When the blood pressure is too low!
definition
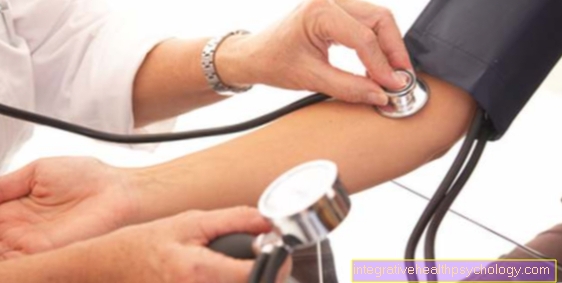
Low blood pressure (hypotension) means a blood pressure below 105/60 mmHg. The normal value for blood pressure is 120/80 mmHg.
The first value of the blood pressure arises during the ejection phase of the heart, the so-called systole. This is where the heart pumps blood to the body. A higher pressure must be built up during this phase. One also speaks of the systolic value.
The second value, the diastolic value, corresponds to the diastole of the heart. During this phase, the heart relaxes so that it can fill with sufficient blood.
Low blood pressure isn't really a disease. On the contrary - it is assumed that a low blood pressure has a favorable prognostic effect. However, a blood pressure that is too low should not be aimed for.

When does low blood pressure become dangerous?
According to the definition, from a medical point of view, blood pressure values below 105/60 mmHg are too low. However, since symptoms that occur are not always necessarily linked to certain limit values, it is difficult to determine when low blood pressure becomes critical for the person concerned. Low blood pressure will potentially have a protective effect. When a therapeutic indication exists is a controversial discussion among doctors. Some doctors assume a treatment indication from blood pressure values of below 90/60 mmHg. Blood pressure can become dangerous if there are several complications. Particularly important is the occurrence of syncope with consecutive falls, which can have far-reaching consequences for those affected. Severe daytime sleepiness with sleep disorders and the general decrease in performance can also severely restrict the person's private and work day.
Read more on the subject at: When does low blood pressure become dangerous?
At what blood pressure do you faint?
The point at which a person faints varies greatly depending on the individual, gender and situation. In women, one speaks of hypotension from values of 100/60 mmHg, while this is only present in men from values of 110/70 mmHg. In principle, one can also faint at values above this reference, for example if there is a rapid drop in blood pressure. For example, the occurrence of fainting also depends on a person's normal blood pressure level. Roughly, one can say that with blood pressure values around 70/40 mmHg, incidents with fainting often occur.
Symptoms

For many people with low blood pressure, the body is already used to this condition and has adapted so that they do not experience any symptoms. Typical symptoms in people with low blood pressure are circulatory problems. Above all, this includes dizziness. The dizziness mainly occurs in the morning and when getting up from lying or sitting. Sometimes you get ringing in the ears and a flicker in front of your eyes or you go black and you may faint. Some also notice their low blood pressure by trembling hands. Fatigue and poor performance can be associated with low blood pressure. Those affected often also have difficulty concentrating. The body tries to counteract the low blood pressure by increasing the heart rate, among other things. In this way he tries to ensure that all organs can be adequately supplied despite the low blood pressure. Due to the increased heart rate, those affected may feel a palpitation of the heart. Cold hands and feet are also a common symptom.
Read more on the subject at: Symptoms of low blood pressure
While it is still relatively easy for young people to compensate for the symptoms of low blood pressure, in older people too low blood pressure often leads to falls or the like. In older people, important blood vessels, such as the coronary arteries (vessels that supply the heart with blood), are often already calcified and therefore narrowed in diameter. If the blood pressure is too low or if the blood pressure regulation is too weak after getting up from sitting or lying down, organs such as the brain can be supplied with too little blood, so that the balance cannot be maintained in some cases and it leads to a fall comes.
More information can be found here
- Dizziness on standing up
- Circulatory weakness
Low blood pressure and high pulse
Blood pressure values should be in the range of 120 to 80 mmHg in healthy individuals. The normal pulse (heart rate) in healthy people is 70, in athletes the resting pulse can be up to around 50 beats per minute. If it comes to a combination of low blood pressure and a high pulse, this does not usually mean that there is a serious illness behind it. On the contrary, this combination is very common.
