Edema of the eye
introduction
Edema is the accumulation of fluid in the tissue. An edema of the eye is accordingly an accumulation of fluid in the area of the eyelid.
The eyelids are very well supplied with blood and contain a large number of blood and lymph vessels. In the vessels, liquid is constantly pressed into the environment and then absorbed again.
If there is an imbalance in this cycle, e.g. increased fluid in the tissue. As a result, the eye swells significantly and the eyelids protrude.

Causes of edema of the eye
There are several reasons why edema forms in the human body. Either the pressure inside the blood vessels rises and more fluid is released into the tissue, or the vessel walls show increased permeability. But disorders of the lymphatic drainage or a lack of protein in the blood also lead to edema formation.
Edema of the eye is very common and often has no disease value. Almost everyone has woken up with puffy eyes at some point. This is also an edema of the eye, which occurs because the fluid in the tissue can more difficult to drain off at night when lying down.
Especially after consuming alcohol, tobacco or very salty food, the eyelids are particularly swollen in the morning. Even strong crying causes increased fluid build-up in the eye tissue. However, this is a harmless edema that normally resolves itself within a few hours.
Other causes of edema are inflammatory processes in the eye, such as conjunctivitis (conjunctivitis) or allergies (e.g. to pollen or animal hair). The inflammation makes the vessels more permeable and more fluid gets into the spaces between the tissues.
A number of pathogens, such as bacteria or parasites, can also lead to inflammatory eyelid swelling. These clinical pictures include eyelid abscesses, eyelid phlegmon or barley grains. Often the infections are caused by bacteria of the genus staphylococcus or streptococcus.
Foreign bodies or chemicals can also cause edema in the eye by causing severe irritation to the eye.
You might also be interested in:
- Conjunctivitis- Symptoms & Treatment
- Abscess on the eye - is it dangerous?
- Treat stye
Edema of the eye from stress
An unhealthy lifestyle can cause edema of the eye. These include, above all, chronic stress and persistent psychological stress.
Stressed people are often restless and have problems sleeping. In particular, too little sleep leads to waking up with swollen eyelids in the morning.
In such cases, extensive recovery phases and a conscious lifestyle help. By reducing tiredness and stress, the problem of puffy eyes will in most cases go away on its own.
You can also find out more at: Reduce stress - this is how it works!
What other symptoms do eye edema have?
Edema of the eye is characterized by a more or less pronounced swelling of the eyelids. Depending on the cause, the swelling can either appear on one side or affect both eyes. In some cases, the swelling can be so severe that vision is impaired.
Itching, reddening or increased tear production often occur as accompanying symptoms, especially in irritated or inflamed eyes. Especially in the morning, the eyes are often stuck together with dried secretions. The eyelids can be dry and painful.
Sometimes those affected also suffer from a pronounced feeling of foreign bodies in the eyes or an increased sensitivity to light. In acute allergic reactions, swelling of the eyelids is often accompanied by raised redness, lumpy skin changes, and weeping blisters.
Read also under: Swelling of the eyes
How do you treat edema of the eye?
Usually, the eye swelling will go away on its own after a few hours. Lots of fluids, avoiding alcohol and foods with high salty content, and getting enough sleep help the edema resolve quickly and can prevent puffy eyes after waking up. Cooling the eyes with cold compresses also has a decongestant effect.
Medical treatment may be required for edema caused by inflammation or allergies. Even if the swelling has no explainable cause or persists for a long period of time, an ophthalmologist should be consulted.
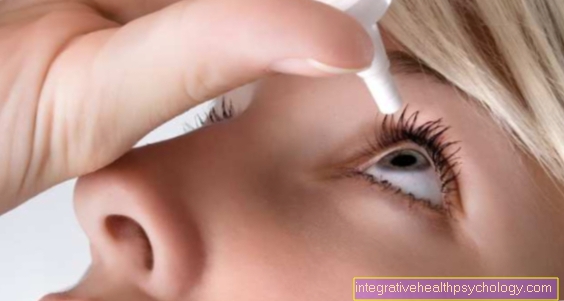
In the case of allergies, the cause must be found out by means of an allergy test and the cause - if possible - eliminated. Eye drops containing cortisone or anithistamines help against the symptoms.
Bacterial infections are usually treated with antibiotic therapy.
Learn more at: Eye drops and ointments
Diagnosis of eye edema
Edema of the eye does not have to be examined by a doctor in every case. Especially if the swelling was caused by too little sleep or strong crying, there is no urgent need for action.
Only edema that persists over a long period of time, cannot be explained by harmless causes, or is accompanied by accompanying symptoms should be examined by a doctor.
The doctor diagnoses edema of the eye based on the characteristic swelling around the eyelid. If a bacterial infection is suspected as the cause, the doctor can take a swab of the eye secretion and have it examined microbiologically.
If an allergic reaction is suspected, blood will be drawn and a series of allergy tests performed.
Duration of edema on the eye
How long edema of the eye lasts depends on the type of edema and the cause.
- In the case of swelling caused by too little sleep or after long crying, it usually only takes a few hours until the excess fluid has been removed from the tissue and the edema has disappeared.
- In the case of allergies, it may take longer, depending on how strong the allergic reaction is and how long the contact with the allergy-causing substance is.
- Edema of the eye caused by inflammation, such as a bacterial infection, can persist for up to several days. The administration of antibiotics usually leads to rapid improvement.
What is Quincke's edema of the eye?
Quincke edema is also known medically as angioedema or angioneurotic edema.
This is an acute swelling of the skin that mainly affects the eyes, lips and tongue. Quincke's edema is not an independent clinical picture, but a symptom that can be traced back to another cause.However, it becomes dangerous if the swelling affects the larynx as well as the tongue, as this disrupts breathing and the patient can suffocate.
Quincke's edema of the eye is characterized by the sudden onset of swelling. Usually the swelling will go away on its own within a few hours.
A distinction is made between the allergic and a non-allergic form of Quincke's edema.
- The non-allergic angioedema is often triggered by drugs (e.g. antihypertensive drugs such as ACE inhibitors or AT1 blockers).
- An allergic Quincke edema is treated with cortisone and antihistamines, whereas these drugs have no effect in the non-allergic form.
What causes edema only on the eyelid?
Edema can only affect the eyelid. The eyelid area in particular is very sensitive. The skin is very thin and pervaded by many vessels.
Very often a hailstone causes swelling only on the upper eyelid. A hailstone is also known as a chalazion. This is a blockage of the ducts of certain glands in the eye, the meibomian glands. These special glands are sebum glands that are located on the edge of the eyelid. As a result of the blockage, the sebum can no longer drain properly and a hard, painless knot forms - the hailstone.
Inflammation of the eyelid margin (blepharitis) can also lead to swelling only on the eyelid. Most of the time, the inflammation is bacterial and associated with other symptoms such as dry eyes, redness and eyelash loss.
Recommendations from the editorial team
This could also be of interest to you:
- edema
- Puffy eyes- what to do?
- Swelling of the eyes
- Angioedema








.jpg)