Jumping finger
Introduction / definition
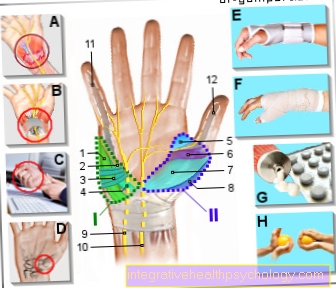
As jumping or flicking fingers (Latin digitus saltans) is called a Sliding disorder the tendons of the hand. The terms become synonymous Tendovaginosis or Tendovaginitis stenosans used. It is named after the symptomatic jumping of the finger when trying to stretch it out. Here the finger only hooks into the Flexion position firmly to then after overcoming the blockade to rush forward.

The disease affects Women more often than men, the maximum age being beyond the age of 60. In rare cases, however, an inborn thickening of the Finger tendons as jumping finger become symptomatic. The most commonly affected is the thumb, as this is the most stressed in daily use. Often, however, the thief is also used as a thief Index and middle fingers affected, in principle any finger can be affected. Infestation of several fingers, sometimes at different times, is possible and not unusual.
If your thumb is affected, we recommend our more specific topic: flicking thumb
Symptoms
The disease often manifests itself initially through unspecific pain or Feelings of tension in the affected finger. Palm pain, a Pull on the outside or inside of a finger, or an occasional one Snap a finger can herald a jumping finger and should be taken seriously. A visit to the doctor is therefore always advisable, especially if the symptoms persist. The typical Jumping the finger often only shows up in the later stage. The extended finger cannot be flexed with this clinical picture, the patient feels that the movement is blocked because the thickened tendon the Ring band (Annular ligament) cannot happen. So it is a so-called Ring ligament stenosis (Narrowing). If more force is used, a noticeable tension builds up. If the use of force is sufficient, the thickened tendon overcomes the ring ligament and one develops jerky flexion of the affected finger. It is crucial that this phenomenon usually occurs reproduce leaves. In many patients this is the jumping of the finger painfulbut not for others. With some affected people, a thickened tendon knot under the skin can be felt while bending or stretching the affected finger. In some cases, the tendon knot can widen swellingso that the finger freezes in a bent or stretched position and cannot be moved back into the starting position even with maximum effort. This phenomenon is also called caught finger and can partially resolve itself. If this is not the case, however, rapid operative intervention is required. The ring ligament is split, which prevents long-term irreversible functional restrictions of the finger.
Appointment with ?

I would be happy to advise you!
Who am I?
My name is I am a specialist in orthopedics and the founder of .
Various television programs and print media report regularly about my work. On HR television you can see me every 6 weeks live on "Hallo Hessen".
But now enough is indicated ;-)
In order to be able to treat successfully in orthopedics, a thorough examination, diagnosis and a medical history are required.
In our very economic world in particular, there is too little time to thoroughly grasp the complex diseases of orthopedics and thus initiate targeted treatment.
I don't want to join the ranks of "quick knife pullers".
The aim of any treatment is treatment without surgery.
Which therapy achieves the best results in the long term can only be determined after looking at all of the information (Examination, X-ray, ultrasound, MRI, etc.) be assessed.
You will find me:
- - orthopedic surgeons
14
You can make an appointment here.
Unfortunately, it is currently only possible to make an appointment with private health insurers. I hope for your understanding!
For more information about myself, see - Orthopedists.
root cause
Of the jumping fingers is in most cases due to wear and occurs frequently in the advanced age on. The wear and tear leads to a Thickening of the flexor tendons of the hand. This makes it difficult for the tendons to slide through the ring ligaments of the finger when the finger is stretched or flexed. The Ring bands ensure that the tendons remain in contact with the bone when the fingers are bent. With a thickening of the tendons in front of a ring ligament, the tendon can only pass this with greater force when bending, which is typical Leap of the finger expresses. Another name for this jerky rush is Pocket knife phenomenon. The cause of the thickening is not yet fully understood, being next to one predisposing higher age also one innate predisposition, stressful activities or injuries. Often a jumping finger occurs as Occupational disease in certain professional groups such as craftsmen, athletes or piano players who put a lot of strain on their fingers and hands for years. Unusual intense stress such as gardening can also lead to overexertion and thickening of the tendons of the hand. The intense stress on the tendon causes it to tiny injuries the tendon that become more frequent and too persistent inflammation being able to lead. There follows one Thickening of the tendon. The jumping finger phenomenon occurs frequently in connection with rheumatic diseases or one Carpal tunnel syndrome on.
diagnosis
Diagnosing one jumping finger is usually provided by the doctor as part of the clinical examination. Other diseases that require treatment, such as bone diseases or a Joint wear (arthrosis), we recommend making a X-ray. In rare cases, a sonographic examination of the soft tissue can be used with an ultrasound device or a cross-sectional imaging method to diagnose or rule out other diseases.
therapy
The therapy of the jumping finger is a smooth gliding restore the finger tendon through the conductive ring ligaments. Before a Operative treatment is displayed, but should be attempted with conservative measures achieve a cure. A Decongestion the thickened tendon can be replaced by a Immobilization of the affected finger can be reached using a splint. The finger is splinted for four to six weeks and the lack of load reduces the swelling of the thickened tendon. However, with this treatment there is a risk of stiffening of the joint, what about long term Movement and function restrictions can lead. Another therapy option is the local one Cortisone therapy. For this, cortisone is injected into the affected finger, where it takes effect after one to two days. Cortisone has anti-inflammatory, direct decongestant and analgesic effects. This improves the symptoms of those affected in a few days, although the full effect of the cortisone can only develop later. Similar effects can also be achieved with the help of a local anesthetic, which is why this can be applied in combination with cortisone or alone. Often times, however, the cortisone injection does not provide lasting relief, as symptoms can return as the medication wears off. The triggering factors such as playing the piano, sport and manual work should be temporarily reduced until the symptoms no longer occur.
If the thickening is already so pronounced that the desired effect cannot be achieved with the cortisone injection, or if the symptoms return within a few months after repeated cortisone injections, an operation is indicated. It is a minor intervention that occurs in local anesthesia (Local anesthesia) and outpatient (without inpatient hospitalization). The duration of the operation is only a few minutes, ideally the surgeon specializes in hand surgery. A small incision is made on the flexor side (inner surface) of the affected finger and the constricting one Ring band completely severed. Particular care must be taken to protect blood vessels and nerves that run parallel to each other. Then the cut is sewn with a few cuts and a bandage is applied. After the anesthesia has subsided, the finger can now move freely again. The free Dexterity is restored after the anesthesia has subsided. A postoperative one physiotherapy exercise treatment is only necessary in rare cases. Depending on the thread material used, these only need to be pulled after about ten days. The Chances of recovery This surgical procedure is very good, so that almost all patients are relieved of their complaints and can move their fingers freely again immediately after the procedure. Cutting the ring ligament does not usually cause any restrictions, as its function is taken over by the other ring ligaments of the corresponding finger. Complications such as infection, allergic reactions to the anesthetic, excessive scarring or nerve or vascular damage only occur in exceptional cases.
forecast
Many patients can already benefit from a conservative treatment help, which is very low-risk and uncomplicated. If conservative treatment is not enough, the chances of recovery from the surgical intervention are still very good, so that almost all patients are relieved of their symptoms and can move their fingers freely again immediately after the operation.