The medical background of this condition is that the body undertakes a compensation mechanism in the event of low blood pressure. In particular, he tries to compensate for the reduced blood volume in the vascular system with low blood pressure by increasing the heart rate and, as a rule, increasing the stroke volume. This special combination can also occur depending on the situation. It is therefore advisable to collect the values through repeated measurements. The person concerned should determine the resting heart rate in the morning. If, however, a pulse of more than 100 / minute and hypotension (especially systolic blood pressure below 90 mmHg) are present after repeated measurements, then there may be a more serious cause.
Are you more interested in this topic? Read our next article below: Low blood pressure and high pulse
Low blood pressure and pulse
The blood pressure falls as a result of impaired heart function and low blood pressure sets in. The primary cause here is not in the peripheral vascular system, but in the heart itself. When heart failure begins, the heart first tries to keep the blood pressure high by increasing the heart rate and stroke volume. Due to the resulting shortened diastole and an overall increase in heart enlargement with decreasing ability to contract, this mechanism does not work in the long term. At some point the heart can no longer maintain its heart rate and stroke volume if the heart failure progresses (heart failure). So the pulse and blood pressure drop.
The same applies to certain cardiac arrhythmias. A continuously targeted blood ejection cannot take place here, which is why the pulse and blood pressure can drop.
For more information on this topic, read also: Low blood pressure and pulse
Low blood pressure and headache
A very typical combination of low blood pressure and headache is common on hot summer days. Here the body loses a lot of fluid volume through sweat. In addition, exposure to the sun (especially between 11 a.m. and 3 p.m.) can cause heat stress for the head. When it comes to low blood pressure, the blood flow to the brain is temporarily reduced. This insufficient supply of oxygen-containing blood to the brain can manifest itself in the form of pulsating, often stabbing headaches. Typically, this condition is a reversible pathomechanism. The headache can go away by drinking enough water and, if necessary, avoiding too much sunlight on the head. Exercise is generally beneficial when it comes to low blood pressure due to a lack of volume. This increases the circulation of the blood.
Read more on the subject at: Low blood pressure and headache
Low blood pressure and dizziness
In addition to typical symptoms of low blood pressure, low blood pressure can also be associated with dizziness. In particular, dizziness, which is not infrequently associated with visual disturbances, is one of the most common symptoms of low blood pressure. As with headache as a result of low blood pressure, dizziness is caused by insufficient blood supply to the brain. The dizziness is also often accompanied by a ringing in the ears.
Particularly dangerous in the occurrence of dizziness with low blood pressure is the potential risk of falling. Hypotension-induced falls can have far-reaching consequences, especially in pregnant women and the elderly. Traumatic damage to the fetus can occur in pregnant women. Elderly people are predestined for bone fractures such as the femoral neck fracture due to reduced bone density and frequent osteoporosis. Dizziness is very common in what is known as orthostatic dysfunction. The change in position of the body from lying to standing causes the blood to sink into the lower extremity. The brain is temporarily undersupplied, which is why dizziness and visual disturbances can result.
Low blood pressure and tiredness
In the course of hypotension, there is often a decrease in performance and poor concentration due to fatigue. This constellation is based on a generally reduced supply of certain organs that ensure the performance of the body. This mainly includes the brain, but also the muscles and others. However, it is precisely these that need an adequate supply of oxygen and nutrients. If the blood pressure is low, the supply of these important substances can be inferior to the need, which is why the performance is limited.
In addition, associated sleep disorders can also occur with low blood pressure. The development of fatigue as a result of this pathomechanism also appears possible. A lack of sleep, or sleep that is not very restful, can lead to severe daytime sleepiness and depression. A therapeutic intervention is important here, on the one hand to maintain the ability of the person concerned to work and on the other hand to avoid complications. These can be, for example, accidents as a result of microsleep.
Low blood pressure and tingling sensations
Low blood pressure can lead to sensitivity disorders, especially in the distal sections of the fingers and toes as well as the acra (nose, ears). As with the feeling of cold, the cause is a reduced blood supply to these peripheral parts of the body. This leads to irritation of the neuromuscular function. Moving your fingers or toes sufficiently should reduce the tingling sensation.
