Stem cell donation
definition
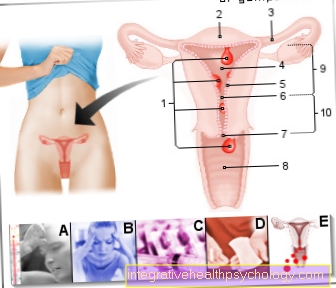
Under one Stem cell donation one understands one at leukemia (Blood cancer) to be applied measure in which the sick person Stem cells are transferred from a healthy donor to be responsible for the production of healthy blood cells in the future.
The stem cells must first be obtained from the donor's body.

Stem cell donation process
In order to be able to carry out a stem cell transfer successfully, a suitable donor must be found in a first and complex step. For this purpose, typing actions are carried out at regular intervals.
The likelihood that the exact characteristics of a potential donor will match the recipient is very small. Around 14,000 matches must be suitable to be considered a donor.
In order to be typed as a donor, blood is first drawn. Alternatively, a mouth swab can be performed with a cotton swab.
However, due to the high costs involved, blood sampling is almost always used.
If most of the components of the donor's blood match that of the recipient, further blood samples and further tests are carried out in a second step.
In some cases, complete matches are found, which then entitles the donor to transplant.
There are two different ways to obtain stem cells.
One possibility is that the patient is given an injection of medication. This then releases the blood cell-producing cells, the so-called stem cells, from the bone marrow and flushes them into the peripheral blood.
This is then removed from the donor and the stem cells are isolated. In the meantime, chemotherapy and radiation almost completely shut down the recipient's immune system.
This is important so that the recipient's body does not start an immunological reaction to the transfused stem cells.
During this time, the recipient is in complete isolation, as infection must be avoided at all costs.
If his immune system stops working, the donor's stem cells are transferred to him. These immediately find a place in the bone marrow and start producing healthy blood.
Another way of obtaining stem cells is bone marrow puncture. For this purpose, the donor is admitted to the hospital for approx. 5 days and bone marrow is extracted from the iliac crest with a drill under local anesthesia.
Here, too, the stem cells are then isolated and, after appropriate preparation, can be transfused to the recipient.
Bone marrow aspiration is often more painful for the donor than the first method, but it does not involve the use of medication.
The donor is released from work for the procedure; the costs are covered by large transplant organizations such as the DKMS and by the health insurance company.
Read more on the subject at: Bone marrow donation
As part of the stem cell donation, HLA is also determined in order to avoid rejection by the recipient. For detailed information, read the following article: HLA - Human Leukocyte Antigen
Risk to the donor
Despite some downplaying media advertising, some should Risks be considered when donating stem cells.
The Bone marrow aspiration is a surgical procedure. It can allergic reaction occur on the anesthetic, it can be severe Secondary bleeding come at the puncture of the bone marrow in the iliac crest.
It can increase during the procedure Irritation or Injuries to nerve tracts come.
During and after the procedure is the infection a dreaded complication that must be avoided at all costs.
In addition, it can close to the wound from which the bone marrow and the stem cells contained therein were punctured Wound healing disorders come that must be treated further.
In the medicinal stem cell extraction a drug is administered to the potential donor that is supposed to detach stem cells from the bone marrow and flush them into the peripheral blood.
Here it can allergic reactions come on the drug. Probably the most decisive risk in medicinal stem cell production is the still unclear state of studies about the Long-term consequences.
So far the studies show no connection between the medicinal stem cell lavage and the occurrence of a leukemia, however, due to the lack of long-term observation, no final assessment is possible.
Risk to the recipient
Before the recipient can get the stem cells transfused, there is a Turning off his immune system urgently needed to avoid a rejection reaction against the foreign stem cells.
The immune system gets through Chemotherapy and radiation almost completely eliminated. This carries the great danger of infectionto which the recipient's body is now very vulnerable.
For this reason, he is strictly isolated in the hospital with regular blood tests.
Even so, there is still a risk of infection and a great risk.
