Multiple endocrine neoplasia
All information given here is only of a general nature, tumor therapy always belongs in the hands of an experienced oncologist!
Synonyms
Medical: Hormone producing tumor
Also read:
- Multiple endocrine neoplasia type 2
introduction
In the multiple endocrine neoplasia is it a autosomal dominant inherited disease. This is associated with hormone release and is a rare syndrome. The MEN neoplasms (multiple endocrine neoplasia) manifest in different organs and therefore lead to different clinical pictures, depending on the hormone exposure of the organ.
Classification
The multiple endocrine neoplasia is divided into 2 types, which manifest themselves in different organs. This is how you distinguish MEN type 1, also as Wermer syndrome referred to, from MEN type 2. For the sake of clarity, the two types with symptoms, therapy and diagnostics are considered separately below.
Men type 1 Wermer syndrome
Of the Type 1 multiple endocrine neoplasia is characterized by a familial accumulation of tumors of the Pituitary gland, Parathyroid and the pancreas (Pancreas).
frequency
The multiple endocrine neoplasia is a rare disease. The prevalence is around 1: 100,000.
root cause
The clinical picture of Wermer syndrome (multiple endocrine neoplasia) can be familial, but also sporadic. In some cases, the endocrine neoplasia is due to one Gene mutation in the menin gene. This is on chromosome 11 and is suppressed when it functions correctly Tumor growth (Tumor suppressor). This gene is accessible for genetic analysis and can therefore be tested in cases of multiple endocrine neoplasias that occur in families.
Symptoms
The symptoms of multiple endocrine neoplasia depend on the location of the tumors. Basically, the tumors in Pituitary gland, Parathyroid and pancreas all occur over time, but in different chronological order. Usually that determines First manifestation of the tumor the symptoms. Also, not every tumor produces all of the hormones listed below. Accordingly, the clinical picture is composed of the various hormone effects, depending on the tumor manifestation and function. In addition, both benign and malignant tumors can occur mixed.
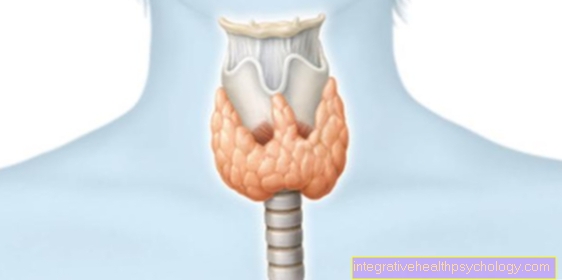
Pituitary gland
The Pituitary gland produces various hormones. This includes, among other things Growth hormone STH. In the case of overproduction, there is a clinical result here Tall stature (Acromegaly). Of these are especially those Feet and hands, such as nose and Ears affected. In addition, the internal organs also grow increasingly and can thus lead to space problems and functional restrictions. The pituitary gland also produces the adrenocorticotropic hormone (ACTH). This stimulates the Adrenal cortex and thus leads to Cushing's Syndrome.
The reason for this is an excessive production of Cortisolwhich leads to a typical external appearance with Moon face, Trunk obesity and Bull neck leads. The pituitary gland also produces prolactin. This hormone is during the pregnancy responsible for milk production. If the prolactin is overproduced by a tumor, irregularities or the absence of the Menstrual period. It can also lead to milk production and secretion from the mammary glands. Of course, this is only clinically noticeable if there is no pregnancy or if there is no breastfeeding. A Overproduction of prolactin however, it can also proceed without symptoms.
Parathyroid
The Parathyroid forms the parathyroid hormone. This regulates that Calcium and phosphate balance in the body and is responsible for building and breaking bones. According to this function, it can be provided by a Parathyroid tumor calcium and phosphate imbalances occur. Symptomatic this leads too clearly increased need to urinate and accordingly also significantly increased Feeling thirsty. Also can nausea and Vomit occur (multiple endocrine neoplasia).
pancreas
Also the pancreas produces several hormones which lead to different clinical pictures. At Overproduction of gastrin that arises Zollinger-Ellison Syndrome. This goes with more Occurrence of gastric ulcers hand in hand. Clinically, this leads to stomach pain and Bleeding in the stomach. In some cases, these may initially be completely asymptomatic. If the tumor produces an increased amount of insulin, it can sudden drops in blood sugar occur. Especially if no food has been consumed for a few hours. Here it comes to nausea, malaise, Tremble, sweat and unconsciousness. If there is an overproduction of the vasoactive intestinal polypeptide, the clinical picture of Verner-Morrison syndrome arises. This is accompanied by massive watery diarrhea and a large loss of potassium. This potassium deficiency can result in cardiac arrhythmias. Forms the pancreas through the Tumor too much glucagon, it often happens to typical skin symptoms. In addition, the sugar tolerance in the body is disturbed. Will be increased Serotonin Formed in the tumor, the picture shows increased mobility in the gastrointestinal tract. this leads to stomach pain and watery Diarrhea.
Diagnosis
The Investigation of the multiple endocrine neoplasia type 1 relies on the symptoms and increased hormone levels of each of the tumors above. Genetic testing should always be carried out in patients with this neoplasm to rule out a gene mutation. In addition, if the gene mutation is present, a family history should be taken. Patients with the MEN-1 mutation should be examined regularly in order to detect the tumor as early as possible and to be able to treat treatment before symptoms appear.
therapy
The Therapy of multiple endocrine neoplasia generally consists of the surgical removal of the tumor. In addition, the individual hormone effects can be suppressed with the help of hormones. This can also shrink the tumor and make surgery avoidable.
forecast
The familial multiple endocrine neoplasia is better treatable and better curable than the sporadically occurring neoplasms. This is primarily related to the early diagnosis and thus the possibility of early therapy.