Orlistat
What is orlistat?
Orlistat is a drug from the group of lipase inhibitors that can be used to support a weight-reducing diet. Orlistat inhibits the fat-digesting enzymes in the intestine, so-called lipases, and thus ensures that less fat is absorbed from food. This happens without the sufferer developing less appetite. The intake should enable those affected to lose about ten percent of their body weight. In Germany, Orlistat is only available on prescription under the trade name Xenical. However, medications containing orlistat are also available over the counter in lower doses.
Also read the article on the topic: Appetite suppressants

INDICATIONS for ingestion
Orlistat is a pharmacy-only and partly prescription drug, which should only be taken under certain conditions. Those affected with a body mass index of over 30kg / m2 can take orlistat to accompany a reduced-calorie diet.
If the body mass index is greater than 28kg / m2 and there are risk factors for obesity-induced diseases, it can also be taken. The intake should always be checked by a doctor and not be carried out independently without the corresponding requirements.
You might also be interested in this topic: How can you boost fat burning?
PRINCIPLE OF WORK: How does Orlistat work?
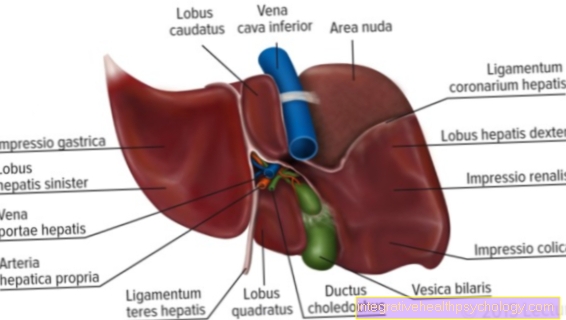
The active ingredient orlistat is an inhibitor of gastrointestinal lipases. These are enzymes that break down and convert food fats in the gastrointestinal tract so that they can be absorbed by the body. These lipases are also found in other parts of the body, but since orlistat is hardly absorbed, the effect is largely limited to the intestines.
Orlistat's effects are long-lasting and specific to this task. Orlistat works in the stomach and continues to work in the small intestine. The active ingredient attaches itself to a certain chemical ending, the serine residue, of the enzymes covalently. This means that the bond is permanent and this enzyme can no longer fulfill its task. The converted enzymes can no longer break down the triglycerides, i.e. dietary fats, into their individual components and the body cannot absorb these fats. The body then has to create new enzymes to break down fat.
Orlistat does not have a 100% hit rate, but only reduces the amount of functioning fat-splitting enzymes. Due to the reduced absorption of fats, less fat arrives in the body cells and fat stores. The body has to draw energy from existing reserves and the person affected can easily reduce their weight.
Also read the article on the topic: Fat blockers
How much can you lose weight with Orlistat?
Weight loss with Orlistat should always be combined with a reduced calorie diet. Studies have shown that people who take orlistat can experience a 5 percent weight loss after about 12 weeks. If this is not the case, it should be stopped as orlistat will not work for everyone. Those affected lose up to 10 percent of their body weight within a year. In both cases this is slightly better than with an exclusively reduced-calorie diet. The exact weight reduction depends on many factors and must be viewed very individually.
This article might also interest you: Dietary supplement for weight loss
SIDE EFFECTS: What are the side effects?
As with all drugs, Orlistat also categorizes possible side effects according to their frequency.
The very common side effects, which affect more than ten percent of the users, include:
- a headache
- Upper respiratory tract infections
- stomach pain
- Fatty stool
- Flatulence (gas)
- diarrhea
- Hypoglycaemia (only for people with diabetes as a pre-existing condition)
At one to ten percent, the following side effects are common side effects:
- Lower respiratory tract infections
- Rectal pain
- Fecal incontinence
- Tension in the stomach
- Dental discomfort
- Urinary tract infections
- Exhaustion
- Menstrual irregularities
- Feeling anxious.
Less common side effects that occurred during the study phase are:
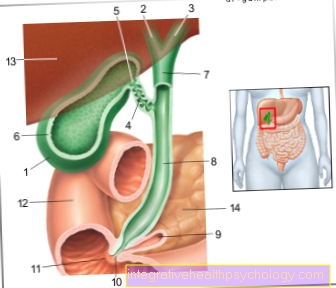
- Biliary tract disease
- Inflammation of the liver
- Kidney failure
- allergic reactions up to allergic shock and intestinal bleeding
As the percentages already suggest, side effects are not something that everyone should expect, but rather symptoms that may occur. In the event of side effects, a doctor should be contacted and the intake possibly stopped. With certain pre-existing conditions, the risk of side effects can be significantly increased. These include diseases of the gastrointestinal tract, diabetes and underactive kidneys.
