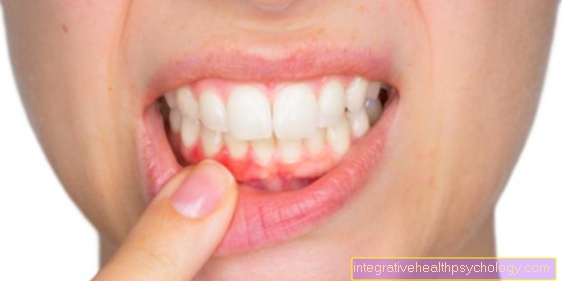
Abscess in the lower jaw
definition
An abscess is an encapsulated collection of pus caused by inflammation that spreads through tissue.
Abscesses in the lower jaw usually arise because of untreated tooth root inflammation. They are usually extremely painful and can lead to fever and general fatigue in those affected. But severe pain does not always have to be accompanied by an abscess in the lower jaw.
A visit to the dentist or family doctor is strongly recommended because an untreated lower jaw abscess can swell and cause shortness of breath.
You might also be interested in: Abscess on the tooth

How dangerous is an abscess in the lower jaw?
An abscess in the lower jaw must always be treated, otherwise complications can arise. Without treatment, it can destroy bones, connective tissue and nerves and thereby lead to irreversible damage.
Another very dangerous complication of a mandibular abscess is blood poisoning (sepsis) caused by germs getting into the bloodstream. This potentially life-threatening clinical picture can be avoided by having a lower jaw abscess treated by a doctor at an early stage.
Due to the close positional relationship of the lower jaw to the throat, the swelling associated with an abscess can lead to a narrowing of the airways and breathing passages. The following shortness of breath is life threatening. Therefore, if you feel tight or short of breath, you should go to the hospital immediately.
What are the symptoms of an abscess in the lower jaw?
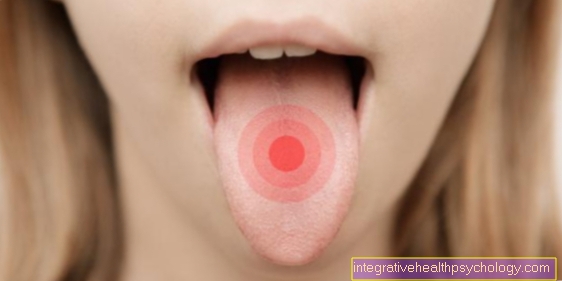
Typically, an abscess is accompanied by massive and rapidly developing swelling.
Superficial abscesses lead to visible reddening and warming of the skin on the cheeks. The skin looks tense, shiny and is very painful to the touch. In the case of very advanced abscesses in the lower jaw, the skin can even break through, i.e. the pus comes to the surface (like a pimple). At this point at the latest, a doctor should be consulted.
The pain is usually throbbing and is aggravated by pressure. The location of the tongue in the lower jaw can make chewing and speaking difficult. A wide opening of the mouth is not always possible. Swallowing and / or breathing may be impeded by the abscess spreading to the throat and palate. Here, too, it is important to see a doctor as soon as possible.
Fever and general fatigue are also typical symptoms of a lower jaw abscess. In the worst case, there is a risk of blood poisoning if the germs spread into the bloodstream (Sepsis). This is a life-threatening clinical picture and must be treated with antibiotics immediately in the hospital.
Damage to the surrounding soft tissues, nerves and bones as well as teeth is also possible.
Read more about this: Abscess in the jaw
Aching abscess in the lower jaw
An abscess is usually an extremely painful clinical picture.
A throbbing pain that is sometimes stronger and sometimes less pronounced is typical. The pain intensity can increase and decrease again and again in the course. Pressure on the jaw or cheek increases the pain, which is why those affected tend to avoid contact.
Chewing and speaking can also be affected by the pain. A complete opening of the mouth is usually also restricted.
If the abscess spreads to the roof of the mouth or throat, the pain may also make swallowing difficult or impossible.
In individual cases, a painless abscess of the lower jaw is also possible.
How to treat an abscess in the lower jaw
A superficial abscess of the lower jaw should always be surgically opened and rinsed out. Depending on the size of the abscess, a hospital stay of several days is necessary because a drainage is placed to drain the pus to completely empty the abscess.
Depending on where the abscess is exactly, it can be opened from the outside or the inside. The incision is made either on the outer edge of the lower jaw or the temporal region, or it is made within the oral cavity.
