Causes of Rheumatoid Arthritis
definition
In the rheumatoid arthritis is it a chronic inflammatory systemic disease. Rheumatoid arthritis is typical for the majority of joints and inflammation of the joints at least five different joints triggers in the body. This clinical picture is called "Polyarthritis“.

The inflammation runs in recurring attacks and the Destruction in the joint is constantly progressing. According to the current state of research, the destruction of the joint cannot and can not be reversed only slow down therapeutically.
Also read our topic: Therapy of rheumatoid arthritis
Pathogenesis of Rheumatoid Arthritis
The exact origin of rheumatoid arthritis is not fully understood. However, the idea that the cartilage of the joint is attacked by inflammatory processes has largely been refuted. Triggering factors are among others that gender, one genetic predisposition but also external influences, such as psychological factors and suffered illnesses.
Typical cells of rheumatoid arthritis are the Fibroblasts (Cells of connective tissue) that immigrate to healthy jointswhich allows the inflammation to spread anywhere. Recent research results from the assumption that the cartilage breakdown in the joint does not affect the acute alone Inflammation in the joint and the release of regulating proteins, so-called Cytokines, can lead back. Rather, it is assumed that large groups of cells in the cartilage multiply like a tumor growth. They migrate into the cartilage tissue and spread there. These cells in turn make enzymesthat have a “proteolytic” effect, ie Dissolve cartilage tissue can. Shortly after immigrating into the cartilage tissue, the large cells perish again. The dead cells cause a Inflammatory response, which as a growth, so-called "pannus", is typical for rheumatoid arthritis.
The acute is also dangerous Tissue death, so-called Necrosis, in the body. Rheumatoid arthritis sometimes leads to the formation of necroses, which in turn release enzymes that break down healthy tissue and thus destroy it. This can help outside of joints Blood vessels destroyed and cardiovascular complications arise.

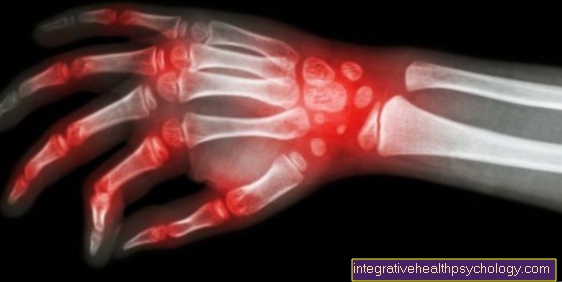
In the joints, other structures apart from the joint bone can be affected. Rheumatoid nodules under the skin are a common accompanying symptom. Likewise, enzymes can attack the tendons and cause diseases like that Carpal tunnel syndrome or that Ulnar syndrome to lead. Also Damage to the tendons until Tear off muscle bundles are conceivable.
Typical clinical pictures that can arise outside the joints can be found primarily in the heart, eyes and blood vessels. Rheumatoid arthritis can affect all structures in the heart. Common long-term consequences are Heart valve insufficiency. At the eye is sometimes the Dermis affected and in the long run is one Blindness the consequence. Rheumatoid arthritis can also manifest itself in the lungs, liver and kidneys.
Further information on the subject can be found at: Rheumatoid arthritis

The decisive factors for detecting rheumatoid arthritis are clinical symptoms on the affected joints. Pain and stiffness of the joints, especially in the morning (Morning stiffness) are pioneering symptoms. In the Blood test will be on Inflammatory factors and special Rheumatism characteristics examined.
The typical inflammatory factors that are also increased in rheumatoid arthritis are these C-reactive protein, as well as the Sedimentation rate. In addition, a rheumatoid factor and a rheumatoid-specific antibody can be detected. Together with clinical symptoms, a reliable diagnosis can be made according to a guideline based on 7 criteria.
Since rheumatoid arthritis is a Autoimmune disease drug therapy cannot treat the cause itself. It is primarily directed against the inflammatory component of the diseases. The process of Joint destruction cannot completely stop treatmenthowever, it can moderate the subsequent inflammatory reaction. This can sometimes prevent secondary diseases and slow down joint destruction.
Drug therapy ranges from Anti-inflammatories, how Ibuprofen from the group of NSAIDs, up to strong ones Immunosuppressants (Drugs that suppress the immune system). Next Cortisone Newly developed specific antibodies are also used. The sooner in the beginning of the inflammation and destruction of the joints therapy begins The lower fall the Consequential damage out.
Inheritance of Rheumatoid Arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis is one multifactorial disease. This means that multiple triggers work together to ultimately trigger the autoimmune disease. A There is no direct inheritance of the disease, but there is evidence that single genes, the inherited will be related to the onset of the disease. Only when several of these genes appear together does the risk of the disease increase, but an outbreak is never guaranteed. Likewise, the absence of genes does not mean that one will be spared the disease in any case.
A connection to the so-called HLA complexes, these are genes that play an essential role in the immune system (e.g. also in organ transplants). Variations in the HLA genes are suspected to be inflammatory rheumatic diseases favor. Variations of genes for certain regulatory proteins (Cytokines) and other immunomodulators are related to rheumatoid arthritis.
The figures for the actual heritability in the case of genetic abnormalities vary from study to study. It is believed that the risk of developing the disease in first-degree relatives roughly triples.
Psychological causes of rheumatoid arthritis
It is noticeable that rheumatoid arthritis is closely related to psychological factors and emotional states. Many patients develop such an autoimmune disease after losing a loved one, one Illness in the family but also after phases of great emotions like sadness and anger.
The physical consequence of the joint inflammation brings about an almost relieving pain that makes you forget the emotional situation.
Just like the psychological factors that trigger rheumatoid arthritis, an effect on the course of the disease can also be observed. A passive attitude towards the disease has a negative effect, whereas recognizing and consciously fighting against the disease can promote significant treatment success.
Rheumatoid arthritis is one of the seven psychosomatoses. These are physical illnesses that can be triggered by psychological stress.
Please also read our topic: Psychosomatics
stress
Stress is also a stressful psychological condition that can promote rheumatoid arthritis. Studies have shown that stress isn't just that Breakout probability increasedbut also the Inflammation worsens, the Symptoms intensified and promotes new flare-ups of the disease.
It should be noted that in particular one persistent stress level affects health, less often the major stress factors, for example severe life events.
For rheumatism patients, psychological care and treatment is particularly important. It offers great additional help to drug therapy and can actively improve symptoms and disease progression.
Also read our topic: How can you Reduce stress?