Pain in the inner ankle
introduction
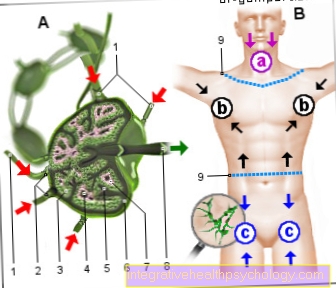
Under the name of pain in the inner ankle (Medial malleolus) Various options must be considered, depending on which structures in this area are affected. Mostly it affects the bones, tendons, ligaments or muscles, but vascular diseases or systemic diseases such as rheumatism can also cause pain in the inner ankle.
When differentiating, it is also important whether the pain has been for a long time (chronic) or acutely (e.g. after exercise) and which accompanying symptoms such as redness and swelling are present.

causes
Inside ankle pain can have many different causes. It can be roughly divided into traumatic and non-traumatic causes. The latter can be caused by an underlying disease such as Rheumatism or gout develop. But also chronic inappropriate loads, e.g. Incorrect footwear or excessive exercise can cause pain in the inner ankle. It is also possible that these stresses can lead to traumatic consequences due to the inflammation in the area. This includes e.g. the classic twisting of the ankle.
The most common causes of medial ankle pain arise from the surrounding muscles, tendons, and ligaments. Most of the time, incorrect stress caused by unsuitable footwear (e.g. flat running shoes when jogging, but also high-heeled heels in everyday life), chronic overload (long jogging) or overweight are in the foreground.
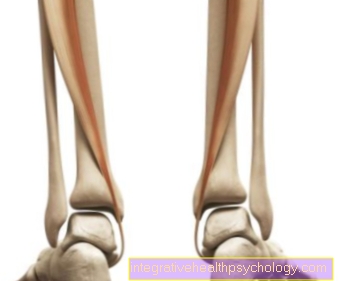
Tendonitis of the tibialis posterior muscle
The tibialis posterior muscle is part of the calf muscles and is, among other things, involved in foot extension (Plantar flexion) and the stabilization of the transverse arch of the foot. The tendon runs along the back and inside of the calf and then pulls behind the inner ankle to the underside of the foot, where it branches.
Often, pain in the muscle or in the area around the tendon are the first signs of tendinitis (Tendovaginitis). This is an inflammatory change in the tendon sheath, mostly due to excessive or incorrect loading. ly affected are Middle-aged women, runners (unsuitable shoes and excessive strain), but also overweight and lack of exercise can play a role. It is also important to have a basic illness such as To rule out rheumatism or gout as a cause.
If the symptoms are ignored and no measures are taken to remedy the causes, a flat foot develops (flattening of the transverse arch) and in the worst case even a tendon tear.
Therapeutically, in the acute phase mainly Anti-inflammatory drugs (so-called NSAIDs) and immobilization into consideration. In the long run, however, you should treat the causes (e.g. wrong shoes or overweight).
Read more about this under Tendonitis of the tibialis posterior tendon
Delta ligament injury
The delta band (Deltoid ligament) is made up of four parts and serves to stabilize the ankle joint. The tendons of the posterior tibial muscle (M. tibialis posterior) and the long toe flexor (Flexor digitorum longus) cross the ribbon.
Injuries to the ligament structures on the ankle usually occur. by twisting the foot, with almost 95% of the outer ligaments being affected. Inward buckling and thus damage to the delta ligament rarely occurs. Does it still happen that the delta band is caused by an exaggerated inward rotation (Pronation movement) tears, it usually has to be sutured as part of an operation.
Concomitant symptoms
-
Swelling
-
Redness
-
Pain
-
warming
-
Bleeding (bruise)
-
Function losses
-
Relief postures
swelling
A swelling per se can have many different causes. In general, there is an increased accumulation of fluid, mostly due to an inflammatory reaction.
If there is swelling of the inner ankle, the affected person often has other symptoms such as Pain at rest or when walking, or reddened skin in this area. Most often the swelling is preceded by an event, e.g. an inward bend in the ankle. Or there have been symptoms such as pain for a long time, which get worse over time and the movement in the joint causes more and more problems. That speaks more for a chronic inappropriate or excessive stress.
However, swelling can also have systemic causes, such as Diseases in the lymphatic or vascular system or in the context of rheumatoid arthritis.
In general, it is recommended to have the exact causes clarified by a doctor in order to rule out some serious illnesses.
For detailed information on this topic, see: Swollen ankles
What does pain in the inner ankle without swelling indicate?
Swelling can occur with the causes described, but does not have to be. It only occurs relatively often as part of the inflammatory reaction that occurs, and often only after a delay. Pain in the inner ankle is basically our body's first warning signal that something is wrong. This can range from the wrong stress, overweight, a pinched nerve, hardened muscles to systemic or neurological diseases.
In this context, it is important to know whether the pain can be attributed to a certain event as a trigger or whether the problems have gradually worsened. In general, it is advisable to seek medical advice when in doubt so that the symptoms do not worsen or underlying diseases remain undetected.
Read more about this under
- Tarsal tunnel syndrome
- Pain in the foot on the inside
These symptoms suggest a thrombosis
When diagnosing thrombosis, there are further differentiations to consider. So one differentiates e.g. between arterial or venous thrombosis and the superficial or deep position of the affected vessels.
Roughly, it can be said that thrombosis can lead to severe pain, swelling of the leg and a feeling of tension. However, it is unlikely that these signs will only affect the inner ankle, but rather affect the entire lower leg or leg.
If a thrombosis is suspected, a doctor should be consulted promptly in order to make a reliable diagnosis or diagnosis of exclusion.
Read more about this under
- Thrombosis pain
- How can you recognize a thrombosis?
Pain above the medial ankle
If the pain occurs above the inner ankle, it usually affects the same structures and causes that would also be noticeable below the ankle. The surrounding muscles, tendons and ligaments are almost all structures that pull over the ankle or ankle and symptoms such as pain can thus also spread upwards towards the knee.
When differentiating, it is important to have a precise description of the accompanying symptoms, the time of occurrence and the frequency.
diagnosis
The doctor gains the best clues about the possible cause by taking anamnesis (questioning the patient). It is very helpful to give as precise answers as possible to the questions. So-called image diagnostics using ultrasound, MRI or X-rays are also often used in order to be able to reliably diagnose injuries to soft tissues or bones, depending on the suspicion. In addition, a blood test in the laboratory can provide information on inflammation values.
Treatment and therapy
Depending on the underlying cause, different approaches can be considered.
The so-called “PECH” rule is used for most sports injuries.
-
P for pause
-
E for ice cream
-
C for compression
-
H for high camps
The aim is to keep the damage as low as possible and e.g. promote swelling of the surrounding tissue. The PECH rule is basically a kind of first aid for almost all muscle and joint injuries.
There are also aids for immobilization such as Rails available. Drugs that have analgesic and anti-inflammatory effects, such as NSAIDs, may be prescribed by a doctor. The possible influencing factors such as To optimize or change footwear, but also overweight as a possible factor.
Duration
The duration of the treatment depends of course on the respective illness or injury as well as the behavior and cooperation of the person concerned.
Injuries to the tendons and ligaments usually last several weeks. Muscular injuries should also be taken seriously and healed properly so that no long-term damage occurs.