Low blood pressure and fibrillation
Eye flicker as a result of low blood pressure is expressed by bright points of light in the field of vision, which can change their colors several times. The view can be partially, but also markedly restricted by these light stimuli. The eye flicker occurs for different times. The reason for this has not yet been clarified. The fibrillation of the eyes is presumably a reaction to the insufficient supply of the arteries of the eye. Often other symptoms such as tiredness, headache, feeling of coldness in the fingers appear, which make the diagnosis of hypotension likely.
causes
In most cases, the low blood pressure is due to harmless causes. Many people are predisposed to low blood pressure. In our body there are various mechanisms that intervene when blood pressure is too high and reduce it again. In people with predisposed low blood pressure, these mechanisms are often more pronounced, so that the blood pressure is lowered more than necessary. Conversely, this can also happen in people with inherited high blood pressure.
Young and slim women are often affected by low blood pressure. Unsporting women in particular often suffer from low blood pressure. With them, the so-called orthostatic response is often inadequate. Orthostasis is the upright posture. Young women often feel dizzy after getting up from sitting or lying down. A lot of blood sinks into the legs while sitting. Normally, the sympathetic nervous system of the body ensures that the heart rate is increased and the blood pressure rises during and after getting up so that the blood can be transported sufficiently against the force of gravity to the organs and especially to the brain.
If this reflex is inadequately developed, the brain may briefly receive too little blood, which can cause temporary dizziness or black out. The sympathetic nervous system ensures that the heart rate increases in those affected, but the blood pressure still falls. Of course, this is not a serious shortage of blood in the brain.
Too low blood pressure can also be caused by reduced resistance of the blood vessels, too low a volume of blood, inadequate pumping function of the heart, as well as reduced return flow from the blood to the heart.
In the short term, blood pressure can also drop in the event of a gastrointestinal infection, as a lot of fluids and salts are lost through vomiting and diarrhea.The loss of the salts further increases the loss of fluid, as salts normally ensure that fluid is absorbed. This is why it is important to drink a lot in the event of an acute infection.
Illnesses can also lead to low blood pressure. Above all, this includes hypothyroidism or hypothyroidism of the parathyroid gland.
In patients with varicose veins, i.e. bulging venous blood vessels in the legs, blood can increasingly sink into the legs, which can also lead to low blood pressure. Wearing compression stockings helps against this.
If the antihypertensive drugs are dosed too high in people with high blood pressure, such as the frequently used water tablets, this can also lead to low blood pressure.
Heavy blood loss also leads to low blood pressure. This can also occur as part of a gradual process, for example if blood is chronically lost through the stool.
In addition to the causes already mentioned, a weak heart or a heart valve defect can also ensure that too little blood is pumped into the body's circulation, so that the blood pressure drops.
Are you more interested in this topic? You can read more about this here: Causes of Low Blood Pressure
Low blood pressure during pregnancy
Blood pressure is typically low during pregnancy. This occurs in the first six months of pregnancy. This is due to the fact that there is a redistribution of the blood volume, since during pregnancy the child also has to be supplied with blood via the placenta. The pregnancy hormone progesterone ensures that the blood vessels dilate. As a result, a lot of blood sinks into the legs according to the force of gravity and blood pressure drops. In the last third of pregnancy, mechanisms that raise blood pressure and normalize it again intervene.
However, the blood pressure must not drop too much during pregnancy, as otherwise the growing child cannot be adequately supplied with blood. This can occur, for example, when the child presses on the inferior vena cava in the womb. This is a large vein that carries blood back to the heart.
Read more about this under
- Hypotension during pregnancy
- Dizziness during pregnancy
Low blood pressure in children
Younger children are usually not affected by low blood pressure. Then come the children to the puberty occur with many circulatory problems. This is especially the case with slim girls. During puberty, the body's hormonal balance changes and there is strong growth. The circulatory reactions in adolescents are usually an already explained orthostatic reaction, i.e. the blood pressure drops after getting up and the brain is briefly not adequately supplied with oxygen / blood. Around 20 percent of all young people suffer a brief circulatory collapse up to the age of 15.
