpal tunnel. To therapy can be a sedative rail as well as the administration of anti-inflammatory drugs.
If this does not show any noticeable improvement, the ligament structure that limits the carpal tunnel at the top can be split by the surgeon so that the structures running in the carpal tunnel are given more space.
Cause scaphoid pseudoarthrosis
Scaphoid bone pseudoarthrosis can also cause pain when propping up the wrist. A Pseudarthrosis arises from inadequate fracture healing.
The scaphoid bone is a carpal bone related to the wrist. A scaphoid spinal osteoarthritis develops after one Scaphoid fractureif the fracture has not healed properly and scar tissue has formed between the fragments.
The fracture gap remains, creating an unstable situation that leads to the tilting of the joint surfaces with subsequent destruction of the articular cartilage (arthrosis). Ultimately, this leads to permanent damage to the navicular bone and pronounced osteoarthritis in the wrist, which can cause pain when propping up, among other things. To avoid this, scaphoid arthrosis should always be surgically stabilized. (Even if there are little or no symptoms) The aim of the operation is to reunite the two fragments and thus restore the navicular bone.
To do this, a bone chip, usually from the iliac crest, must be removed and inserted between the two fragments
Also a ganglion (Over leg) can lead to pain when propping up the hand.,
Pain when grasping
For Pain when grasping there are also several possible causes. On the one hand, this can also be done by a Tendinitis be provoked, as the muscles or tendons of the finger flexors run through the tendon sheaths.
Carpal tunnel syndrome can also cause pain when grasping, as the Median nervewhich runs through the carpal tunnel and is narrowed and irritated there as part of the syndrome, supplies the muscles that are responsible for flexing the fingers. In addition to tendonitis and carpal tunnel syndrome, one is also common Arthrosis in the thumb saddle joint (Rhizarthrosis) responsible for pain when grasping.
Rhizarthrosis mainly affects women over 50. Osteoarthritis can result from mechanical overload or it can also be provoked by hormonal changes.
Splinting, physiotherapy, analgesic and anti-inflammatory drugs are used therapeutically. Only if these measures do not improve the situation can an operation be considered.
therapy
The therapy depends on the type of illness and the cause.
In the case of a fracture, either a surgical intervention with screw connections etc. become necessary or it is sufficient to have one conservative therapy perform. Conservative therapy consists of Immobilization, cooling, and drug pain management.
In the case of osteoarthritis, this type of occurs almost exclusively conservative therapy for use. Immobilization should not be carried out, however, as joints that are held still for longer can stiffen. Cooling and pain therapy are among the most important therapeutic measures. B.
The main form of therapy for carpal tunnel syndrome is the operative splitting of the ligament over the carpal tunnel to take the pressure off the underlying nerves.
prevention
One can also fracture through fall preventive measures rather not prevent it. Especially with pathological fractures, such as fractures triggered by osteoporotic changes, there are only a few preventive measures. Arthrosis in the hand and wrist cannot usually be stopped or prevented. The situation is different with osteoarthritis caused by rheumatoid arthritis. The earlier and the more successfully rheumatoid arthritis is treated, the lower the risk of osteoarthritis in the wrist. There are numerous risk factors for carpal tunnel syndromes. This can only influence obesity and thus reduce the occurrence of carpal tunnel syndrome.
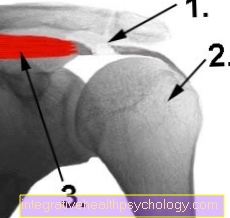
Illustration wrist pain

A - Chronic causes
B - Acute causes
- Rheumatoid Arthritis (RA) -
inflammatory disease
the joints - Arthrosis -
Joint wear - Carpal Tunnel Syndrome (KTS) -
constriction of the median nerve - Ganglion (upper leg) -
benign tumor formation - Torn ligament -
Rupture of a joint ligament - Finger dislocation -
Dislocated finger - Broken finger (finger fracture) -
a - distal
b - medial
c - promaximal - Wrist hernias
(here scaphoid fracture)
I - I - metacarpal joint -
Articulatio metacarpophalangea
II - II - Carpal-metacarpal joints -
Articulationes carpometacarpales
III - III - Lower wrist -
(distal)
Articulatio mediocarpalis
IV - IV - Upper wrist -
(proximal)
Articulatio radiocarpalis
You can find an overview of all Dr-Gumpert images at: medical illustrations
Summary
Pain in hand can different causes to have.
There must be between acute and chronic events can be distinguished.
In most cases, acute causes are Fractures after accidents. Chronic causes are mostly degenerative changes due to poor posture or age-related changes.
Besides the bones that lead to the pain in the hand, you can also Nerve damage or impaired vessels to blame for hand pain. The so-called Carpal tunnel syndrome the nerve tracts supplying the hand are constricted due to a constriction at the transition between the forearm and the palm side. Besides the pain in the hand you can also Functional impairments come to light.
The diagnostic means are chosen according to the suspected cause of the pain. So would a X-ray of the hand especially showing fractures in the hand. A Magnetic resonance imaging could show swelling of the muscle but also changes in the ligamentous apparatus or injuries to the capsules of the hand.
Therapeutically, one has either the option to treat conservatively or operational. Conservative measures include Cooling and immobilization of the hand, but also physical measures which should help to minimize inflammation and pain are used. Fractures can be operated on and stabilized using wires and screws. The carpal tunnel syndrome can also be treated surgically by cutting the ligament that leads over this anatomical constriction and relieving the pressure of the nerves supplying the hand. Chronic causes that lead to pain in the hand (e.g. arthrosis) are usually treated conservatively.
















.jpg)

.jpg)