Antibiotics are also used in therapy. In the case of an abscess on the face, the antibiotics are always given through the vein. The antibiotics of choice are 1st generation cephalosporins. If you are allergic to penicillin, the antibiotic clindamycin can also be used.
You can also find out more at: What helps with an abscess?
Surgery to treat a lower jaw abscess
In the case of an abscess of the lower jaw, surgical opening and clearing of the abscess should always be carried out. The pus is removed and the wound is rinsed out. One then speaks of an operation.
This is accompanied by a treatment with antibiotics to kill the germs. Depending on where the abscess is located on the lower jaw and in which regions it is expanding, the incision is made to open the abscess. Some lower jaw abscesses are opened from the outside, while other abscesses are opened from the inside through the oral cavity.
Furthermore, superficial abscesses that are not very extensive can be opened by the dentist (or oral surgeon) under local anesthesia. Deeper abscesses that affect the bones or deep-seated soft tissues are always treated in the hospital under general anesthesia.
Do home remedies help with abscess in the lower jaw?
A jaw abscess is a clinical picture that absolutely must be treated by a doctor in order to avoid sometimes serious complications. While cooling can temporarily relieve pain, it does not cure the underlying problem.
The use of home remedies is therefore to be viewed as critical, since as little manipulation as possible should be carried out on an abscess. Touching, including by applying home remedies, can drain the abscess and lead to the germs being carried into the bloodstream. The consequences would be fatal.
The use of home remedies should therefore be avoided. If there is a suspicion of an abscess in the lower jaw, a doctor or the hospital should definitely be consulted.
Often attempts are made to treat the abscess in the lower jaw with ointments.However, this alone helps in the rarest of cases and only with small abscesses. Find out more at: Ointments for abscess therapy
Causes of an abscess in the lower jaw
- A common cause of a lower jaw abscess is untreated tooth root inflammation. Usually the cause is spreading caries that is hidden behind the tooth root inflammation. If left untreated, the infection can spread and lead to a purulent abscess on the lower jaw. Pain, fever, and loss of the tooth are possible consequences.
- But not only tooth root inflammation can be the cause of an abscess on the lower jaw. Complications during dental operations or other operations on the lower jaw may also be responsible for the penetration of germs and the development of an abscess.
- In addition, abscesses can also appear for no apparent cause.
- In addition, tooth remains, such as the remains of wisdom teeth in the jaw, can lead to an abscess in the lower jaw.
- Dental implants that have become loose are also a possible cause of an abscess in the lower jaw.
- Injuries to the soft tissues or inflammation of the lymph nodes in the lower jaw are also potential causes of an abscess.
Abscess in the lower jaw and cheek
One cause of an abscess in the cheek can be remnants of the wisdom teeth and inflammatory processes in this region on the lower jaw. Swelling, similar to that after removal of the wisdom teeth, is possible.
"Hamster cheeks" are typical, whereby the abscess is more likely to be found on one side than on both sides. In any case, treatment must be given, as the abscess can spread to neighboring regions, such as the roof of the mouth and throat. There is a risk of breathing difficulties and shortness of breath.
Duration of the abscess in the lower jaw
An abscess can develop over several weeks and last for months without treatment. However, depending on the extent of the abscess, complications, such as blood poisoning, can also occur during the course, which is why the natural course of the abscess should not be waited for.
An abscess doesn't heal on its own. In the meantime, there may be less or no pain sensation, but that does not mean that the abscess in the lower jaw has disappeared.
Medical treatment is always necessary. An abscess in the lower jaw can develop at different speeds and, depending on how quickly it is treated, it can last longer or shorter. A relapse, i.e. a recurrence of an abscess after successful treatment, is also possible.
Diagnosis of an abscess in the lower jaw
Abscesses are often diagnosed by their appearance. This is particularly possible if your situation is relatively superficial.
Imaging methods can also be used for more precise diagnostics. With the help of these advanced diagnostics, the extent of the abscess can be assessed well. Ultrasound and CT are important diagnostic tools (Computed tomography) or MRI (Magnetic resonance tomography)..
Especially in the case of the lower jaw, it is easy to assess whether the abscess only affects the soft tissues or also the bone and how far it extends into the tissue. If necessary, additional smears can be made and laboratory tests carried out. The blood test mainly reveals increased inflammation values.