CONTRAINDICATIONS: What are the dangers of Orlistat?
As with almost all drugs, serious side effects, such as an allergic shock, are possible with Orlistat. There have also been isolated reports of kidney and liver failure, some of which were fatal. Interactions with other drugs are also possible. For example, Orlistat can reduce the effectiveness of HiV drugs. Breast-feeding may cause harm to the newborn as it is not known whether orlistat passes into breast milk.
When should Orlistat not be taken?
Orlistat should not be used with some pre-existing conditions. If you are hypersensitive or allergic to the active ingredient or other components of the drug, Orlistat should not be taken as life-threatening allergic reactions can occur. Orlistat is also unsuitable for chronic malabsorption syndrome as it exacerbates the symptoms. Biliary tract diseases can also rule out an intake. Since it is not known whether orlistat passes into breast milk, breastfeeding mothers should also avoid orlistat.
INTERACTION: What is the interaction?
Orlistat can interact with other medicines. Treatment for HIV may be reduced when taking orlistat. The effects of birth control pills can also be impaired. Simultaneous use of Orlistat with ciclosporine is also not recommended, as this also reduces the effect.
When taking oral anticoagulants such as Marcumar, the INR values should be monitored more closely. An influence on therapy with anti-epileptic drugs cannot be excluded. The simultaneous intake of orlistat with statins, sartans, digoxin and amitryptyline is unproblematic. An interaction with alcohol could not be proven either.
Effectiveness of the pill
A direct interaction between the pill and orlistat could not be demonstrated in the studies. The effect should not be directly impaired. However, orlistat can cause diarrhea and so the absorption of the active ingredient in the pill may be reduced. In exceptional cases, this can lead to unplanned pregnancies. Therefore, additional contraception should be used when taking orlistat and especially if there are side effects.
You can read detailed information on the subject of the pill's effectiveness under: Which drugs affect the effect of the pill?
Orlistat and alcohol
No interactions between orlistat and alcohol have been found in studies. Alcohol can therefore be consumed in moderate amounts while taking orlistat. As part of a low-calorie diet, attention should be paid to the high calorie content of alcoholic beverages. Drinks with a lot of sugar and high alcohol content in particular also contain a lot of calories, which should be added to the daily requirement.
DOSAGE of orlistat
It is recommended to take 120mg orlistat in the immediate vicinity, i.e. shortly before or after the main meals. If the main meal is skipped, the orlistat intake should also be skipped. No additional benefit can be expected from taking more than three units a day, but an overdose is also not critical. A dose adjustment may be necessary for certain pre-existing conditions. This should be discussed with the attending physician.
PRICE from Orlistat
The over-the-counter orlistat preparations with 60mg of active ingredient cost around 16 euros per 42 tablets. Larger packs are slightly cheaper per tablet. The prescription dosage of 120mg is 70 euros for 84 tablets. These are only available with a prescription.
Orlistat is in most cases a private prescription and the costs must be borne by the person concerned. In some cases, the health insurance companies take over the costs afterwards.
OTHER IMPORTANT QUESTIONS:
Is there Orlistat available without a prescription?
Orlistat supplements are available in different dosages. The preparations with an active ingredient quantity of up to 60mg per tablet are available from pharmacies without a prescription. The dosage of 120mg per tablet requires a prescription. The taking of the over-the-counter preparations should also be discussed with the treating doctor, as this can prevent possible side effects and interactions.
What alternatives are there to Orlistat?
The most important alternative to orlistat is a healthy and balanced diet with reduced calories and exercise. Additional medication should be discussed with the attending physician. Another class of active ingredients than lipase inhibitors are anorectics. These work by reducing the feeling of hunger and increasing the body's basal metabolic rate. These include the amphetamines. Due to the high risk of side effects, these are usually not recommended.
You might also be interested in this topic: Tips on how to best lose weight
Can Orlistat be taken during pregnancy and breastfeeding?
There are no studies on the effects of orlistat in pregnancy. Its use is therefore not recommended. However, since orlistat is only absorbed into the body in small quantities, it is usually not critical to take it before the pregnancy is known. It is not known whether orlistat can pass into breast milk, so avoid taking it while breastfeeding. The newborn has a high need for calories and could develop complications from breast milk ingestion.
For detailed information, see: Medication during pregnancy