Low blood pressure in case of thyroid dysfunction
If the low blood pressure is triggered by an illness, it is called one secondary hypotension. The most common cause is one Hypothyroidism A hypothyroidism can be congenital and acquired. A familial accumulation can be observed. As for the production of thyroid hormones iodine is needed can also be a Iodine deficiency trigger an underactive thyroid. The thyroid increases many metabolic processes. If the thyroid is underactive, the metabolism slows down, so that both physical and mental performance is reduced. The lack of drive causes blood pressure to drop. Affected people also feel tired, unable to cope with stress, are sensitive to cold, suffer from hair loss and constipation and gain weight. Often the psyche also suffers from the disease. Not all of these symptoms have to be present in a patient.
Low blood pressure after exercise
After active sports sessions, a drop in blood pressure can lead to symptoms such as headache, dizziness, visual disturbances, etc. Very often the cause is a lack of fluid in the body. As a result of increased sweating, several liters of body fluid including electrolytes can be lost. If you don't drink enough during the exercise, your blood pressure will drop. The genesis due to excessive muscle training is also possible.
Low blood pressure from diet
Usually a medical professional's first thought is that an unhealthy diet can lead to arterial hypertension. For example, a fatty, salty and low-fiber diet play a major role here. In addition, the fructose of many types of fruit attacks the vessel wall, which can lead to arteriosclerosis and hypertension in the long term. But diet can also be associated with low blood pressure. Low blood pressure may occur after eating a meal. This arises from the fact that in the course of the digestive process in the gastrointestinal tract a pathologically increased amount of blood is drawn. As a result, the blood flow is concentrated in the digestive tract, whereas in the central cardiovascular system (heart, brain) there is an undersupply of blood. Often people suffer from this postprandial hypotension, who otherwise suffer from arterial hypertension (high blood pressure). In addition to a connection with food intake, an overdose of antihypertensive drugs should be considered. In the presence of manifest postprandial hypotension, small, dosed portions should be taken with food.
Low blood pressure from alcohol
With heavy consumption of alcohol it can in principle lead to a temporary low blood pressure. The reason for this is the vasodilating effect of alcohol. This can lead to typical symptoms such as facial flushing. It is important to know that the antihypertensive effect is only temporary.
On the contrary, manifest alcohol addiction can aggravate the condition of arterial hypertension. Since intensified emotions usually occur during alcohol consumption, a vasodilatation can very quickly lead to a vascular contraction. In addition, alcohol-related hormones that increase blood pressure are increasingly released in the brain. Alcohol consumption should be limited to 10 to 20 grams (women) or 20 to 30 grams (men). Even a small beer contains between 10 and 15 grams of alcohol! The consumption of alcohol usually results in high levels of calories being absorbed, which in the long term cause increased blood pressure. The heart rate is also increased through increased affective and impulsive effects. In combination with the high blood pressure associated with alcoholism, this can overload the heart.
Low blood pressure at a young age
Even young age can in principle lead to low blood pressure. Mostly this is because younger people are very thin in some cases. Especially in adolescence, the body faces the challenge of growing quickly. The young people are relatively thin. The blood pressure is therefore usually lower than in adults. Up to about 20% of all children up to the age of 15 suffer one or more collapses due to poor circulation. In most cases, this is due to orthostatic dysregulation. So-called vasovagal syncope is also very common. This leads to a pathological drop in blood pressure and sinking of the blood in the lower extremities after standing up. In this case, the brain is temporarily undersupplied with blood and a circulatory collapse can develop.
Low blood pressure from iron deficiency
An iron deficiency can lead to low blood pressure. A pronounced iron deficiency leads to anemia (anemia). This comes about because iron is required for the formation of blood cells in the bone marrow. In the case of reduced blood formation, the circulating blood volume can be restricted, which leads to hypotension. Since women are particularly often suffering from an iron deficiency (for example due to blood loss during menstruation), this constellation of findings often occurs in gynecology.
Low blood pressure after weight loss
Weight loss can effectively lower blood pressure. Unfortunately, I do not know the exact medical background.
Low blood pressure hazards
If the blood pressure does not drop too much, you can live with low blood pressure. In the long run, the body gets used to the condition, so that many sufferers often do not notice that their blood pressure is too low. In contrast to blood pressure that is too high, blood pressure that is too low does not cause permanent damage and is not a risk factor for cardiovascular diseases such as a heart attack. Since the low blood pressure does not put any stress on the blood vessel walls, there is a risk of a heart attack or a stroke in people with low blood pressure levels. This tends to result in a longer life expectancy for people with low blood pressure. A danger only arises if the low blood pressure frequently leads to fainting attacks. Low blood pressure can also be dangerous during pregnancy.
therapy
As a rule, too low blood pressure does not have to be treated with medication, as is the case with blood pressure that is too high. Simple rules of conduct are sufficient to counteract this.