Despite the immune system being switched off, there is also the risk of Rejection reaction on the infused stem cells, which would mean severe health consequences for the patient's body and would have to be treated with strong medicinal measures. In very extreme cases, the recipient can die due to extreme rejection reactions of the body.
If the response to the new stem cells is good, the patient must remain in isolation for a few days until his immune system is restored and works normally.
Side effects
The Stem cell donation has some side effects for both the donor and the recipient. With medicinal stem cell flushing, the donor is given a drug called G-CSF injected, which is supposed to flush the stem cells into the peripheral bloodstream.
Symptoms and flu-like symptoms can occur after administration of medication Bone pain, muscle pain, nausea, vomiting, or diarrhea come.
Continue to be Changes in the blood count, Lung and airway infections and enlarged spleen mentioned.
Patient with Sickle cell disease should not take the drug as it is life-threatening Multiple organ failure can come.
In the case of bone marrow aspiration from the Iliac crest it may too after the procedure Weakness, bone pain in the puncture area, and pain when walking come.
The transplant can also be too high for the recipient Fever, severe weakness and general symptoms to lead. In this context, it should not be forgotten that the recipient's immune system has been switched off and the drugs that are used for this have a variety of side effects.
Minimum age for stem cell donation
Stem cell donors can be any healthy adult between the ages 18 and 55 years become. There are also some exclusion criteria that must be observed. For example, a minimum weight of 50 kg is required.
All typed potential donors are stored in a card index.
At the age of 61, every donor is deleted from the file because he is no longer eligible as a donor due to possible age-related illnesses.
DKMS
The German bone marrow donor register is a company that focuses on the Typing of possible bone marrow donors specialized.
The non-profit organization was founded in 1991 and is based in Tübingen. The DKMS has been a foundation since 1997.
The main task is the organization of typing campaigns all over Germany, in which the population is called upon to undergo a blood sample.
The data obtained are sent to the central Bone Marrow Donor Register supplied, which has its seat in Ulm. This is the switch point and the worldwide access point to all data.
The DKMS organizes its typing campaigns at the local level. Usually a patient who is ill in a certain location is presented and the population is asked to be typed.
The data obtained are then not only intended for the named patient, but can also lead to a transplant worldwide if the relevant characteristics match.
DKMS is also active globally. It has agencies in Spain, Poland, the USA and England.
In Germany the DKMS file has reached a considerable size. In this country approx. 4.3 million people listed and are potentially eligible for a donation. Around 6 million people worldwide are listed in the DKMS index.
By 2016, a total of 54,000 stem cell transplants, which can be traced back to typing by the DKMS, had been carried out.
The DKMS is now financed 100% from donations. It used to be supported by the German Cancer Aid and the Ministry of Health with funding. DKMS works with numerous laboratories in Germany and around the world.
Stem Cell Transplant Cost
The cost of typing is around 40 EUR, that of the DKMS be financed by donations. Every potential donor can financially do the typing himself and claim this as a donation for tax purposes.
Complete stem cell production including transplantation is very expensive. You have to reckon with around 100,000 euros. The costs are covered by the health insurance.
If a stem cell donor has been found, this must be released by the employer. Every stem cell donor is rewarded for this loss of work as long as he is unable to work (hospitalization).
However, no further funds are paid for the patient. The donation is therefore free of charge. After about two days, the patient will be after one Bone marrow puncture released from hospital. In the event of complaints, it may be necessary that he has to stay at home for a few days and be on sick leave. The costs are then covered by the health insurance.
Stem cell transplant pain
In the case of medicinal stem cell collection, a drug is administered to the donor for about 5 days.
The side effects also include Bone painwhich occur over the period of ingestion and shortly afterwards and can spread throughout the body.
In the Bone marrow aspiration the iliac crest is punctured with a kind of drill and bone marrow is obtained. This intervention can also take place under general anesthetic carried out.
After the procedure, the patient can be mobilized again quickly.
However, bone pain is more common in the area of bone marrow puncture. The pain can occur during exercise, but also at rest, but should have disappeared no later than a week after the procedure.
Prolonged pain should medically clarified become.