Patients with low blood pressure should take care to drink enough. If little liquid is supplied from the outside, the result is a low blood volume and the ratio of blood volume to blood vessel diameter is incorrect. The blood pressure will be correspondingly lower. This can be effectively counteracted by drinking a sufficient amount of at least two liters per day. Drinking coffee can also increase blood pressure, as coffee has a circulatory activation effect.
Exercise also helps to stimulate the circulation and increase blood pressure. Some also use alternating showers, i.e. alternating showering with cold and warm water, which also activates the circulatory system.
If you suffer from dizziness after getting up from lying down, it helps to slow down this process and to give the body more time to increase the blood pressure. For example, after lying down, you can sit down for a minute or two.
If a collapse occurs due to the low blood pressure, the person concerned should lie on their back with their legs about 30 cm high. If there was a brief loss of consciousness, one should remain in bed for a while after regaining consciousness.
If the blood pressure is permanently so low that drugs have to be used, drugs that stimulate the sympathetic system are taken.
Read more on the topic: Low Blood Pressure And Nausea - You Can Do That!
Which drugs help with low blood pressure?
There are various drug options for treating a blood pressure value that is too low.
Prescription drugs that can increase blood pressure in the presence of hypotension include:
- Dihydroergotamine: It is primarily used in the treatment of migraines. The aim here is to constrict the cerebral vessels, since vasodilation is one of the causes of a migraine attack.
- Midodrin: Stabilizes the circulation in general in the presence of hypotension.
- Combination preparation of etilefrine and dihydroergotamine (e.g. Effortil): Effortil can be taken in the form of tablets or as a solution. Effortil is used for circulatory disorders with low blood pressure, which are accompanied by typical symptoms such as paleness, dizziness, sweating, flickering or blackening of the eyes. Adults and children older than six years take 20 to 30 drops up to three times a day. Effortil should be taken in combination with plenty of fluid before meals.
- Combination preparation Akrinor: The dosage form of Akrinor is the injection solution. Akrinor is one of the emergency medication, which is a combination of theodrenaline and cafedrine. It is increasingly used in emergency medicine and anesthesia. After intravenous or intramuscular administration, it has an increasing effect on the myocardial contractility, the heartbeat volume and the peripheral vascular resistance. In this way an effective increase in blood pressure is achieved.
- Phenylephrine: It is used for slightly different indications. It is used as a direct sympathomimetic, especially for local swelling of the mucous membranes (e.g. with colds). One of the advantages of phenylephrine is that it can be absorbed through several routes of administration (intravenous, intramuscular, orally and as drops). In the presence of hypertension and ventricular tachycardias, phenylephrine should not be taken.
Hawthorn preparations are available without prescription in monotherapy or in combination with vitamin E and magnesium as well as with camphor.
You may also be interested in this article: Which drugs help with low blood pressure?
Home remedies
There are different ways to use home remedies for low blood pressure.
For example, beetroot juice is an effective option. Here, 2 glasses within a week should already have a blood pressure-increasing effect. Lemon water, green tea or liquorice root (liquorice) are also household remedies that can raise blood pressure. In green tea, for example, there are certain active ingredients that stimulate the central nervous system and ensure greater concentration. These include caffeine, theophylline and theobromine.
Endurance sports as part of physical activity can also increase blood pressure.
Alternating showers with alternating temperatures can also increase blood pressure. This is due to a sensitization of the regulation of the vessel width, which is reduced when it is cold and expanded when it is warm.
homeopathy
Homeopathic preparations can certainly be used in the treatment of hypotension. An example of this is Pulsatilla pratensis (meadow pasque flower). It was already used in ancient times by Hippocrates as a remedy for anxiety and menstrual disorders. Other substances used are Veratrum album, Acisum phosphoricum and Coffea.
In addition, the herbal medicine Korodin is also used in the therapy against low blood pressure. For more information, the editors recommend the following article: Korodin drops